Final ID: Sa4021
Polygenic Modification of Weight Loss Response to GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) effectively treat obesity, yet weight loss varies among individuals. Polygenic risk scores (PRS) summarize genetic susceptibility to obesity and predict weight trajectories, but their role in modifying GLP-1 RA treatment responses is unclear.
Methods
Using data from the of the nationwide NIH All of Us study, we matched participants prescribed any GLP-1RA (Albiglutide, Dulaglutide, Exenatide, Liraglutide, Lixisenatide, Semaglutide, Tirzepatide) to untreated participants in a 1:5 ratio by time at treatment, sex, age, education, income, deprivation index, and baseline weight. Baseline weight was defined as the median weight within two years before matched time. The outcome was median weight from two weeks to two years after matched time. Linear regression estimated associations of GLP-1RA use, obesity PRS, and their interaction, adjusting for matching factors and the first 10 genetic PC. Subgroup analyses were conducted by type 2 diabetes status. The analysis was replicated in the Mass General Brigham Biobank (MGBB). PRS was conducted by LDpred2 with GWAS from GIANT consortium.
Results
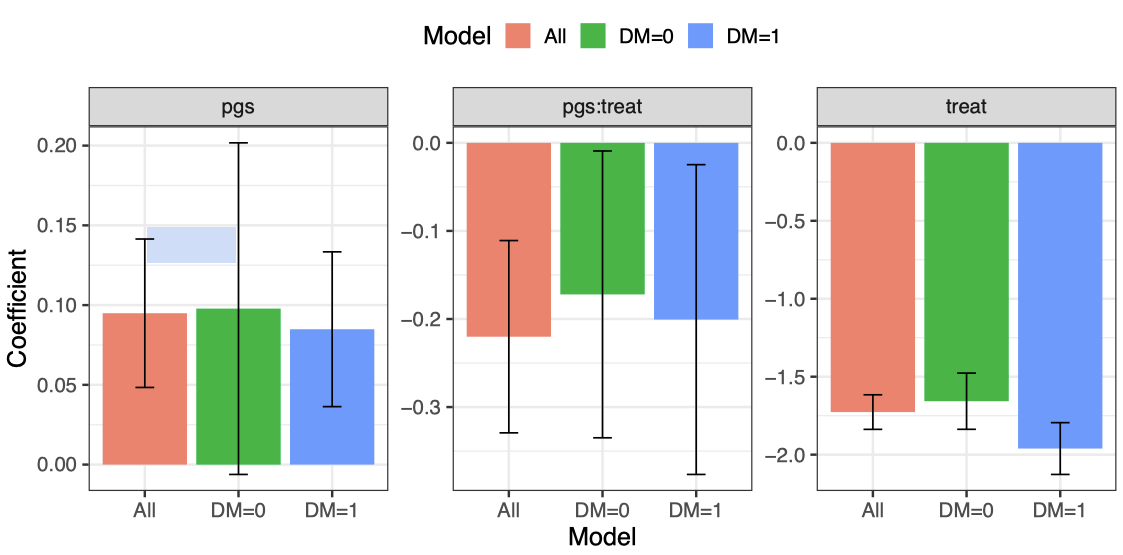
The matched cohort included 27,618 European participants (63% female), with 4,603 prescribed GLP1 RAs. Average weight during follow-up was lower in treated vs. untreated participants (99.41 vs 101.22 kg). In the adjusted analysis, GLP-1RA prescription was associated with a 1.72kg lower weight (P<2×10-16), while higher obesity-related PRS was associated with higher weight (0.09 kg per standard deviation increment, P=1.97×10-6). A significant interaction between GLP1-RA prescription and obesity-related PRS (-0.22kg excess weight loss per BMI PRS SD, P=0.005) indicated greater weight reduction in participants with lower PRS (Figure). Weight loss was greater among participants with prevalent diabetes (-1.98kg, P<2×10-16) compared to those without diabetes (-1.55, P<2×10-16) (Figure). In MGBB cohort, we obtained 3000 matched European individuals; 300 individuals received GLP-1RA treatment. GLP-1RA treatment was significantly associated with 0.4kg (P=0.01). There was also a significant PRS × treatment interaction (β = -0.38 kg excess weight loss per BMI PRS SD; P=0.02).
Conclusion
GLP-1RA treatment led to greater weight loss in those with higher obesity PRS, suggesting enhanced benefit among genetically susceptible individuals. These findings support integrating PRS into personalized obesity treatment strategies.
GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) effectively treat obesity, yet weight loss varies among individuals. Polygenic risk scores (PRS) summarize genetic susceptibility to obesity and predict weight trajectories, but their role in modifying GLP-1 RA treatment responses is unclear.
Methods
Using data from the of the nationwide NIH All of Us study, we matched participants prescribed any GLP-1RA (Albiglutide, Dulaglutide, Exenatide, Liraglutide, Lixisenatide, Semaglutide, Tirzepatide) to untreated participants in a 1:5 ratio by time at treatment, sex, age, education, income, deprivation index, and baseline weight. Baseline weight was defined as the median weight within two years before matched time. The outcome was median weight from two weeks to two years after matched time. Linear regression estimated associations of GLP-1RA use, obesity PRS, and their interaction, adjusting for matching factors and the first 10 genetic PC. Subgroup analyses were conducted by type 2 diabetes status. The analysis was replicated in the Mass General Brigham Biobank (MGBB). PRS was conducted by LDpred2 with GWAS from GIANT consortium.
Results
The matched cohort included 27,618 European participants (63% female), with 4,603 prescribed GLP1 RAs. Average weight during follow-up was lower in treated vs. untreated participants (99.41 vs 101.22 kg). In the adjusted analysis, GLP-1RA prescription was associated with a 1.72kg lower weight (P<2×10-16), while higher obesity-related PRS was associated with higher weight (0.09 kg per standard deviation increment, P=1.97×10-6). A significant interaction between GLP1-RA prescription and obesity-related PRS (-0.22kg excess weight loss per BMI PRS SD, P=0.005) indicated greater weight reduction in participants with lower PRS (Figure). Weight loss was greater among participants with prevalent diabetes (-1.98kg, P<2×10-16) compared to those without diabetes (-1.55, P<2×10-16) (Figure). In MGBB cohort, we obtained 3000 matched European individuals; 300 individuals received GLP-1RA treatment. GLP-1RA treatment was significantly associated with 0.4kg (P=0.01). There was also a significant PRS × treatment interaction (β = -0.38 kg excess weight loss per BMI PRS SD; P=0.02).
Conclusion
GLP-1RA treatment led to greater weight loss in those with higher obesity PRS, suggesting enhanced benefit among genetically susceptible individuals. These findings support integrating PRS into personalized obesity treatment strategies.
More abstracts on this topic:
Activated CD8+HLA-DR+ T Cells as Immune Biomarkers of Metabolic Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Risk in Prediabetes
Alrashed Fatema, Alsaeed Halemah, Alturaiki Wael, Akhter Nadeem, Alosaimi Bandar, Almutairi Saeedah, Mubarak Ayman, Al-mulla Fahd, Ahmad Rasheed
3D Chromatin Architectures and Transcription Regulation in Diabetic Endothelial DysfunctionFeng Yuliang, Cai Liuyang, Wang Yigang, Huang Wei, Jiang Lei