Final ID: MP267
Network Meta-Analysis of Dose-Dependent Effects of Factor XIa Inhibitors vs Direct Oral Anticoagulants for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Factor XIa inhibitors represent a novel class of anticoagulants that target upstream components of the coagulation cascade, aiming to reduce thromboembolic risk. As their clinical development progresses, understanding their comparative efficacy and safety across varying doses remains critical, particularly in relation to established direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) in atrial fibrillation (AF). Existing head-to-head data is limited, and dose-related outcomes have not been systematically compared across agents.
Methods: Embase, Scopus, PubMed, and Cochrane were systematically searched from inception to May 2025 to identify studies comparing XIa inhibitors with DOACs in AF. Risk ratios (RR) with 95% CIs were pooled. Doses were ranked using the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA), ranging from 0 to 1. DOACs served as the reference group. All analyses were conducted using R Studio version 4.3.1.
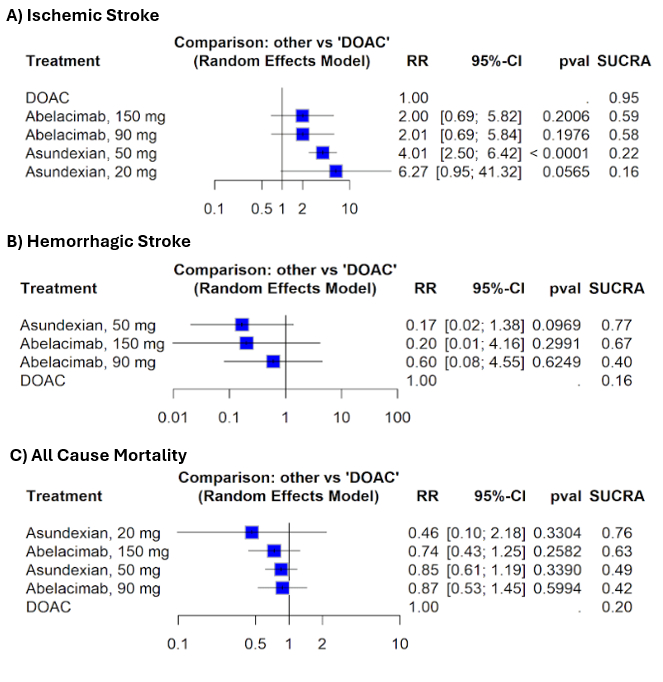
Results: Three RCTs (XIa inhibitors = 8772, DOACs = 8073) were included in this network meta-analysis. Asundexian 50 mg was associated with a significantly higher risk of ischemic stroke compared to DOACs (RR: 4.01, 95% CI: 2.50, 6.42, p<0.0001). DOACs ranked highest in reducing ischemic stroke risk (SUCRA = 0.95), while Asundexian 20 mg ranked lowest (SUCRA = 0.16). For hemorrhagic stroke, no significant differences were found, but Asundexian 50 mg had the highest probability of being safest (SUCRA = 0.77). Regarding all-cause mortality, no treatment showed significant difference; however, Asundexian 20 mg had the highest SUCRA ranking (0.76), and DOACs ranked lowest (0.20).
Conclusion: Current evidence does not support XIa inhibitors superiority over DOACs for AF. The increased risk of ischemic stroke at higher doses, particularly with Asundexian 50 mg, is clinically unacceptable when compared to established DOACs. While some doses show favorable safety rankings, these do not translate into clear clinical benefit. Broader adoption of XIa inhibitors should await robust data confirming a favorable risk-benefit profile.
Methods: Embase, Scopus, PubMed, and Cochrane were systematically searched from inception to May 2025 to identify studies comparing XIa inhibitors with DOACs in AF. Risk ratios (RR) with 95% CIs were pooled. Doses were ranked using the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA), ranging from 0 to 1. DOACs served as the reference group. All analyses were conducted using R Studio version 4.3.1.
Results: Three RCTs (XIa inhibitors = 8772, DOACs = 8073) were included in this network meta-analysis. Asundexian 50 mg was associated with a significantly higher risk of ischemic stroke compared to DOACs (RR: 4.01, 95% CI: 2.50, 6.42, p<0.0001). DOACs ranked highest in reducing ischemic stroke risk (SUCRA = 0.95), while Asundexian 20 mg ranked lowest (SUCRA = 0.16). For hemorrhagic stroke, no significant differences were found, but Asundexian 50 mg had the highest probability of being safest (SUCRA = 0.77). Regarding all-cause mortality, no treatment showed significant difference; however, Asundexian 20 mg had the highest SUCRA ranking (0.76), and DOACs ranked lowest (0.20).
Conclusion: Current evidence does not support XIa inhibitors superiority over DOACs for AF. The increased risk of ischemic stroke at higher doses, particularly with Asundexian 50 mg, is clinically unacceptable when compared to established DOACs. While some doses show favorable safety rankings, these do not translate into clear clinical benefit. Broader adoption of XIa inhibitors should await robust data confirming a favorable risk-benefit profile.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Curious Case of Clozapine Carditis with Cardiac Convalescence
Maamari Dimitri, Koshti Vivek, Yaros Katarina, Berbarie Rafic
Imatinib Mesylate and Sirolimus Inhibit Fibrogenic Activation of Endocardial Endothelial CellsVon Mueffling Alexa, Friehs Ingeborg, Gaal Julia, Zajac Cindy, Lee Umji, Diaz-gil Daniel, Jenkins Kathy, Melero-martin Juan, Del Nido Pedro, Mayer John