Final ID: MP981
Electrocardiogram-Based Artificial Intelligence to Improve the Efficiency of Atrial Fibrillation Screening: A VITAL-AF Trial Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is common and highly morbid. AF screening may detect AF earlier and facilitate preventive measures (e.g., anticoagulation to prevent stroke). However, current AF screening approaches using a guideline age-based threshold of 65 years have shown limited yield. AF screening informed by AF risk models, including emerging artificial intelligence (AI)-based methods, may improve AF screening efficiency.
Research Question: In a large AF screening trial, we sought to assess whether the effect of AF screening was higher among individuals with elevated AF risk.
Methods: VITAL-AF was a cluster-randomized trial of patients aged 65 years treated at one of 16 primary care practices affiliated with Massachusetts General Hospital. Patients randomized to a screening practice underwent screening with single-lead ECG. Among individuals in VITAL-AF with 1 12-lead ECG within 3 years prior to enrollment, we estimated AF risk using three validated models derived independent of VITAL-AF: a) the Cohorts of Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology-AF (CHARGE-AF) clinical score, b) an AI-based model utilizing 12-lead ECG alone (ECG-AI), and c) a model combining ECG-AI and CHARGE-AF (CH-AI). Discrimination of 2-year incident AF was quantified using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) and average precision (AP). AF screening effect was defined as the difference in 2-year incident AF diagnosis (%) in screening versus control in the screened population across deciles of AF risk.
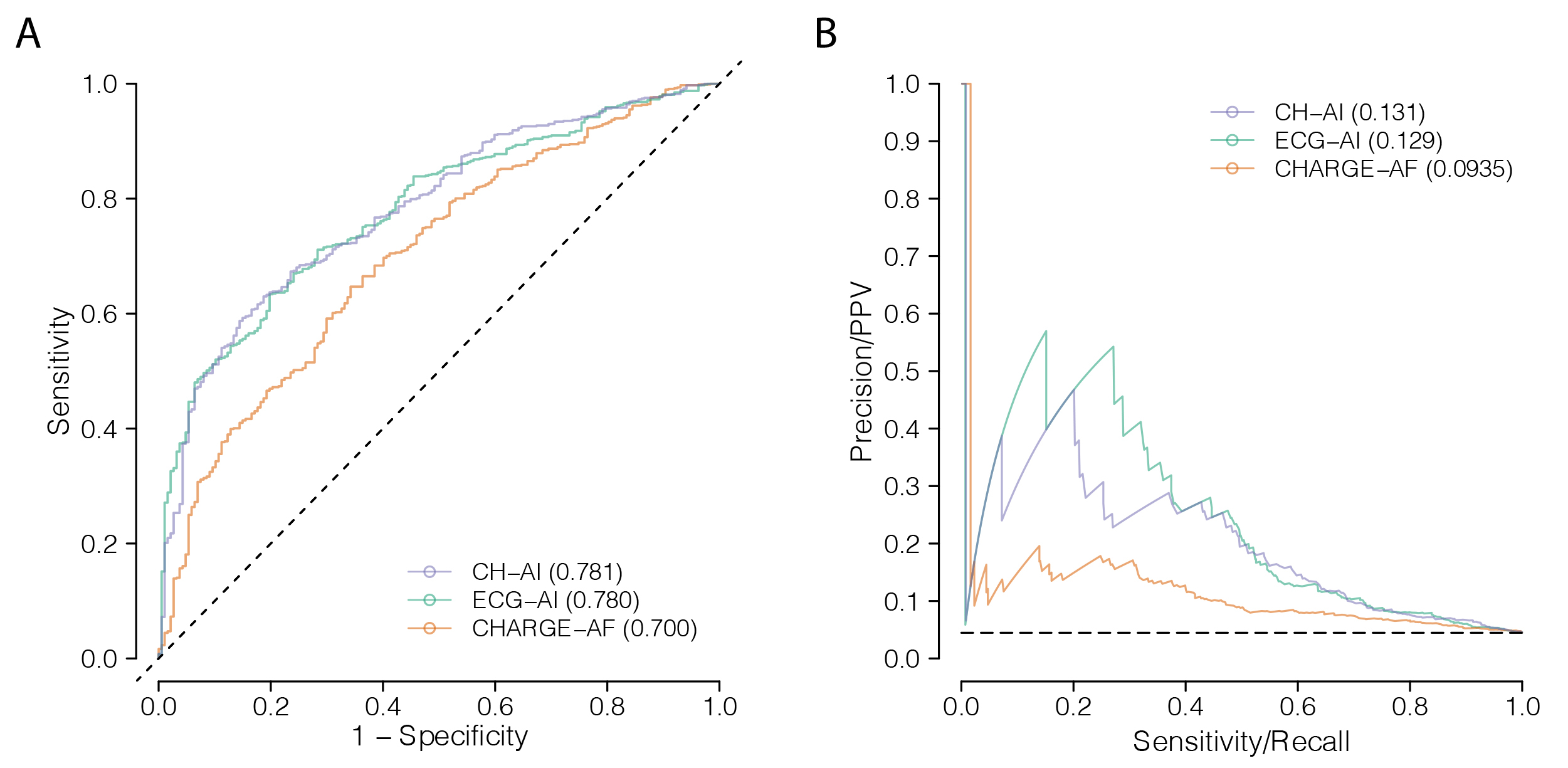
