Final ID: Sa3105
Safety and Efficacy of Reduced-Dose versus Full-Dose Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Patients with cancer-associated venous thromboembolism (VTE) face high risks of recurrent thrombosis and bleeding during prolonged oral anticoagulant therapy. While full-dose oral anticoagulants are commonly used, the safety and efficacy of reduced doses after initial treatment are unclear.
Hypothesis: Reduced-dose oral anticoagulants are as effective as full-dose therapy in preventing thromboembolism, with a lower bleeding risk in patients with cancer-associated VTE.
Methods: We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing reduced-dose and full-dose oral anticoagulants in adults with active cancer and VTE. Searches were conducted in PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases. A random-effects model analyzed outcomes, including major bleeding or clinically relevant non-major bleeding (per International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis criteria), a composite of VTE recurrence, major bleeding, or clinically relevant non-major bleeding, and individual risks of major bleeding, clinically relevant non-major bleeding, VTE recurrence, and all-cause mortality.
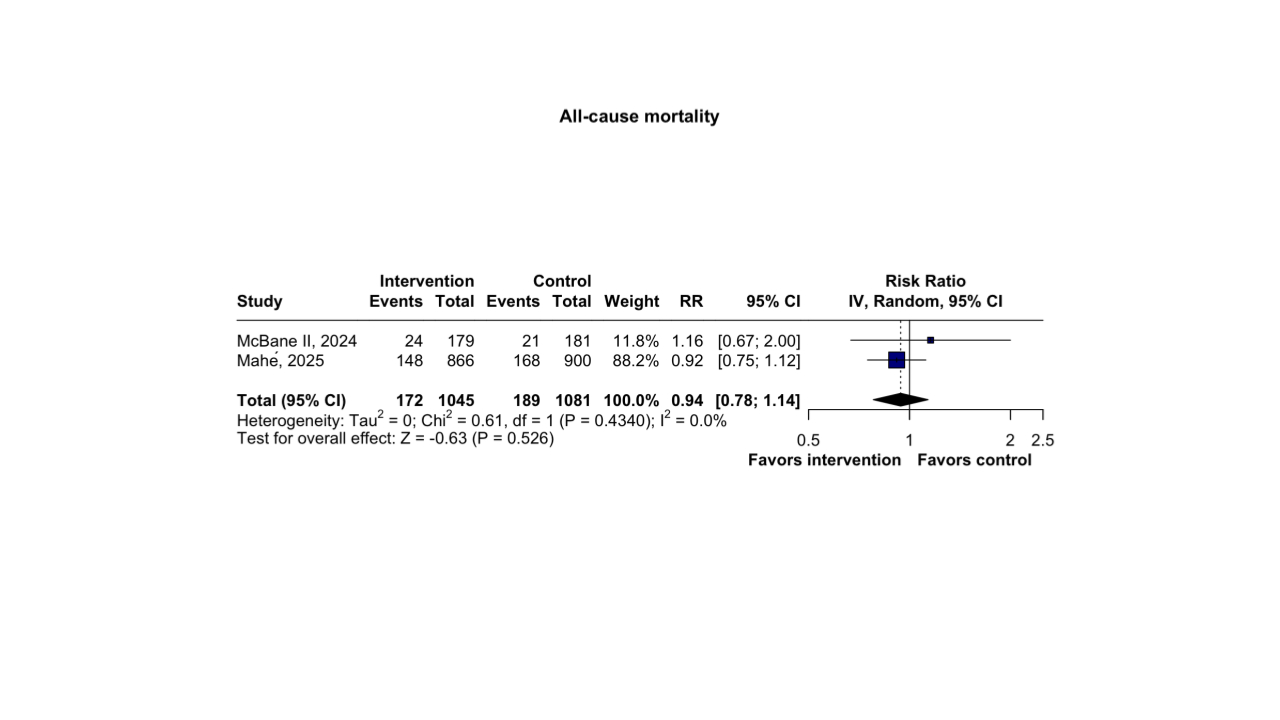
Results: Three RCTs with 2,361 patients were included. Two studies compared apixaban 2.5 mg versus 5 mg twice daily, and one compared rivaroxaban 10 mg versus 20 mg once daily. Reduced-dose therapy significantly lowered the composite outcome risk (RR 0.77; 95% CI 0.64–0.93; p=0.006; Figure 1) and combined major or clinically relevant non-major bleeding risk (RR 0.76; 95% CI 0.62–0.93; p=0.008; Figure 2) versus full-dose therapy. No significant differences were found for major bleeding (RR 0.73; 95% CI 0.46–1.17; p=0.194), clinically relevant non-major bleeding (RR 0.80; 95% CI 0.62–1.02; p=0.076), VTE recurrence (RR 0.84; 95% CI 0.51–1.38; p=0.482), or all-cause mortality (RR 0.94; 95% CI 0.78–1.14; p=0.526; Figure 3).
Conclusions: Our study suggests that reduced-dose oral anticoagulants appear as effective as full-dose therapy for preventing thromboembolism in cancer-associated VTE, with a reduced bleeding risk. This supports reduced-dose therapy as a safe long-term option in selected patients.
Hypothesis: Reduced-dose oral anticoagulants are as effective as full-dose therapy in preventing thromboembolism, with a lower bleeding risk in patients with cancer-associated VTE.
Methods: We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing reduced-dose and full-dose oral anticoagulants in adults with active cancer and VTE. Searches were conducted in PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases. A random-effects model analyzed outcomes, including major bleeding or clinically relevant non-major bleeding (per International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis criteria), a composite of VTE recurrence, major bleeding, or clinically relevant non-major bleeding, and individual risks of major bleeding, clinically relevant non-major bleeding, VTE recurrence, and all-cause mortality.
Results: Three RCTs with 2,361 patients were included. Two studies compared apixaban 2.5 mg versus 5 mg twice daily, and one compared rivaroxaban 10 mg versus 20 mg once daily. Reduced-dose therapy significantly lowered the composite outcome risk (RR 0.77; 95% CI 0.64–0.93; p=0.006; Figure 1) and combined major or clinically relevant non-major bleeding risk (RR 0.76; 95% CI 0.62–0.93; p=0.008; Figure 2) versus full-dose therapy. No significant differences were found for major bleeding (RR 0.73; 95% CI 0.46–1.17; p=0.194), clinically relevant non-major bleeding (RR 0.80; 95% CI 0.62–1.02; p=0.076), VTE recurrence (RR 0.84; 95% CI 0.51–1.38; p=0.482), or all-cause mortality (RR 0.94; 95% CI 0.78–1.14; p=0.526; Figure 3).
Conclusions: Our study suggests that reduced-dose oral anticoagulants appear as effective as full-dose therapy for preventing thromboembolism in cancer-associated VTE, with a reduced bleeding risk. This supports reduced-dose therapy as a safe long-term option in selected patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Rare Case of Acute Undifferentiated Leukemia Presenting as an Isolated Cardiac Mass
Mallipeddi Tarun, Rantanen Petra, Debakey Michael, Cheng Lily, Waheed Nida
Adherence to Guideline-Directed Oral Anticoagulant Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter Admitted in a Tertiary Private Hospital: A Retrospective StudyWong Jasmine, Carandang Frances, Segundo Luigi Pierre