Final ID: Mo4065
Electronic Service Delivery Model in Cardiovascular Genetics Counseling
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Evaluation for genetic testing is recommended for individuals with inherited cardiovascular diseases, but the limited supply of specialists trained in cardiovascular genetics results in delays of care. Therefore, we sought to design and evaluate the feasibility and effectiveness of an electronic genomic educational tool to prime patients as a novel method of care delivery.
Methods:
We recruited patients aged ≥18 years who were scheduled for genetic consultation at a single ambulatory cardiology practice in an integrated health system. Our multi-disciplinary study team composed of genetic counselors, general cardiologists, and advanced heart failure cardiologists iteratively developed an electronic genomic educational tool using animated video software to deliver general knowledge on genomics and types of genetic testing results prior to the in-clinic consultation. Genetic literacy was assessed in all participants before and after viewing the genomic educational tool with questions adapted from a previously validated genomic knowledge survey (GKS) tool. Empowerment with the process of genetic testing after viewing the electronic tool was assessed with the 4-item validated SURE survey tool. Patients answering “yes” to all four questions on the SURE survey tool were identified as feeling “empowered” with genetic testing.
Results:
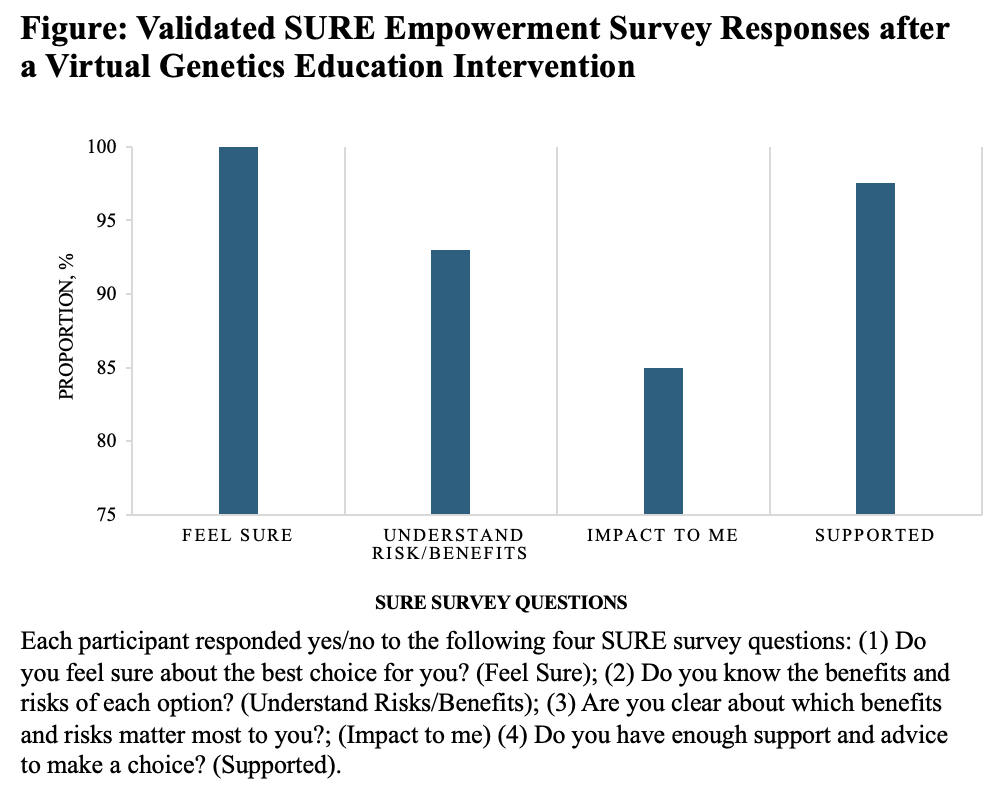
A total of 47 patients were recruited to the study with 41(87%) completing all survey items. Participants were balanced by sex (47% female). Mean (standard deviation) age was 49 (15) years. Cardiomyopathy was the most common indication (50%) for referral for cardiovascular genetics consultation. The mean pre-intervention GKS score was 5.24 (SD 0.89), which increased significantly to 5.63 (SD 0.54, p=0.003) after viewing the electronic tool. The SURE empowerment survey demonstrated that the majority of the patients (N=35 [85%]) responded “yes” or positively to all four survey items around decisions regarding genetic testing (FIGURE).
Conclusions
In this single-center pilot study, an electronic genomic educational resource with animated software increased genetic knowledge and demonstrated high patient sense of empowerment with decisions surrounding genetic testing. This novel method of virtual content delivery could help to reduce the burden placed on the limited genetics workforce needed to provide high-quality pre-test education and guide genetic testing decisions.
Evaluation for genetic testing is recommended for individuals with inherited cardiovascular diseases, but the limited supply of specialists trained in cardiovascular genetics results in delays of care. Therefore, we sought to design and evaluate the feasibility and effectiveness of an electronic genomic educational tool to prime patients as a novel method of care delivery.
Methods:
We recruited patients aged ≥18 years who were scheduled for genetic consultation at a single ambulatory cardiology practice in an integrated health system. Our multi-disciplinary study team composed of genetic counselors, general cardiologists, and advanced heart failure cardiologists iteratively developed an electronic genomic educational tool using animated video software to deliver general knowledge on genomics and types of genetic testing results prior to the in-clinic consultation. Genetic literacy was assessed in all participants before and after viewing the genomic educational tool with questions adapted from a previously validated genomic knowledge survey (GKS) tool. Empowerment with the process of genetic testing after viewing the electronic tool was assessed with the 4-item validated SURE survey tool. Patients answering “yes” to all four questions on the SURE survey tool were identified as feeling “empowered” with genetic testing.
Results:
A total of 47 patients were recruited to the study with 41(87%) completing all survey items. Participants were balanced by sex (47% female). Mean (standard deviation) age was 49 (15) years. Cardiomyopathy was the most common indication (50%) for referral for cardiovascular genetics consultation. The mean pre-intervention GKS score was 5.24 (SD 0.89), which increased significantly to 5.63 (SD 0.54, p=0.003) after viewing the electronic tool. The SURE empowerment survey demonstrated that the majority of the patients (N=35 [85%]) responded “yes” or positively to all four survey items around decisions regarding genetic testing (FIGURE).
Conclusions
In this single-center pilot study, an electronic genomic educational resource with animated software increased genetic knowledge and demonstrated high patient sense of empowerment with decisions surrounding genetic testing. This novel method of virtual content delivery could help to reduce the burden placed on the limited genetics workforce needed to provide high-quality pre-test education and guide genetic testing decisions.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Recurrent Acute Coronary Syndrome and Cardiogenic Shock due to Apolipoprotein A-IV Amyloidosis
Muthukkumar Rashmi, Holmes Taylor, Friede Kevin
A-band titin-truncating variant promotes the development of arrhythmia-induced cardiomyopathy in a novel genetically-engineered porcine modelLee Kwonjae, Del Rio Carlos, Mcnally Elizabeth, Pfenniger Anna, Bhatnagar Ashita, Glinton Kristofor, Burrell Amy, Ober Rebecca, Mcluckie Alicia, Bishop Brian, Rogers Christopher, Geist Gail