Final ID: Sa2106
Increased Prevalence of High Lipoprotein(a) in Autoimmune or Inflammatory Diseases: A Multi-Center Cohort Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] and autoimmune or inflammatory diseases (AIIDs) are both independently associated with CVD. Systemic inflammation may increase Lp(a) levels through poorly understood mechanisms. Large studies are needed to better understand the relationship between individual AIIDs and the risk of elevated Lp(a).
Aims: We aimed to assess the relationship between Lp(a) and 6 AIIDs: systemic lupus erythematous (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis (AS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and gout. We hypothesized that patients with AIIDs were more likely to have elevated Lp(a) than patients without AIIDs and without ASCVD.
Methods: Data were retrospectively collected across five University of California Medical Centers between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2024. We compared 3 groups, all having at least one Lp(a) measure performed as part of routine medical care: 1) adults who carried an ICD-10 diagnosis of an AIID, 2) adults with a diagnosis of ASCVD (without AIID) and 3) adults without an AIID or ASCVD. Multivariable logistic regression was used to determine the odds of having elevated Lp(a) > 70 mg/dL, adjusted for age, sex, BMI and race/ethnicity.
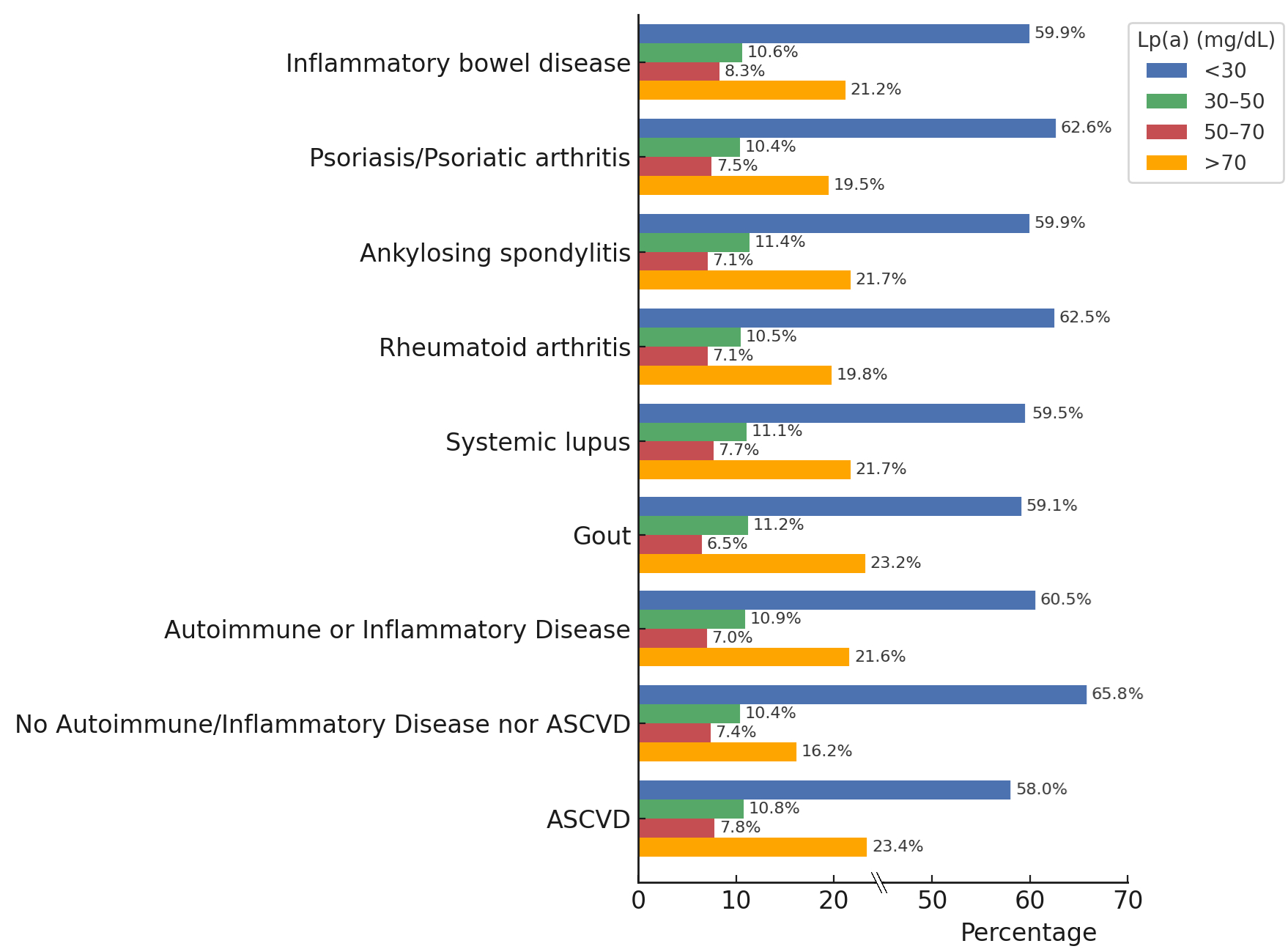
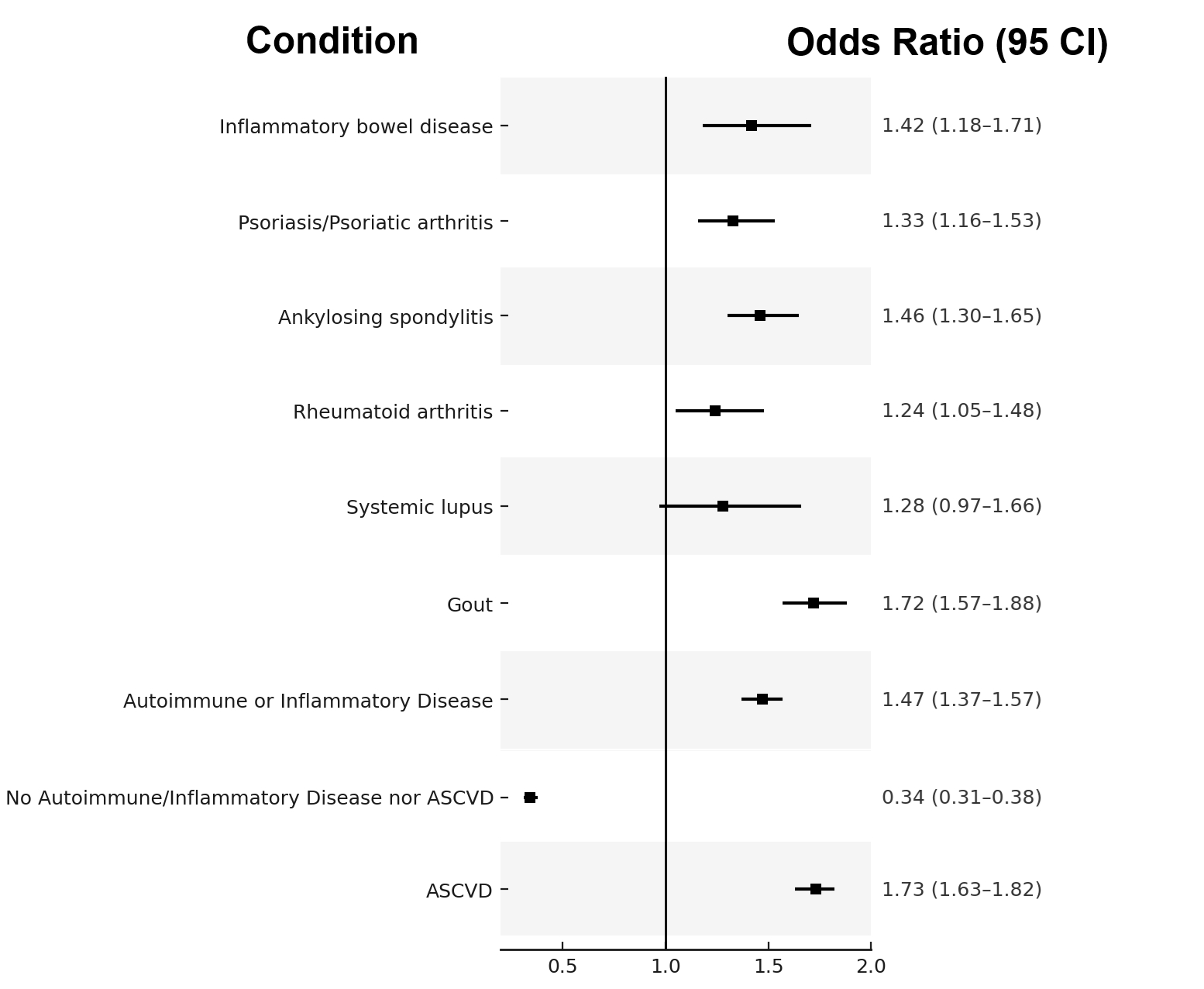
Results: A total of 49,503 patients were included, representing 8073 with AIID: 378 with SLE (5%), 968 with RA (12%), 2028 with AS (25%), 1547 with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis (19%), 806 with IBD (10%) and 3790 with gout (47%). Additionally, 19,279 patients with ASCVD and 28,844 patients with neither disease were included for comparison. For the entire cohort, mean±SD age was 56±16 years with 47% women, 65% White, 11% Asian, 10% Hispanic/Latino, 3% Black, and < 1% Native Hawaiian or Native American. Using a threshold of Lp(a) >70 mg/dL, 21.3% (n = 1717) of patients with AIID conditions had elevated Lp(a) (similar to 23.4% of patients with ASCVD), vs 16.2% (n = 4252) of patients without AIID or ASCVD (p<0.001) (Figure 1). In confounder-adjusted logistic regression, the ratio of patients with elevated Lp(a) (>70 mg/dL) to those with normal-range Lp(a) (<30 mg/dL) was significantly higher among individuals with AIID compared to those with neither AIID nor ASCVD (OR=1.43, 95% CI: 1.33–1.52, p<0.001) (Figure 2).
