Final ID: MP1096
Polygenic Risk Score Associated With Kidney Disease Progression In Patients With Cardiometabolic Risk Factors
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is associated with significant morbidity and mortality, especially in patients with concurrent heart disease who share many similar risk factors. Recent studies support a polygenic contribution to CKD, suggesting that a polygenic risk score (PRS) may have utility in predicting clinically significant progression of kidney disease.
Methods:
All patients who consented for genetic testing in 3 large TIMI clinical trials (SAVOR, FOURIER, DECLARE) were included in the study. Pts were binned as high (top 20%), intermediate, or low (bottom 20%) genetic risk using a genome-wide PRS developed to predict CKD in a diverse population (Mandla et al., 2024, Wuttke et al., 2019). A Cox model was used to calculate adjusted hazard ratios (aHR) across genetic risk groups for a 3-point renal composite outcome (eGFR decrease ≥40%, end-stage renal disease, or renal death). HRs were adjusted for age, sex, genetic ancestry, HTN, DM, CAD, PAD, smoking, and hyperlipidemia.
Results:
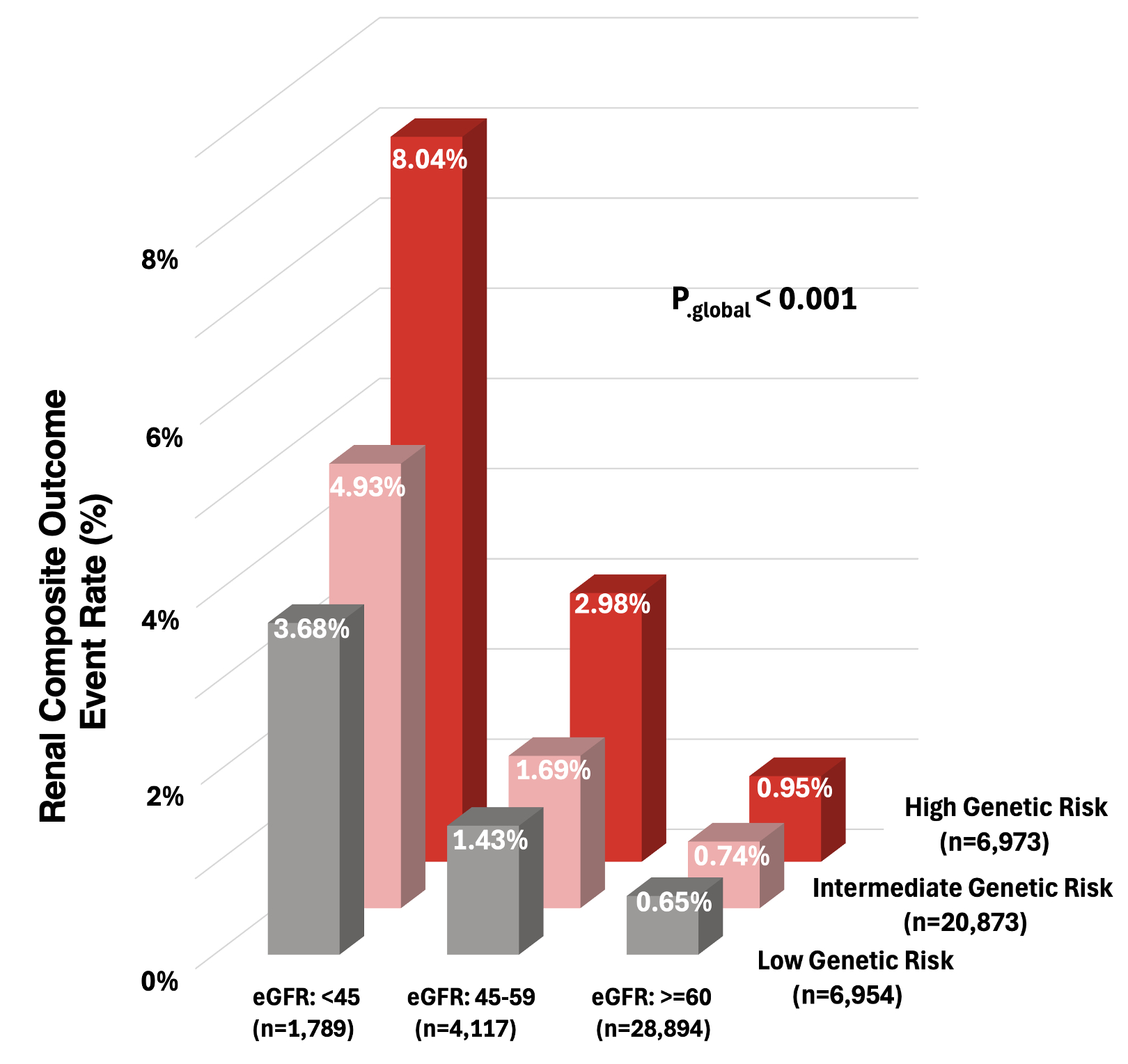
Of 35,182 pts across the 3 trials, 514 (1.46%) had a composite renal outcome over 2.5-yrs median follow-up with Kaplan-Meier event rates for those in low, intermediate, and high genetic risk groups of 0.83% (n=76), 1.05% (n=283), 1.59% (n=147), respectively (p-trend<0.001). After adjustment for clinical risk factors, the PRS was independently associated with an aHR (per 1-SD) for the composite renal outcome of 1.17 (95% CI, 1.10-1.26, p<0.001). The PRS predicts risk of the composite renal outcome across the range of baseline eGFRs (Fig. 1). Notably, the PRS was associated with an enhanced ability to predict for the renal composite outcome in patients with eGFR <60 (aHR per 1-SD of 1.23 [1.10-1.38], p<0.001) compared to 1.11 [1.02-1.22, p=0.0196] in patients with eGFR≥60 (p-heterogeneity=0.03). Indeed, in patients with at least CKD stage 3B (eGFR <45), the absolute excess risk of the renal composite outcome in patients with high vs. low genetic risk over 2.5 yrs was 4.36% compared to 0.30% in high vs. low genetic risk patients with CKD stage 2B or better (eGFR ≥60).
