Final ID: Sa3125
Recurrences of the Infective Endocarditis: are we looking hard enough? Results from the Polish Infective Endocarditis Registry (POL-ENDO
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): BACKGROUND: Patients with prior infective endocarditis are associated with an increased risk of recurrence.
AIMS: This study aimed to assess the clinical profile and treatment results of recurrent IE patients in Poland and compare them to European recurrent IE profile.
METHODS: A prospective multicenter observational cohort study of recurrent IE and first-episode IE patients from 160 medical centers in Poland registered between August 2022 and August 2024 was conducted. Polish recurrent IE cases were compared with those recorded in the ESC-EORP EURO-ENDO registry.
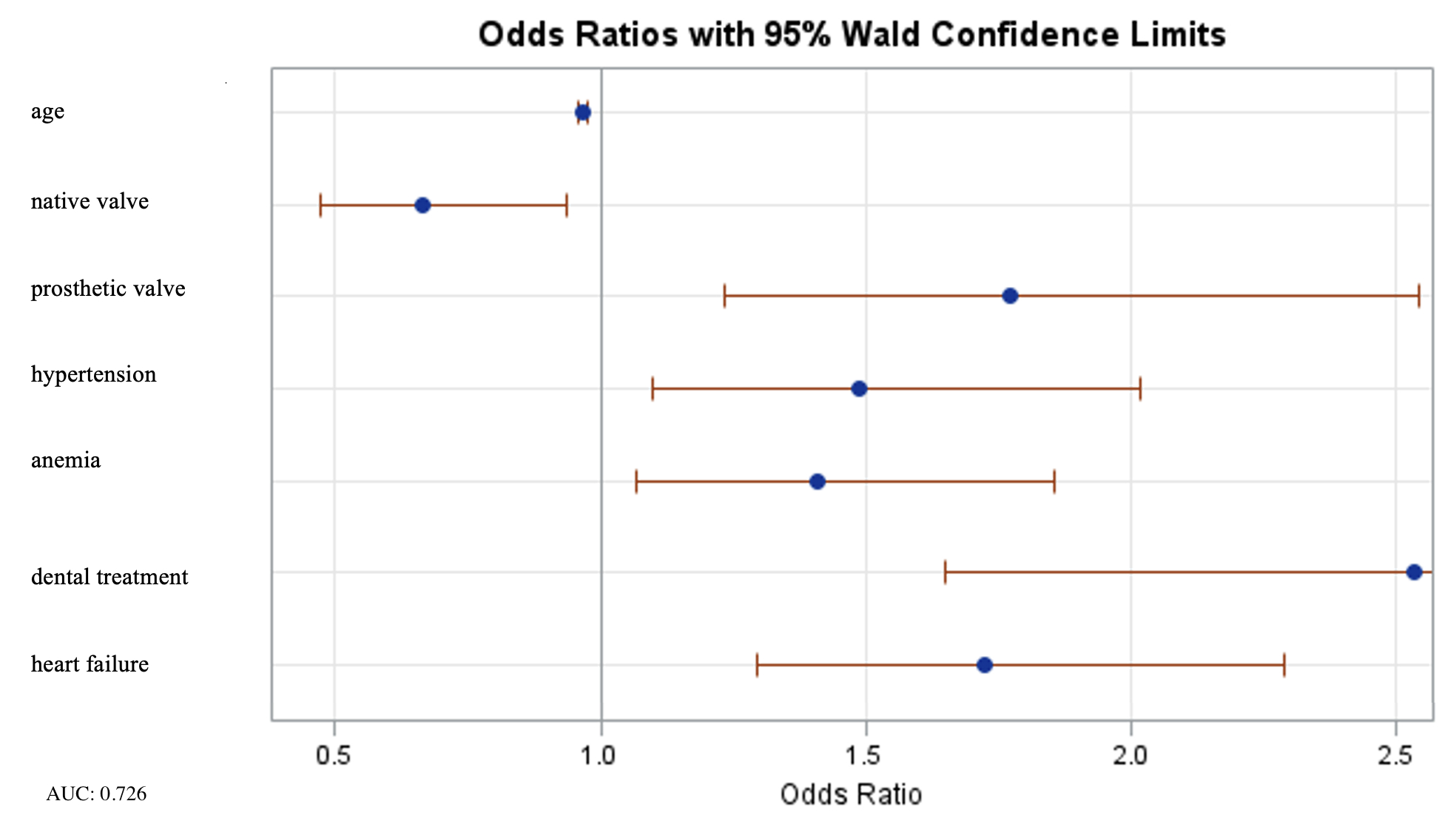
RESULTS: Of a total of 1758 IE patients, recurrent IE patients (n=371) were younger than first-episode IE (n=1387) patients [58.2 ± 16.6 vs. 62.6 ± 16.2, p<0.001] and predominated in Poland [21.1% vs. 8.6%, p<0.001]. Dental treatment was a key predisposing factor to IE recurrence [12.8% vs. 5.5%, odds ratios (OR) 2.534, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.648-3.897, p<0.001] followed by presence of valve prosthesis [45.3% vs. 24%, odds ratios (OR) 1.771, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.233-2.543, p<0.001]. Fever >38° was observed less often among recurrent IE cases [34.8% vs. 54.1 %, p<0.001]. Negative blood culture predominated among recurrent IE cases [43.3% vs. 27.2%, p<0.001]. Recurrent IE patients were rarely operated in Poland [55.2% vs. 64.8%, p=0.032]. The embolic indication for surgery was less prominent in Poland [0.08% vs. 20.2%, p<0.001].
