Final ID: Sa3040
Trends in Incidence and Mortality of Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection (SCAD) from 2010 to 2024: A real world data Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection (SCAD) is an increasingly recognized cause of acute coronary syndromes, particularly in younger and otherwise healthy individuals. This study aims to examine temporal trends in SCAD incidence and mortality across various demographic groups using a large, real-world clinical database.
Method:
By utilizing the TriNetX database, we identified all inpatient admissions between January 1, 2010, and December 31, 2024. New cases of SCAD were captured using ICD-10 codes (I25–I45). Out of 22,652,125 patients, a total of 28,518 were diagnosed with SCAD. Incidence and mortality trends were analyzed and compared over time and across baseline characteristics including sex, age, race, and ethnicity.
Result:
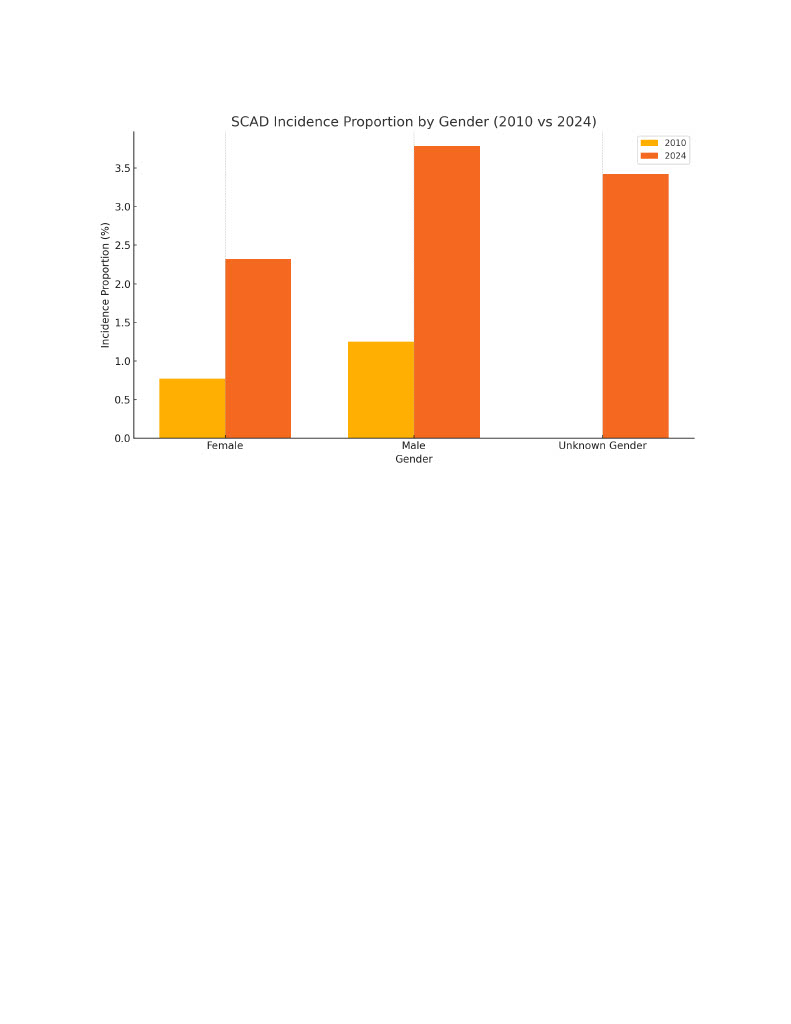
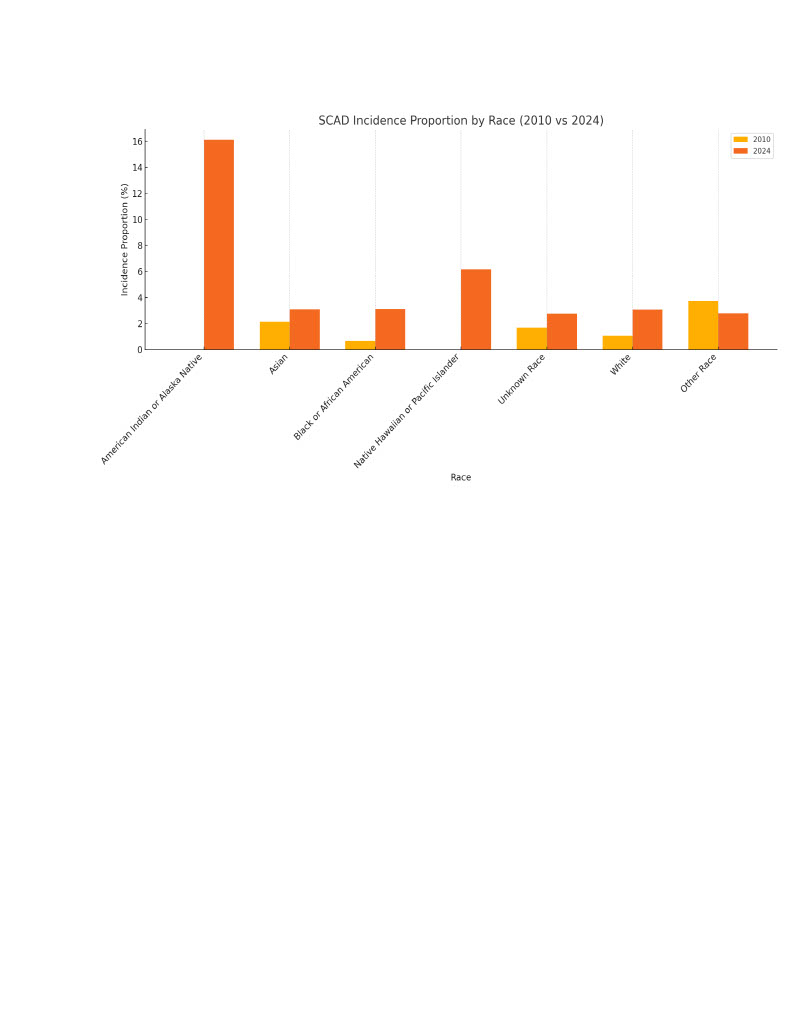
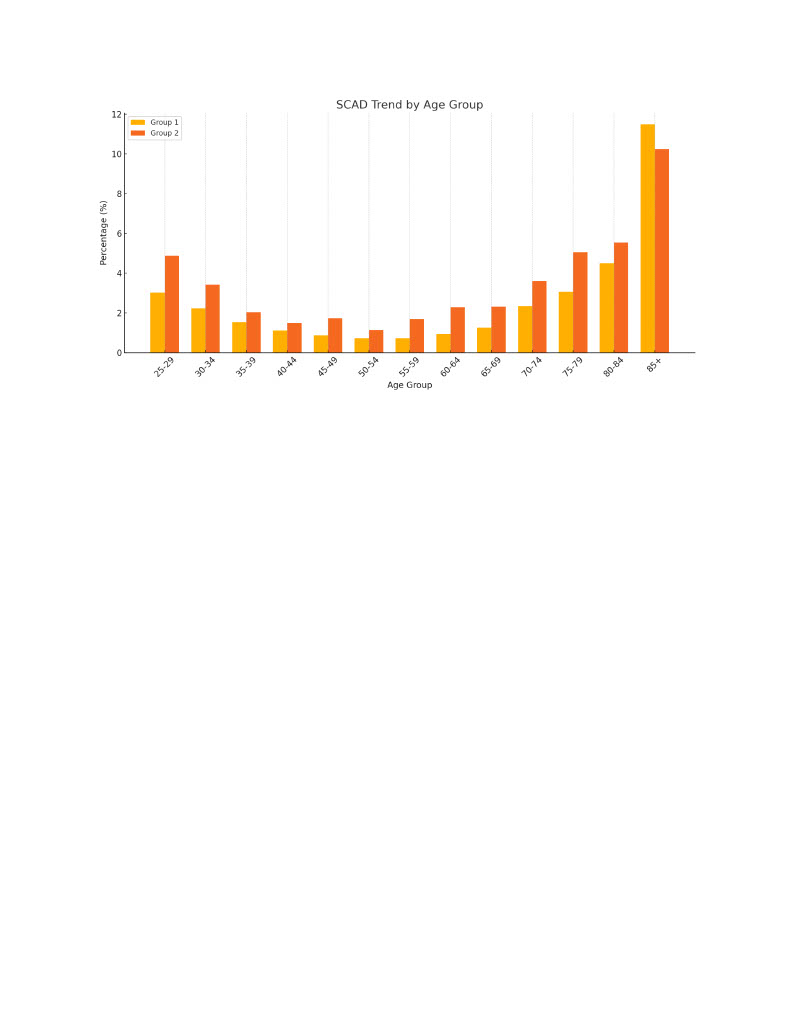
A total of 28,518 patients were diagnosed with SCAD between 2010 and 2024. The incidence proportion increased significantly from 0.004% (340 cases) in 2010 to 0.029% (2,495 cases) in 2024 (p < 0.01). Among males, incidence rose from 0.005% (193 cases) to 0.037% (1,245 cases), and among females from 0.003% (146 cases) to 0.023% (1,177 cases) (p < 0.01 for both). The incidence in Asian patients increased from 0.005% to 0.037%, and among individuals identified as Not Hispanic or Latino, from 0.004% to 0.029%. SCAD incidence rose across all adult age groups, with the most pronounced increase observed in patients aged ≥60 years, reaching 0.045% in 2024 (p < 0.01). Mortality