Final ID: MP2504
Temporal Trends in Cardiac Arrest and Cancer-Related Mortality Among Adults in the United States, 1999-2023
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Cardiac arrest (CA) remains a major contributor to cardiovascular-related mortality in the United States. The coexistence of cancer significantly exacerbates overall disease burden. This study investigates CA and cancer-related trends and demographic disparities in adults from 1999 to 2023.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of CDC WONDER data was conducted to investigate the trends in mortality associated with CA (ICD codes: I46.x) in patients with cancer (ICD codes: C00-C97). Using Joinpoint regression analysis, the study calculated age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMR) per 100,000 individuals and corresponding annual percentage changes (APC), along with 95% confidence intervals. The year, sex, race/ethnicity, age groups, and state were used to stratify the data.
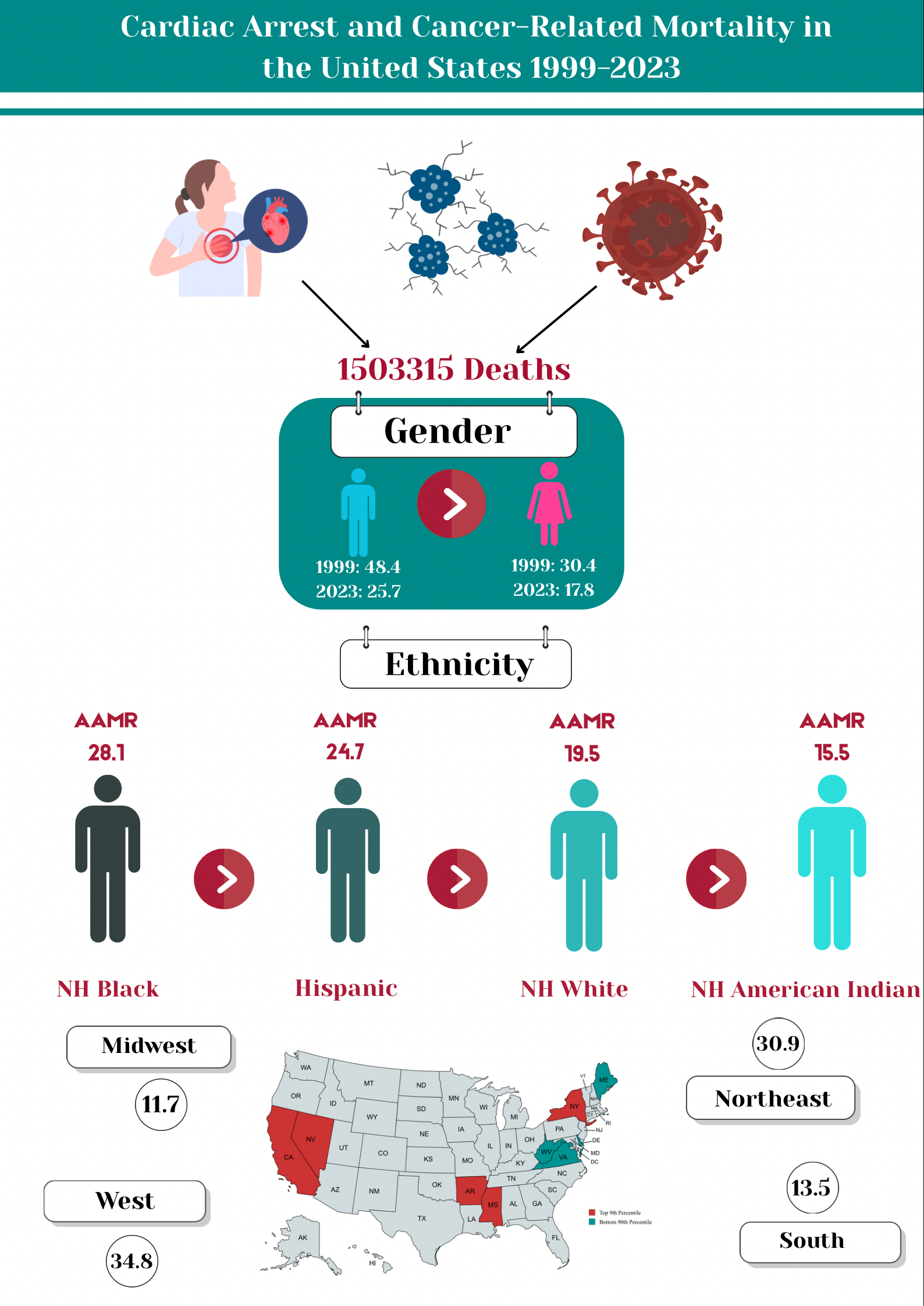
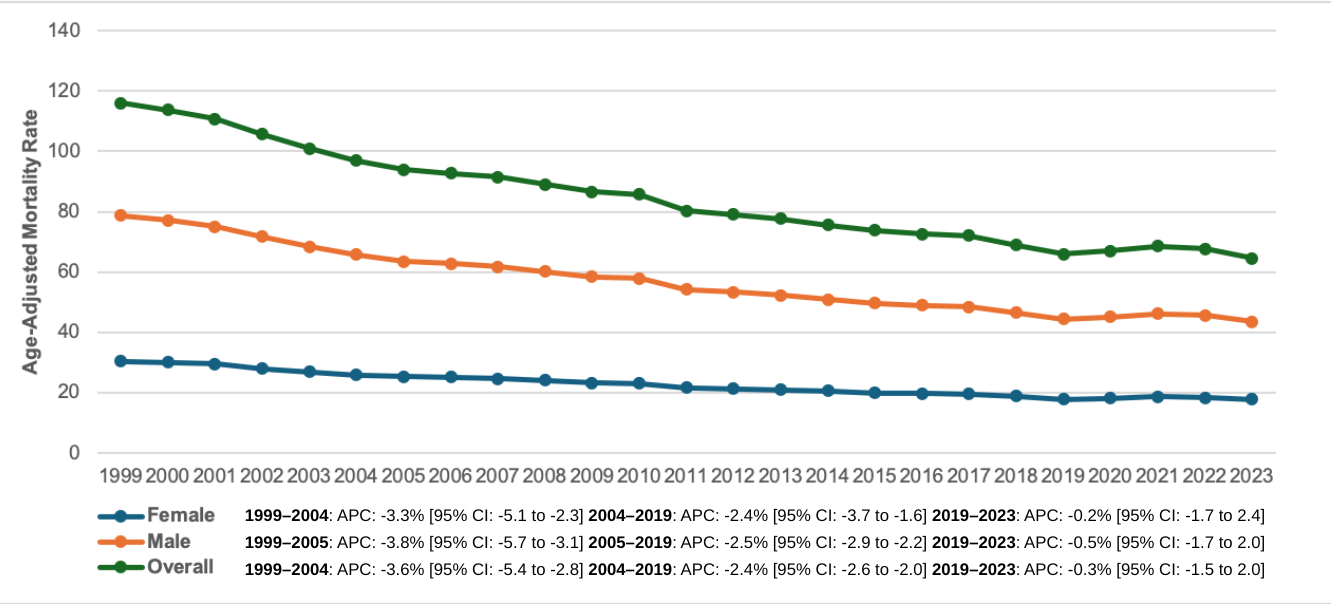
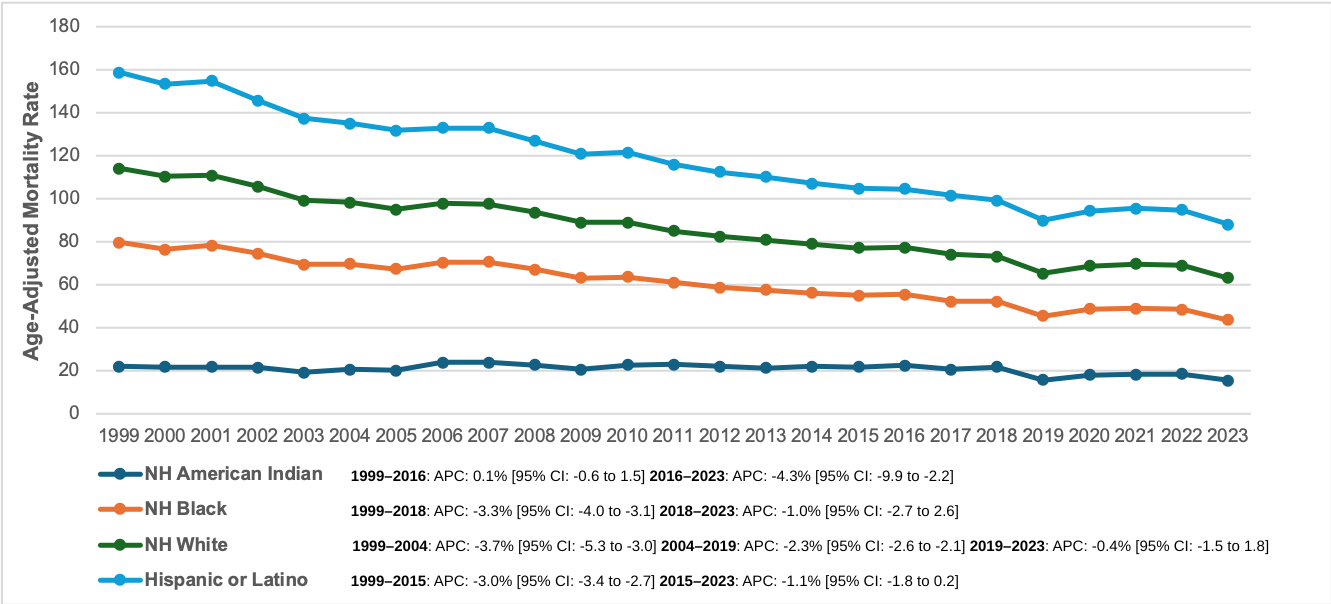
Results: Between 1999 and 2023, CA in cancer was responsible for 1,503,315 deaths. With an AAPC of -2.3 (95% CI: -2.4 to 2.1, p < 0.001), the overall AAMR decreased from 37.3 in 1999 to 21.1 in 2023. Adult men had higher AAMRs than women (men: 48.4; women: 30.4) in 1999 to (men: 25.7; women: 17.8) in 2023, with decline for both sexes [men: AAPC: -2.5, p < 0.001; women: AAPC: -2.4, p < 0.001]. AAMRs varied significantly by race, for NH Black individuals (57.6 to 28.1), NH American Indians (22.1 to 15.5), Hispanics (44.6 to 24.7) and NH Whites (34.4 to 19.5) from 1999 to 2023 respectively. The AAMR decreased for all races from 1999 to 2023, most notably in Black individuals (AAPC: -2.9, p < 0.001). The AAMR decreased for all age