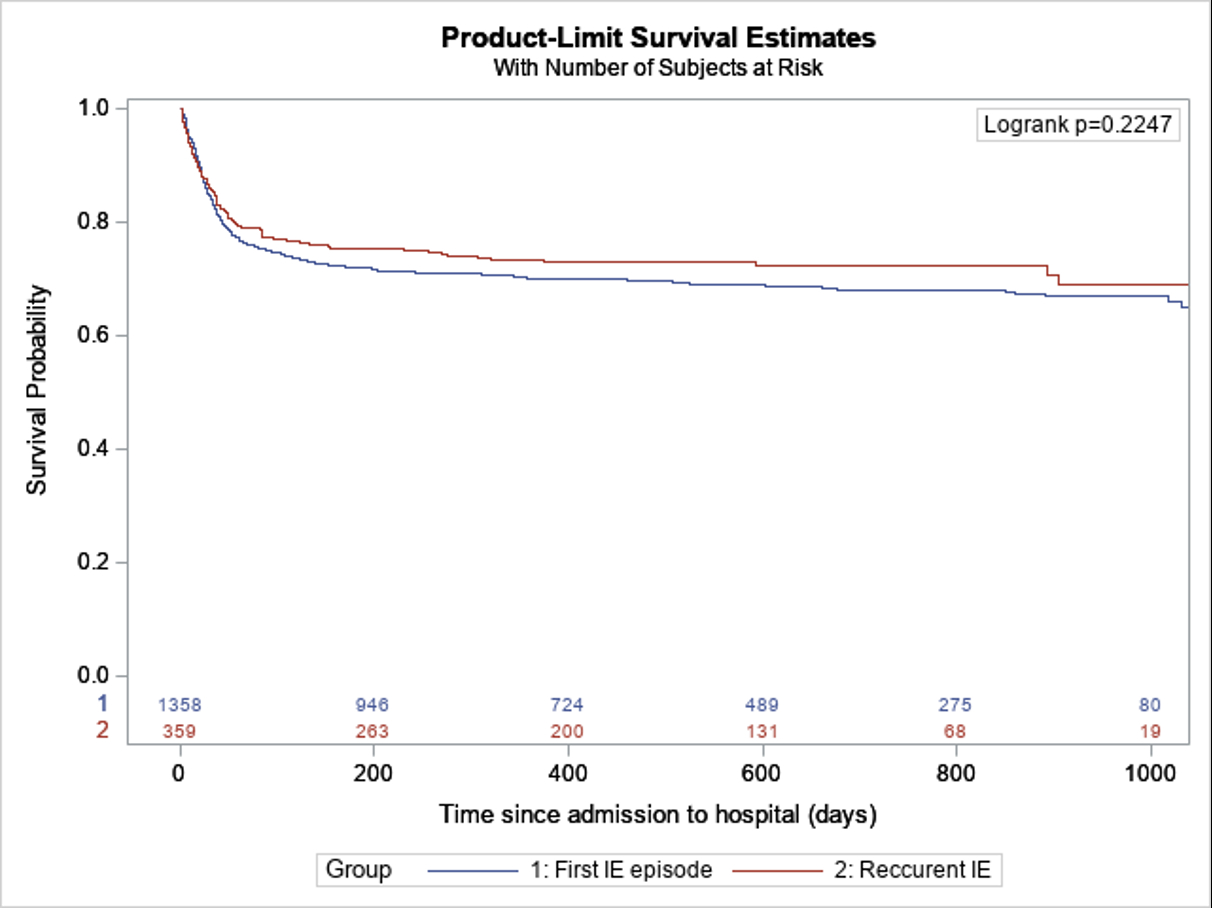
CONCLUSION: The profile of recurrent IE differs from that of the first episode of the disease. The IE recurrence rate in Poland is tremendously greater compared to other European countries. Dental treatment and valve prosthesis predispose to recurrence of IE. Fever >38° as symptom is less often observed among recurrent IE. Negative blood culture incidence is significantly higher among Polish recurrent IE group. Surgical treatment is underutilized among Polish recurrent IE patients. Embolic and uncontrolled infection indications for surgery was underrated in Poland. In-hospital complications were less prominent among recurrent IE patients in Poland. The recurrence of the IE is not associated with increased in-hospital mortality. The diagnostic and therapeutic approach to recurrent IE should be modified in order to improve the prevention of disease recurrence.