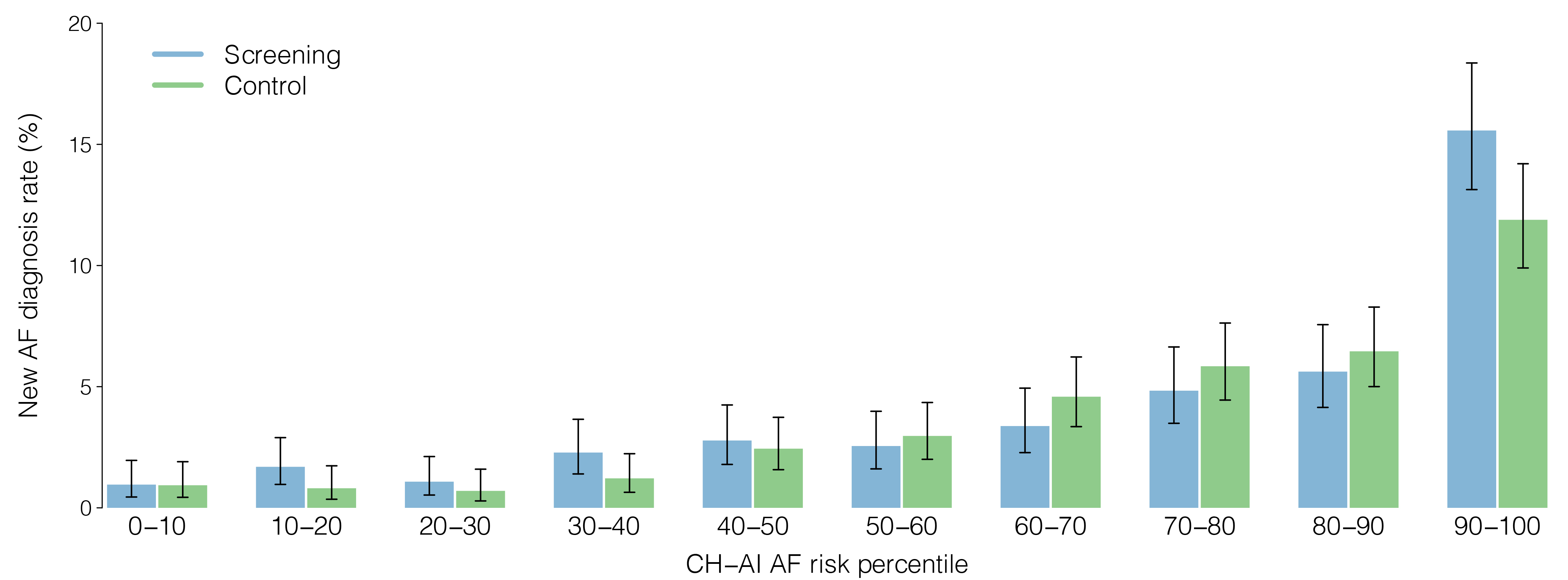
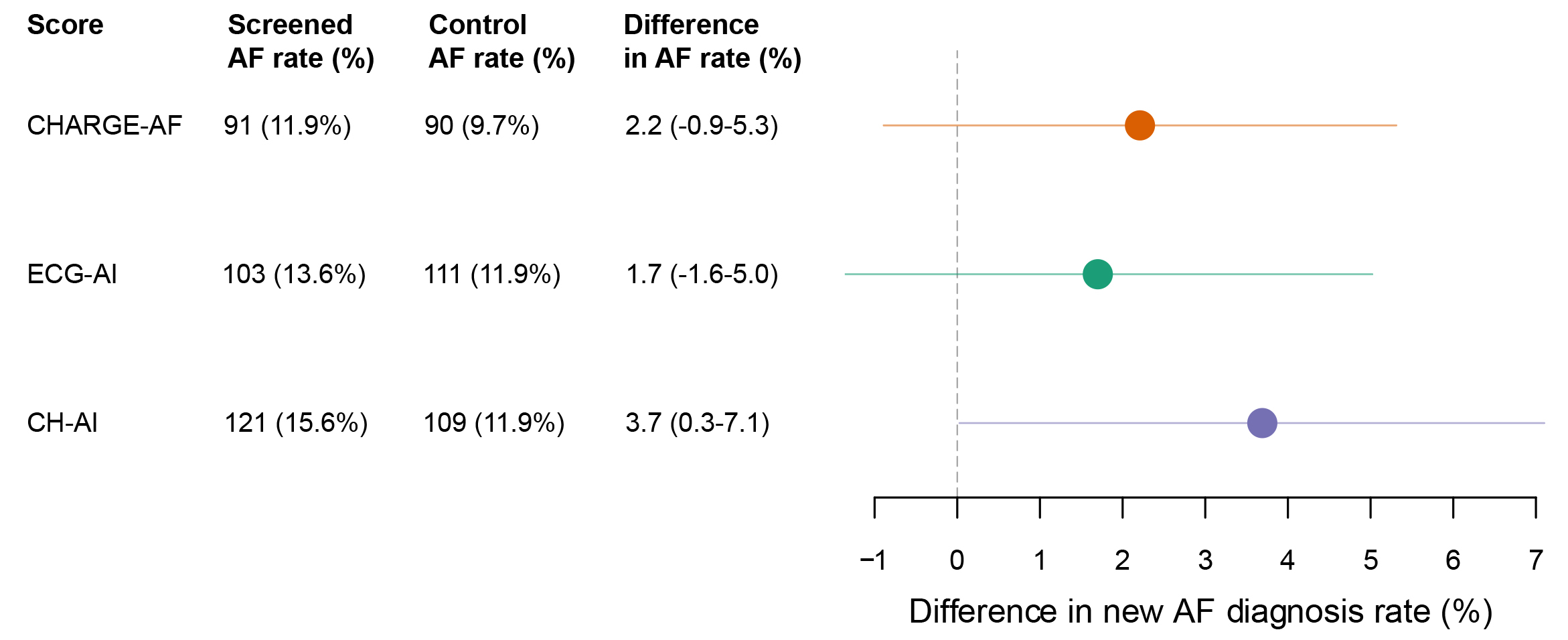
Results: Of 30,630 VITAL-AF participants without prevalent AF, we analyzed 16,937 with available pre-trial ECG and clinical data. Each score discriminated 2-year AF risk (AUROC CHARGE-AF 0.700 [95%CI 0.654-0.739]; ECG-AI 0.780 [0.747-0.810]; CH-AI 0.781 [0.740-0.814]) (AP 0.0935 [0.0818-0.109]; 0.129 [0.111-0.154]; 0.131 [0.115-0.153]) (Figure 1). An AF screening effect was observed in the top decile of CH-AI (2-year AF diagnosis rate 15.6% [13.1-19.4] in screening vs 11.9% [9.9-15.6] in control; difference 3.7% [0.3-7.1]) (Figure 2). The AF screening effect was largest in the top decile of all three scores, but was numerically highest with CH-AI (Figure 3).
Conclusions: In VITAL-AF, the yield of AF screening appeared larger among individuals at high AF risk, particularly using a model combining clinical factors and AI-based ECG analysis. Future trials should assess whether risk-informed AF screening improves outcomes.
Research Question: In a large AF screening trial, we sought to assess whether the effect of AF screening was higher among individuals with elevated AF risk.
Methods: VITAL-AF was a cluster-randomized trial of patients aged 65 years treated at one of 16 primary care practices affiliated with Massachusetts General Hospital. Patients randomized to a screening practice underwent screening with single-lead ECG. Among individuals in VITAL-AF with 1 12-lead ECG within 3 years prior to enrollment, we estimated AF risk using three validated models derived independent of VITAL-AF: a) the Cohorts of Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology-AF (CHARGE-AF) clinical score, b) an AI-based model utilizing 12-lead ECG alone (ECG-AI), and