Final ID: Sa2039
Paradoxical Renal Protection after Euglycemic DKA in a CKD Stage 4 Diabetic Patient on Empagliflozin: A Case Report and Mechanistic Insights
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Over the last few years, studies have demonstrated that the usage of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease has significantly reduced the risk of hospitalisation for heart failure, progression to kidney failure, and all-cause mortality. Notably, a clinical trial evaluating the usage of empagliflozin in CKD revealed that cardiorenal protective effects persisted up to a year after cessation. However, SGLT2 inhibitors have also been associated with an increased incidence of euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (euDKA), a condition characterised by normoglycemia, metabolic acidosis, and ketosis. This case highlights an unexpected renal benefit following euDKA in a patient with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD) on empagliflozin.
Case Description
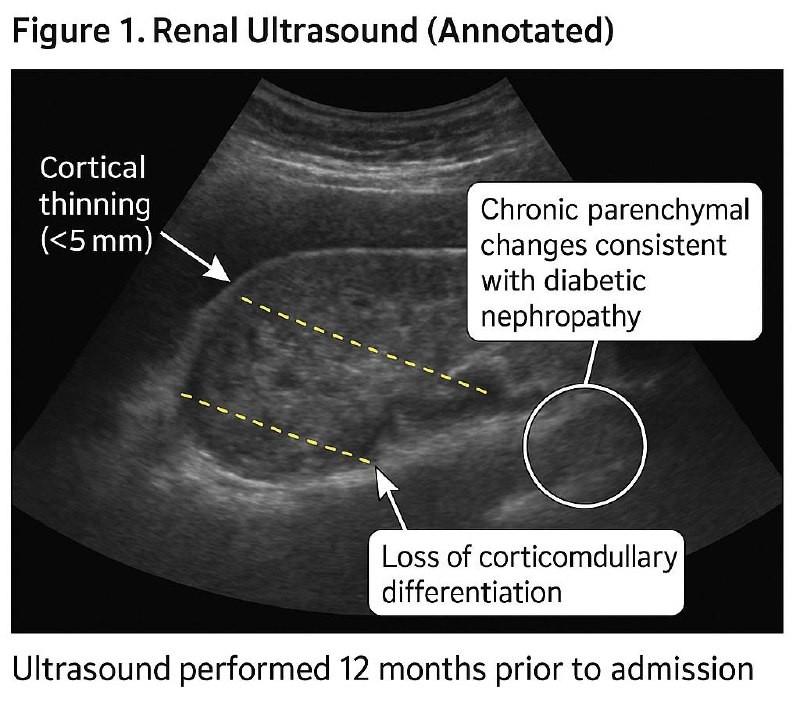
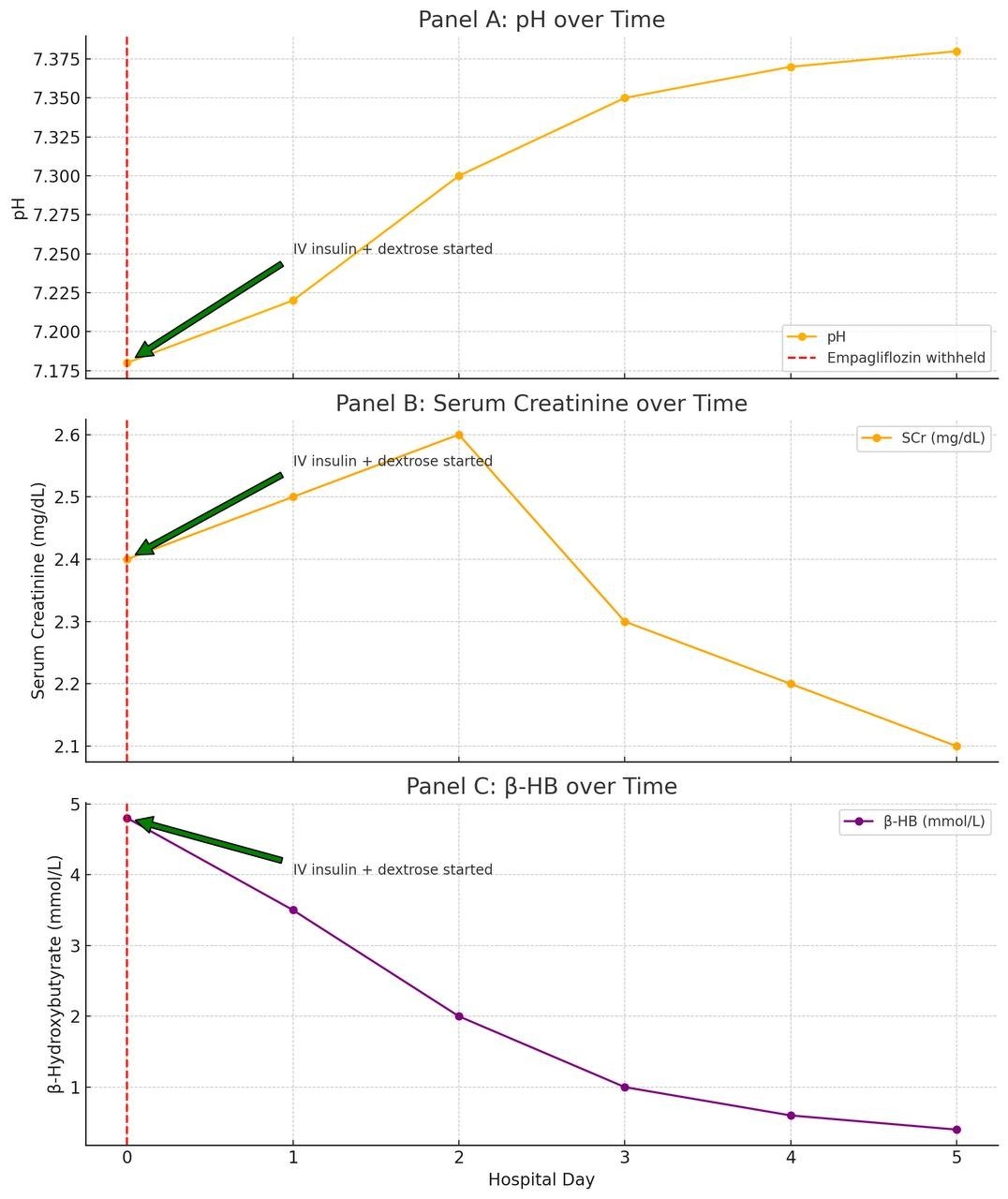
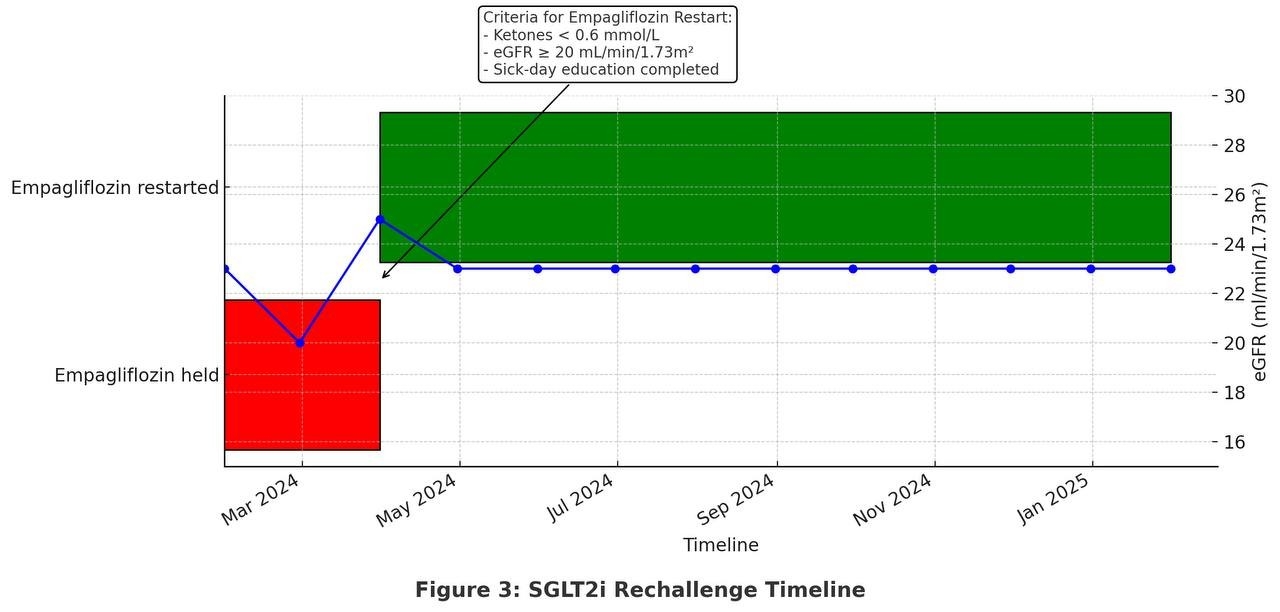
A 58-year-old female with type 2 diabetes (HbA1c 7.8%), CKD stage 4 (eGFR 23 mL/min/1.73msq.), and HFpEF presented with fatigue, nausea, and tachypnea. Blood glucose was 140 mg/dL. She was on empagliflozin (10 mg/day) for cardiorenal protection. Lab results confirmed euDKA (pH 7.18, ketones 4.8 mmol/L, bicarbonate 12 mEq/L), triggered by influenza A and reduced intake. Notably, serum creatinine improved from 2.4 to 2.1 mg/dL during hospitalisation. She was treated with IV insulin, dextrose, and empagliflozin was held. Eight weeks post-discharge, the drug was restarted after stable labs and patient education. Over 12 months, eGFR remained stable (22–25), and there were no further DKA episodes.
