Final ID: MDP1026
Targeted Atrial Fibrillation Screening in Older Adults: A Secondary Analysis of the VITAL-AF Trial
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Screening trials for atrial fibrillation (AF) have produced mixed results; however, it is unclear if there is a subset of individuals for whom screening would be effective. Identifying such a subgroup would support targeted screening.
Methods: We conducted a secondary analysis of VITAL-AF (NCT03515057), a randomized trial of one-time, single-lead ECG screening during primary care visits. We tested two approaches to identify a subgroup that would benefit from screening (i.e., heterogenous screening effects). First, we use a potential outcomes framework to develop an effect-based model. Specifically, we predicted the likelihood of AF diagnosis under both screening and usual care conditions using LASSO, a penalized regression method. The difference between these probabilities was the predicted screening effect. Second, we used the CHARGE-AF score, a validated AF risk model. We used interaction testing to determine if the observed diagnosis rates in the screening and control arms were statistically different when stratified by decile of the predicted screening effect and predicted AF risk.
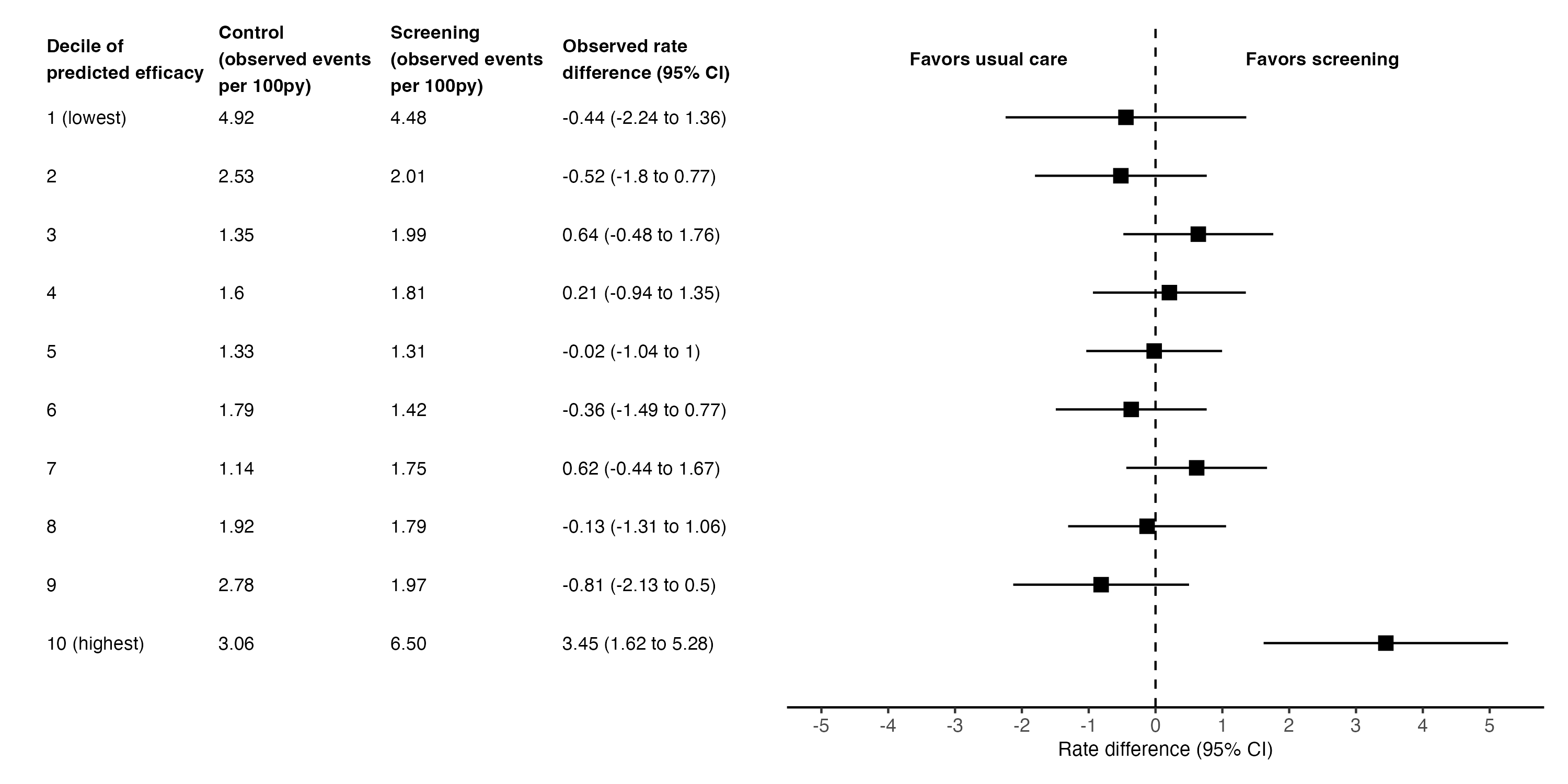
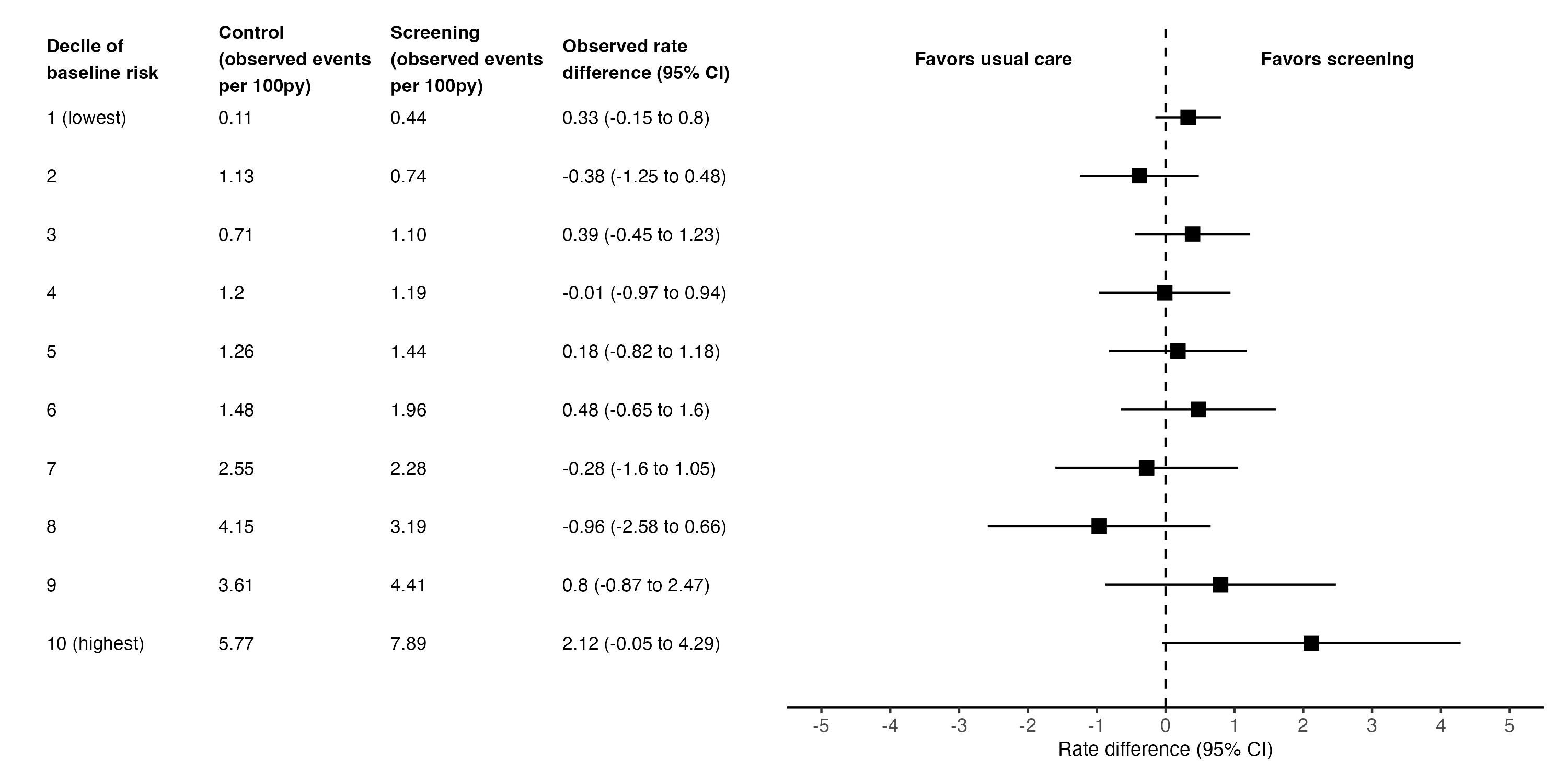
Results: Baseline characteristics were similar between the screening (n=15187) and usual care (n=15078) groups (mean age 74 years, 59% female). On average, screening did not significantly increase the AF diagnosis rate (2.55 vs. 2.30 per 100 person-years, rate difference 0.24, 95%CI -0.18 to 0.67). Patients in the highest decile of predicted screening efficacy (n=3026, 10%) experienced a large and statistically significant increase in AF diagnosis rates due to screening (6.5 vs. 3.06 per 100 person-years, rate difference 3.45, 95%CI 1.62 to 5.28; interaction p-value 0.038) (Figure 1). In this group, the mean age was 84 years and 68% were female. Participants in the highest decile of AF risk using the CHARGE-AF score did not have a statistically significant increase in AF diagnosis rates due to screening (Figure 2). Predicted screening effectiveness and predicted AF risk were poorly correlated (Spearman coefficient 0.13).
Conclusions: One-time screening may increase AF diagnoses in a subgroup of older adults with the largest predicted screening effect. In contrast, predicted AF risk was a poor proxy for predicted screening efficacy. These data caution against the assumption that high AF risk is necessarily correlated with high screening efficacy. Prospective studies are needed to validate whether AF screening is effective in the subgroup identified in this study.
Methods: We conducted a secondary analysis of VITAL-AF (NCT03515057), a randomized trial of one-time, single-lead ECG screening during primary care visits. We tested two approaches to identify a subgroup that would benefit from screening (i.e., heterogenous screening effects). First, we use a potential outcomes framework to develop an effect-based model. Specifically, we predicted the likelihood of AF diagnosis under both screening and usual care conditions using LASSO, a penalized regression method. The difference between these probabilities was the predicted screening effect. Second, we used the CHARGE-AF score, a validated AF risk model. We used interaction testing to determine if the observed diagnosis rates in the screening and control arms were statistically different when stratified by decile of the predicted screening effect and predicted AF risk.