c) a model combining ECG-AI and CHARGE-AF (CH-AI). Discrimination of 2-year incident AF was quantified using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) and average precision (AP). AF screening effect was defined as the difference in 2-year incident AF diagnosis (%) in screening versus control in the screened population across deciles of AF risk.
Results: Of 30,630 VITAL-AF participants without prevalent AF, we analyzed 16,937 with available pre-trial ECG and clinical data. Each score discriminated 2-year AF risk (AUROC CHARGE-AF 0.700 [95%CI 0.654-0.739]; ECG-AI 0.780 [0.747-0.810]; CH-AI 0.781 [0.740-0.814]) (AP 0.0935 [0.0818-0.109]; 0.129 [0.111-0.154]; 0.131 [0.115-0.153]) (Figure 1). An AF screening effect was observed in the top decile of CH-AI (2-year AF diagnosis rate 15.6% [13.1-19.4] in screening vs 11.9% [9.9-15.6] in control; difference 3.7% [0.3-7.1]) (Figure 2). The AF screening effect was largest in the top decile of all three scores, but was numerically highest with CH-AI (Figure 3).
Conclusions: In VITAL-AF, the yield of AF screening appeared larger among individuals at high AF risk, particularly using a model combining clinical factors and AI-based ECG analysis. Future trials should assess whether risk-informed AF screening improves outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Qualitative Study of Perspectives on South Asian Dietary Practices: Exploring a Framework for Culturally Tailored Food-is-Medicine Interventions
Kaloth Srivarsha, Fitzgerald Nurgul, Bacalia Karen Mae, Kalbag Aparna, Setoguchi Soko
A Multi-Center Clinic Site Comparison of Patient-level factors Affecting Oral Anticoagulation Prescription for Atrial FibrillationIqbal Fatima, Hoang Kenneth, Chiadika Simbo