groups (2.6 to 1.6) in younger adults (25-44 years), (23.7 to 13.5) in middle-aged adults (45-64 years), and (143.4 to 80.6) in older adults (65+ years) from 1999-2023, but the greatest decline was observed in older adults (AAPC: -2.2, p < 0.001). The AAMR decreased for all census regions, for Northeast (62.3 to 30.9), similarly for Midwest (17.2 to 11.7), South (31.0 to 13.5), and for West it was (46.5 to 34.8) from 1999 to 2023 respectively, but the highest decline was seen in South region (AAPC: -3.3, p < 0.001). AAMRs varied by state, from 5.2 in West Virginia to 55.3 in California during 2023.
Conclusion: This study reveals significant demographic and geographic disparities in CA and cancer-related mortality among U.S. adults from 1999-2023, with a disproportionately high burden observed in older adults, males, and NH Black individuals. These findings underscore the urgent need for targeted, equity-driven public health strategies for high-risk groups.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of CDC WONDER data was conducted to investigate the trends in mortality associated with CA (ICD codes: I46.x) in patients with cancer (ICD codes: C00-C97). Using Joinpoint regression analysis, the study calculated age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMR) per 100,000 individuals and corresponding annual percentage changes (APC), along with 95% confidence intervals. The year, sex, race/ethnicity, age groups, and state were used to stratify the data.
Results: Between 1999 and 2023, CA in cancer was responsible for 1,503,315 deaths. With an AAPC of -2.3 (95% CI: -2.4 to 2.1, p < 0.001), the overall AAMR decreased from 37.3 in 1999 to 21.1 in 2023. Adult men had higher AAMRs than women (men: 48.4; women: 30.4) in 1999 to (men: 25.7; women: 17.8) in 2023, with decline for both sexes [men: AAPC: -2.5, p < 