Results: Baseline characteristics were similar between the screening (n=15187) and usual care (n=15078) groups (mean age 74 years, 59% female). On average, screening did not significantly increase the AF diagnosis rate (2.55 vs. 2.30 per 100 person-years, rate difference 0.24, 95%CI -0.18 to 0.67). Patients in the highest decile of predicted screening efficacy (n=3026, 10%) experienced a large and statistically significant increase in AF diagnosis rates due to screening (6.5 vs. 3.06 per 100 person-years, rate difference 3.45, 95%CI 1.62 to 5.28; interaction p-value 0.038) (Figure 1). In this group, the mean age was 84 years and 68% were female. Participants in the highest decile of AF risk using the CHARGE-AF score did not have a statistically significant increase in AF diagnosis rates due to screening (Figure 2). Predicted screening effectiveness and predicted AF risk were poorly correlated (Spearman coefficient 0.13).
Conclusions: One-time screening may increase AF diagnoses in a subgroup of older adults with the largest predicted screening effect. In contrast, predicted AF risk was a poor proxy for predicted screening efficacy. These data caution against the assumption that high AF risk is necessarily correlated with high screening efficacy. Prospective studies are needed to validate whether AF screening is effective in the subgroup identified in this study.
More abstracts on this topic:
Age-, Sex- and/or Ethnic- specific disparities; Biventricular systolic and diastolic strain, and biomarker, prognostic implications in Acute Tuberculous Pericarditis.
Matshela Mamotabo
Administration of the Recombinant Activated Protein C Rescues the Cardiac Vulnerability to Ischemic Insults in Aging through Modulating Inflammatory Response during Ischemia and ReperfusionSlotabec Lily, Rouhi Nadiyeh, Seale Blaise, Wang Hao, Filho Fernanda, Adenawoola Michael, Li Ji