rate increased from 1.001% (116 deaths) in 2010 to 3.035% (476 deaths) in 2024 (p < 0.01). Mortality was highest among patients aged 70 years and older, reaching approximately 5%. The highest mortality incidence was observed among Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander individuals (6.173%), followed by Asian patients (3.086%).
Conclusion:
The incidence and mortality of SCAD have increased significantly over the past decade, with notable disparities across age, sex, and racial subgroups. These findings underscore the importance of improved recognition, prevention strategies, and risk stratification, especially among high-risk populations.
Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection (SCAD) is an increasingly recognized cause of acute coronary syndromes, particularly in younger and otherwise healthy individuals. This study aims to examine temporal trends in SCAD incidence and mortality across various demographic groups using a large, real-world clinical database.
Method:
By utilizing the TriNetX database, we identified all inpatient admissions between January 1, 2010, and December 31, 2024. New cases of SCAD were captured using ICD-10 codes (I25–I45). Out of 22,652,125 patients, a total of 28,518 were diagnosed with SCAD. Incidence and mortality trends were analyzed and compared over time and across baseline characteristics including sex, age, race, and ethnicity.
Result:
A total of 28,518 patients were diagnosed with SCAD between 2010 and 2024. The incidence proportion increased significantly from 0.004% (340 cases) in 2010 to 0.029% (2,495 cases) in 2024 (p < 0.01). Among males, incidence rose from 0.005% (193 cases) to 0.037% (1,245 cases), and among