Conclusions:
A kidney disease PRS, when added to clinical risk factors, improves the prediction of developing clinically significant renal disease. The absolute risk excess was largest in patients with pre-existing CKD and therefore may be a useful risk marker for disease progression.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is associated with significant morbidity and mortality, especially in patients with concurrent heart disease who share many similar risk factors. Recent studies support a polygenic contribution to CKD, suggesting that a polygenic risk score (PRS) may have utility in predicting clinically significant progression of kidney disease.
Methods:
All patients who consented for genetic testing in 3 large TIMI clinical trials (SAVOR, FOURIER, DECLARE) were included in the study. Pts were binned as high (top 20%), intermediate, or low (bottom 20%) genetic risk using a genome-wide PRS developed to predict CKD in a diverse population (Mandla et al., 2024, Wuttke et al., 2019). A Cox model was used to calculate adjusted hazard ratios (aHR) across genetic risk groups for a 3-point renal composite outcome (eGFR decrease ≥40%, end-stage renal disease, or renal death). HRs were adjusted for age, sex, genetic ancestry, HTN, DM, CAD, PAD, smoking, and hyperlipidemia.
Results:
Of 35,182 pts across the 3 trials, 514 (1.46%) had a composite renal outcome over 2.5-yrs median follow-up with Kaplan-Meier event rates for those in low, intermediate, and high genetic risk groups of 0.83% (n=76), 1.05% (n=283), 1.59% (n=147), respectively (p-trend<0.001). After adjustment for clinical risk factors, the PRS was independently associated with an aHR (per 1-SD) for the composite renal outcome of 1.17 (95% CI, 1.10-1.26, p<0.001). The PRS predicts risk of the composite renal outcome across the range of baseline eGFRs (Fig. 1). Notably, the PRS was associated with an enhanced ability to predict for the renal composite outcome in patients with eGFR <60 (aHR per 1-SD of 1.23 [1.10-1.38], p<0.001) compared to 1.11 [1.02-1.22, p=0.0196] in patients with eGFR≥60 (p-heterogeneity=0.03). Indeed, in patients with at least CKD stage 3B (eGFR <45), the absolute excess risk of the renal composite outcome in patients with high vs. low genetic risk over 2.5 yrs was 4.36% compared to 0.30% in high vs. low genetic risk patients with CKD stage 2B or better (eGFR ≥60).
Conclusions:
A kidney disease PRS, when added to clinical risk factors, improves the prediction of developing clinically significant renal disease. The absolute risk excess was largest in patients with pre-existing CKD and therefore may be a useful risk marker for disease progression.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Two-year Longitudinal Investigation of Lipoprotein Particle Profile as Cardiometabolic Risk Biomarkers in Family Caregivers of Adult Patients with Cancer
Lee Lena, Shamburek Robert, Son Elisa H, Wallen Gwenyth, Yang Li, Tuason Ralph, Gerrard Chantal, Tsai Thomas, Kim Youngmee
A Machine Learning-Derived Socio-Environmental Risk Score More Accurately Predicts Cardiovascular Events and Better Addresses Health Inequities than Social Deprivation IndexChen Zhuo, Nasir Khurram, Al-kindi Sadeer, Rajagopalan Sanjay, Ponnana Sai Rahul, Dazard Jean-eudes, Zhang Tong, Dong Weichuan, Okyere Robert, Sirasapalli Santosh, Deo Salil, Khraishah Haitham