Discussion
This case defies expectations of AKI in euDKA, particularly in advanced CKD, by demonstrating improved renal function during metabolic stress. Proposed mechanisms include tubular mitochondrial protection, reduced oxidative stress, and anti-inflammatory effects of SGLT2 inhibition. Renal stability post-rechallenge supports the growing evidence of cardiorenal benefits in late-stage chronic kidney disease (CKD). While euDKA remains a serious risk, this case highlights the importance of careful benefit-risk evaluation and structured reintroduction protocols for SGLT2 inhibitors. It also invites further investigation into the non-glycemic benefits of these agents and their role in renal resilience. Standardised clinical protocols for SGLT2i rechallenge post-euDKA could enhance long-term outcomes.
Over the last few years, studies have demonstrated that the usage of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease has significantly reduced the risk of hospitalisation for heart failure, progression to kidney failure, and all-cause mortality. Notably, a clinical trial evaluating the usage of empagliflozin in CKD revealed that cardiorenal protective effects persisted up to a year after cessation. However, SGLT2 inhibitors have also been associated with an increased incidence of euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (euDKA), a condition characterised by normoglycemia, metabolic acidosis, and ketosis. This case highlights an unexpected renal benefit following euDKA in a patient with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD) on empagliflozin.
Case Description
A 58-year-old female with type 2 diabetes (HbA1c 7.8%), CKD stage 4 (eGFR 23 mL/min/1.73msq.), and HFpEF presented with fatigue, nausea, and tachypnea. Blood glucose was 140 mg/dL. She was on empagliflozin (10 mg/day) for cardiorenal protection. Lab results confirmed euDKA (pH 7.18, ketones 4.8 mmol/L, bicarbonate 12 mEq/L), triggered by influenza A and reduced intake. Notably, serum creatinine improved from 2.4 to 2.1 mg/dL during hospitalisation. She was treated with IV insulin, dextrose, and empagliflozin was held. Eight weeks post-discharge, the drug was restarted after stable labs and patient education. Over 12 months, eGFR remained stable (22–25), and there were no further DKA episodes.
Discussion
This case defies expectations of AKI in euDKA, particularly in advanced CKD, by demonstrating improved renal function during metabolic stress. Proposed mechanisms include tubular mitochondrial protection, reduced oxidative stress, and anti-inflammatory effects of SGLT2 inhibition. Renal stability post-rechallenge supports the growing evidence of cardiorenal benefits in late-stage chronic kidney disease (CKD). While euDKA remains a serious risk, this case highlights the importance of careful benefit-risk evaluation and structured reintroduction protocols for SGLT2 inhibitors. It also invites further investigation into the non-glycemic benefits of these agents and their role in renal resilience. Standardised clinical protocols for SGLT2i rechallenge post-euDKA could enhance long-term outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Aortic Valve Calcium as a Predictor of Chronic Kidney Disease in a Multi-Ethnic Cohort: The MESA Study
Abdollahi Ashkan, Rotter Jerome, Post Wendy, Blumenthal Roger, Bluemke David, Lima Joao Ac, Whelton Seamus, Sani Maryam, Shabani Mahsima, Scarpa Bruna, Blaha Michael, Wu Colin, Ambale-venkatesh Bharath, Budoff Matthew, Strom Jordan
Angiopoeitin-2 and Mortality in an End-Stage Renal Disease, Heart Failure PopulationRobbin Vanessa, Bansal Vinod, Siddiqui Fakiha, Fareed Jawed, Syed Mushabbar