females from 0.003% (146 cases) to 0.023% (1,177 cases) (p < 0.01 for both). The incidence in Asian patients increased from 0.005% to 0.037%, and among individuals identified as Not Hispanic or Latino, from 0.004% to 0.029%. SCAD incidence rose across all adult age groups, with the most pronounced increase observed in patients aged ≥60 years, reaching 0.045% in 2024 (p < 0.01). Mortality rate increased from 1.001% (116 deaths) in 2010 to 3.035% (476 deaths) in 2024 (p < 0.01). Mortality was highest among patients aged 70 years and older, reaching approximately 5%. The highest mortality incidence was observed among Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander individuals (6.173%), followed by Asian patients (3.086%).
Conclusion:
The incidence and mortality of SCAD have increased significantly over the past decade, with notable disparities across age, sex, and racial subgroups. These findings underscore the importance of improved recognition, prevention strategies, and risk stratification, especially among high-risk populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
Cardiovascular Events in Hospitalized Patients with Malignant Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Nationwide Analysis
Philip Anil, Banga Akshat, Saeed Muhammad Subhan, Briones-zamora Killen H., Briones-claudett Killen H., Kohli Saksham, Khullar Rohit, George Lina James, Mautong Hans, John Kevin, Varma Revati, Kini Saurav, Khalid Abdullah, Saha Shubhashis, Caputi Zuniga Angelo
APOL1 Risk Variants and Risk of Incident Atrial Fibrillation in Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT)Ahmad Muhammad, Kazibwe Richard, Mostafa Mohamed, Naeem Rimsha, Singh Sanjay, Bansal Nisha, Soliman Elsayed