Final ID: MP1070
The effect of a BMPR2 mutation on cardiac mechanotransduction
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a rare disease that originates in the lungs and patients eventually die of right heart failure. A mutation in the Bone Morphogenetic Protein Receptor Type 2 (BMPR2) gene is present in 70% of hereditary PAH patients. Previous work demonstrated that right ventricular function is more impaired in patients carrying a BMPR2 mutation. However, the underlying mechanism remains elusive. Moreover, natriuretic peptides are secreted from cardiomyocytes upon stretching as an adaptation to increased pressure overload. We hypothesize that the BMPR2 mutation impairs the myocardial response to stress.
Methods: To study the effect of BMPR2 in cardiac adaptation in vitro, we used induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from 2 PAH patients carrying a BMPR2 mutation and their isogenic controls (corrected BMPR2 mutation). iPSCs were differentiated into ventricular cardiomyocytes (iPSC-CMs) and stretched at 10% for 24h at 1Hz on the Flexcell FX-6000 system. Natriuretic peptides (NPPB and NPPA), along with genes involved in their processing, signaling and degradation, and also cardiac mechanosensing and mechanotransduction genes, were quantified via RT-PCR. N-terminal Brain Natriuretic Peptides (NTproBNP) and Mid Regional proAtrial Natriuretic Peptides (MRproANP) secretions were measured on cell supernatants throughout specific immunoassays.
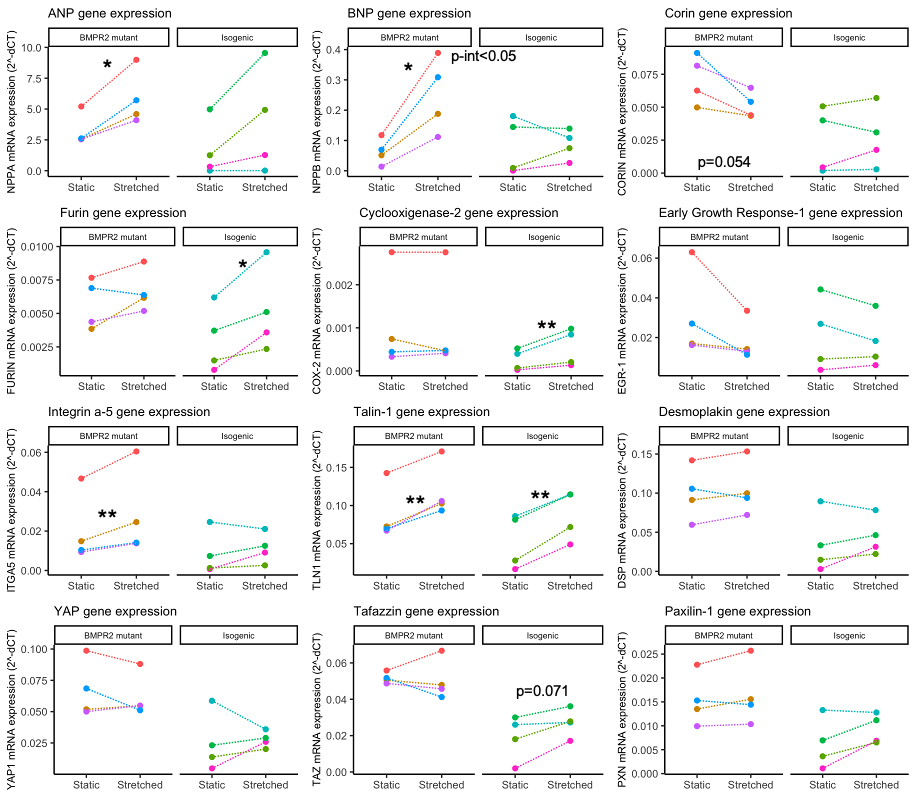
Results: At static conditions, BMPR2 mutant iPSC-CMs showed higher atrial and brain natriuretic peptides expression and release compared to isogenic iPSC-CMs. Upon stretching, both BMPR2 mutant and isogenic iPSC-CMs increased gene and protein expression of atrial and brain natriuretic peptides. In a small group (N=4), differences were observed in natriuretic peptide processing (CORIN, FURIN), mechanosensitive genes (COX-2, EGR1), cardiac mechanosensing (ITGA-5) and mechanotransduction (TLN1, DSP, YAP1, TAZ, PXN) pathways in isogenic and BMPR2 mutant iPSC-CMs.
Conclusions: To conclude, BMPR2 mutated iPSC-CMs showed higher levels of atrial and brain natriuretic peptides in static conditions, whereas the response to stretch was similar. Changes in genes involved in mechanotransduction suggest altered mechanical properties coincide with a BMPR2 mutation. Further analyses will focus on validating these results in a larger experimental set and extending analyses to atrial cardiomyocytes.
Methods: To study the effect of BMPR2 in cardiac adaptation in vitro, we used induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from 2 PAH patients carrying a BMPR2 mutation and their isogenic controls (corrected BMPR2 mutation). iPSCs were differentiated into ventricular cardiomyocytes (iPSC-CMs) and stretched at 10% for 24h at 1Hz on the Flexcell FX-6000 system. Natriuretic peptides (NPPB and NPPA), along with genes involved in their processing, signaling and degradation, and also cardiac mechanosensing and mechanotransduction genes, were quantified via RT-PCR. N-terminal Brain Natriuretic Peptides (NTproBNP) and Mid Regional proAtrial Natriuretic Peptides (MRproANP) secretions were measured on cell supernatants throughout specific immunoassays.
Results: At static conditions, BMPR2 mutant iPSC-CMs showed higher atrial and brain natriuretic peptides expression and release compared to isogenic iPSC-CMs. Upon stretching, both BMPR2 mutant and isogenic iPSC-CMs increased gene and protein expression of atrial and brain natriuretic peptides. In a small group (N=4), differences were observed in natriuretic peptide processing (CORIN, FURIN), mechanosensitive genes (COX-2, EGR1), cardiac mechanosensing (ITGA-5) and mechanotransduction (TLN1, DSP, YAP1, TAZ, PXN) pathways in isogenic and BMPR2 mutant iPSC-CMs.
Conclusions: To conclude, BMPR2 mutated iPSC-CMs showed higher levels of atrial and brain natriuretic peptides in static conditions, whereas the response to stretch was similar. Changes in genes involved in mechanotransduction suggest altered mechanical properties coincide with a BMPR2 mutation. Further analyses will focus on validating these results in a larger experimental set and extending analyses to atrial cardiomyocytes.
More abstracts on this topic:
β1 integrins regulate cellular behavior and cardiomyocyte organization during ventricular wall formation
Miao Lianjie, Schwartz Robert, R Burns Alan, Kumar Ashok, Dipersio C. Michael, Wu Mingfu, Lu Yangyang, Nusrat Anika, Zhao Luqi, Castillo Micah, Xiao Yongqi, Guo Hongyan, Liu Yu, Gunaratne Preethi
A Non-invasive In Vivo Experimental Model of Heart Failure Using Optogenetic Tachypacing in Larval ZebrafishSavoie Emma, Ramadan Ahmed, Purvis Katherine, Stoyek Matthew, Quinn Alex