KEY WORDS: infective endocarditis, recurrence, Poland, registry, valvular disease
AIMS: This study aimed to assess the clinical profile and treatment results of recurrent IE patients in Poland and compare them to European recurrent IE profile.
METHODS: A prospective multicenter observational cohort study of recurrent IE and first-episode IE patients from 160 medical centers in Poland registered between August 2022 and August 2024 was conducted. Polish recurrent IE cases were compared with those recorded in the ESC-EORP EURO-ENDO registry.
RESULTS: Of a total of 1758 IE patients, recurrent IE patients (n=371) were younger than first-episode IE (n=1387) patients [58.2 ± 16.6 vs. 62.6 ± 16.2, p<0.001] and predominated in Poland [21.1% vs. 8.6%, p<0.001]. Dental treatment was a key predisposing factor to IE recurrence [12.8% vs. 5.5%, odds ratios (OR) 2.534, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.648-3.897, p<0.001] followed by presence of valve prosthesis [45.3% vs. 24%, odds ratios (OR) 1.771, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.233-2.543, p<0.001]. Fever >38° was observed less often among recurrent IE cases [34.8% vs. 54.1 %, p<0.001]. Negative blood culture predominated among recurrent IE cases [43.3% vs. 27.2%, p<0.001]. Recurrent IE patients were rarely operated in Poland [55.2% vs. 64.8%, p=0.032]. The embolic indication for surgery was less prominent in Poland [0.08% vs. 20.2%, p<0.001].
CONCLUSION: The profile of recurrent IE differs from that of the first episode of the disease. The IE recurrence rate in Poland is tremendously greater compared to other European countries. Dental treatment and valve prosthesis predispose to recurrence of IE. Fever >38° as symptom is less often observed among recurrent IE. Negative blood culture incidence is significantly higher among Polish recurrent IE group. Surgical treatment is underutilized among Polish recurrent IE patients. Embolic and uncontrolled infection indications for surgery was underrated in Poland. In-hospital complications were less prominent among recurrent IE patients in Poland. The recurrence of the IE is not associated with increased in-hospital mortality. The diagnostic and therapeutic approach to recurrent IE should be modified in order to improve the prevention of disease recurrence.
KEY WORDS: infective endocarditis, recurrence, Poland, registry, valvular disease
More abstracts on this topic:
Air pollutants, road traffic noise, and risk of valvular heart disease: a UK Biobank-based prospective study
Song Yanjun, Lin Zhangyu, Zheng Zhihao, Chen Xinyue, Bian Xiaohui
Analysis of Cardiovascular Events in Cancer Survivors: A Comparative Study of Solid Tumors and Hematologic Malignancies at a Tertiary Cardiovascular CenterAmaro Palomo Eder Jonathan, Cortes Flores Claudia Galilea, Diaz Braiana, Araiza Diego, Arias-mendoza Alexandra, Martinez Rios Marco Antonio, Latapi Ruiz Esparza Ximena, Adib Gracia Anna Elisa, Garate Togo Javier, Sierra Lara Martinez Jorge Daniel, Hernandez-pastrana Sarai, Gonzalez Macedo Eder, Santiago Hernández Alberto, Neri Bale Raul Rodrigo