Conclusions: Patients with AIIDs are more likely to have significantly elevated Lp(a), similar to individuals with ASCVD. The relationship between AIIDs and Lp(a) deserves further study.
Aims: We aimed to assess the relationship between Lp(a) and 6 AIIDs: systemic lupus erythematous (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis (AS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and gout. We hypothesized that patients with AIIDs were more likely to have elevated Lp(a) than patients without AIIDs and without ASCVD.
Methods: Data were retrospectively collected across five University of California Medical Centers between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2024. We compared 3 groups, all having at least one Lp(a) measure performed as part of routine medical care: 1) adults who carried an ICD-10 diagnosis of an AIID, 2) adults with a diagnosis of ASCVD (without AIID) and 3) adults without an AIID or ASCVD. Multivariable logistic regression was used to determine the odds of having elevated Lp(a) > 70 mg/dL, adjusted for age, sex, BMI and race/ethnicity.
Results: A total of 49,503 patients were included, representing 8073 with AIID: 378 with SLE (5%), 968 with RA (12%), 2028 with AS (25%), 1547 with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis (19%), 806 with IBD (10%) and 3790 with gout (47%). Additionally, 19,279 patients with ASCVD and 28,844 patients with neither disease were included for comparison. For the entire cohort, mean±SD age was 56±16 years with 47% women, 65% White, 11% Asian, 10% Hispanic/Latino, 3% Black, and < 1% Native Hawaiian or Native American. Using a threshold of Lp(a) >70 mg/dL, 21.3% (n = 1717) of patients with AIID conditions had elevated Lp(a) (similar to 23.4% of patients with ASCVD), vs 16.2% (n = 4252) of patients without AIID or ASCVD (p<0.001) (Figure 1). In confounder-adjusted logistic regression, the ratio of patients with elevated Lp(a) (>70 mg/dL) to those with normal-range Lp(a) (<30 mg/dL) was significantly higher among individuals with AIID compared to those with neither AIID nor ASCVD (OR=1.43, 95% CI: 1.33–1.52, p<0.001) (Figure 2).
Conclusions: Patients with AIIDs are more likely to have significantly elevated Lp(a), similar to individuals with ASCVD. The relationship between AIIDs and Lp(a) deserves further study.
More abstracts on this topic:
Autoimmunity and Sex Inform Clinical Outcomes of Non-Aortic Arterial Dissections
Gonzalez Moret Yurilu, Chacin Suarez Audry, Musri M. Carolina, Yanamandala Mounica, Lo Kevin, Loscalzo Joseph, Gerhard-herman Marie, Pandey Arvind
A Mast Cell-Specific Receptor Mediates Post-Stroke Brain Inflammation Via a Dural-Brain AxisKothari Ruchita, Caplan Justin, Gonzalez L. Fernando, Jackson Christopher, Bettegowda Chetan, Huang Judy, Koehler Raymond, Tamargo Rafael, Xu Risheng, Dong Xinzhong, Abdulrahim Mostafa, Oh Hyun Jong, Capuzzi Daniel, Nair Sumil, Zhang Yaowu, Limjunyawong Nathachit, Saini Sarbjit, Kim Jennifer