0.001; women: AAPC: -2.4, p < 0.001]. AAMRs varied significantly by race, for NH Black individuals (57.6 to 28.1), NH American Indians (22.1 to 15.5), Hispanics (44.6 to 24.7) and NH Whites (34.4 to 19.5) from 1999 to 2023 respectively. The AAMR decreased for all races from 1999 to 2023, most notably in Black individuals (AAPC: -2.9, p < 0.001). The AAMR decreased for all age groups (2.6 to 1.6) in younger adults (25-44 years), (23.7 to 13.5) in middle-aged adults (45-64 years), and (143.4 to 80.6) in older adults (65+ years) from 1999-2023, but the greatest decline was observed in older adults (AAPC: -2.2, p < 0.001). The AAMR decreased for all census regions, for Northeast (62.3 to 30.9), similarly for Midwest (17.2 to 11.7), South (31.0 to 13.5), and for West it was (46.5 to 34.8) from 1999 to 2023 respectively, but the highest decline was seen in South region (AAPC: -3.3, p < 0.001). AAMRs varied by state, from 5.2 in West Virginia to 55.3 in California during 2023.
Conclusion: This study reveals significant demographic and geographic disparities in CA and cancer-related mortality among U.S. adults from 1999-2023, with a disproportionately high burden observed in older adults, males, and NH Black individuals. These findings underscore the urgent need for targeted, equity-driven public health strategies for high-risk groups.
More abstracts on this topic:
A diagnostic challenge overcome with persistent clinical suspicion in a case of cardiac AL amyloidosis
Zimmerman Allison, Kuriakose Philip, Godfrey Amanda, Ananthasubramaniam Karthikeyan, Cowger Jennifer, Al-darzi Waleed
A Porcine Model of Cardiac Arrest Without Pre-Arrest Fluid Loading, Sternal Molding, or EpinephrineParadis Aidan, Paradis Norman, Gaddy David, Moodie Karen, Mader Timothy, Dufresne Alexandre, Couturier Christine, Dufresne Simon, Davis Daniel, Sims Christopher