Final ID: MP1989
Serum Iron Predicts Long-Term Cardiovascular Outcomes in Diabetic Patients with Coronary Artery Disease, Independent of Iron Status
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Iron status is crucial in the pathophysiology of coronary artery disease (CAD) and diabetes, with both iron deficiency and overload linked to adverse outcomes. However, the role of serum iron in diabetic CAD patients remains unclear.
Objective: To evaluate the prognostic value of iron markers in predicting major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCEs) in diabetic CAD patients.
Research Design and Methods: Serum iron, ferritin, transferrin, transferrin saturation, and soluble transferrin receptor were measured in 416 prospectively enrolled diabetic CAD patients. The primary endpoint was 1-year MACCEs, including cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stroke, revascularization, and heart failure.
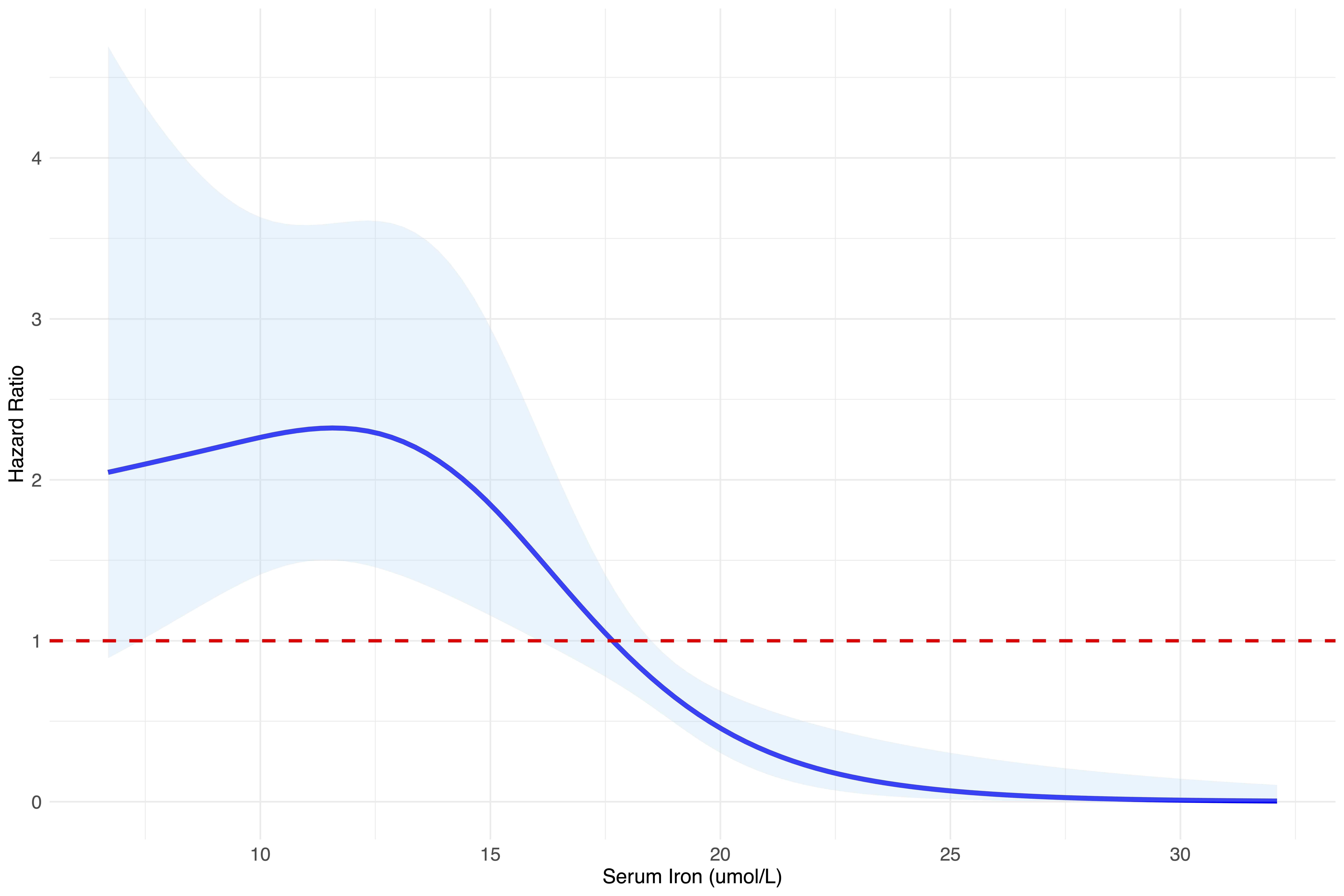
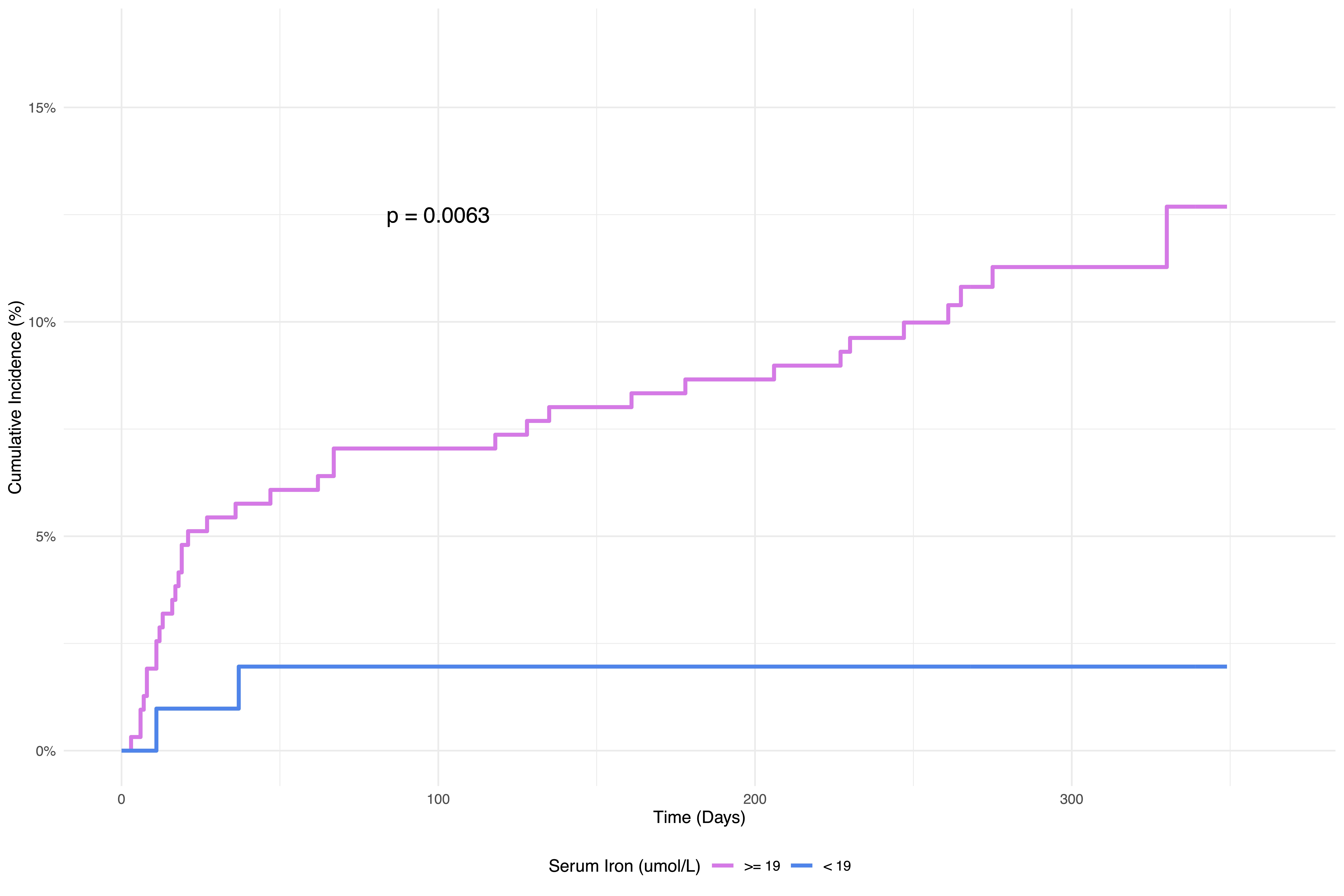
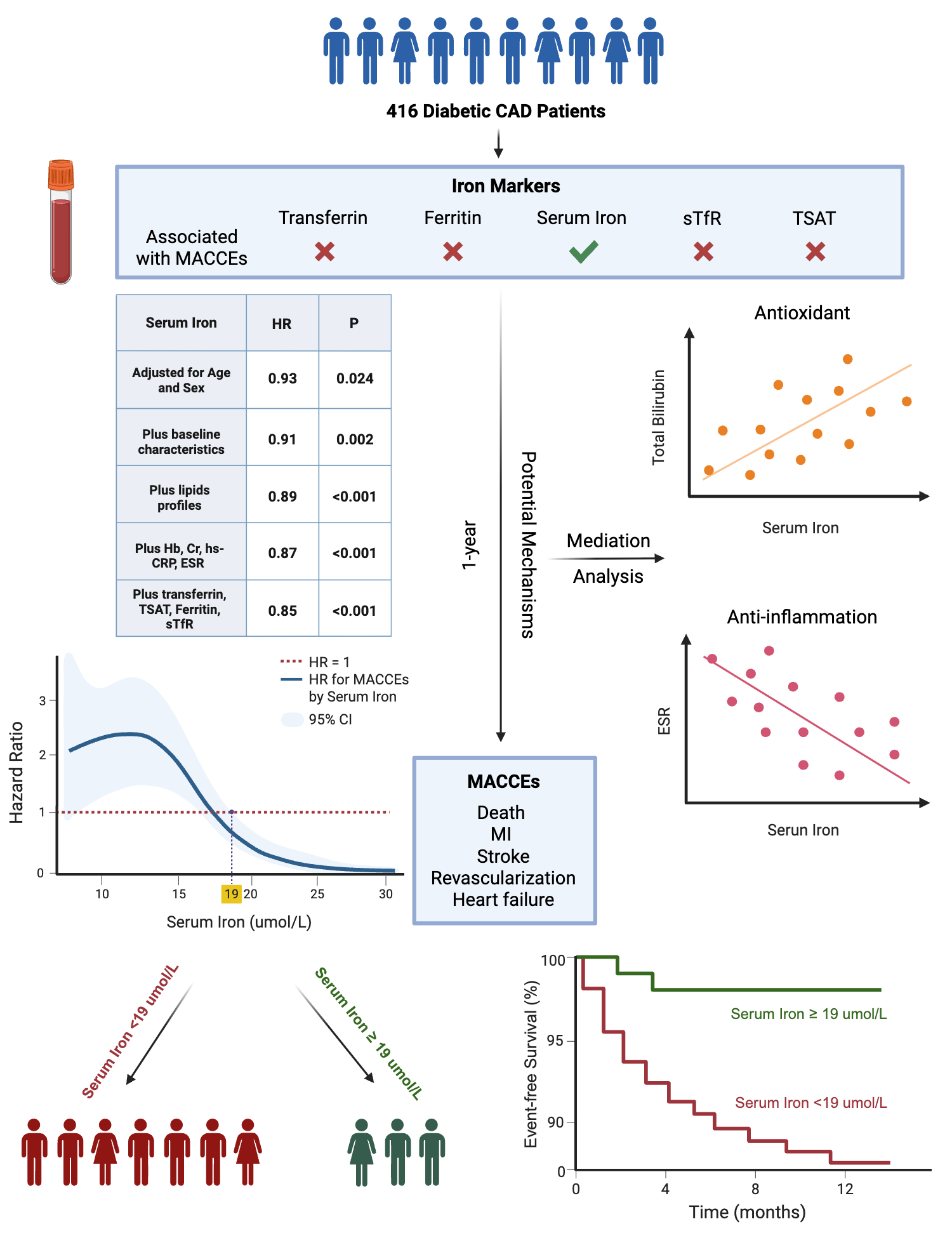
Results: During a median follow-up of 1.13 years, 38 MACCEs were observed (9.1%). Serum iron was an independent predictor of 1-year MACCEs (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.92; 95% CI: 0.88–0.97; P = 0.003), remaining significant after adjusting for baseline variables, hemoglobin, inflammation, lipid profiles, and iron storage markers (HR: 0.88; 95% CI: 0.81–0.96; P = 0.001). A decreasing exponential relationship was observed, identifying a clinically relevant threshold of 19 μmol/L. Patients with serum iron ≥19 μmol/L had significantly lower MACCEs compared to those with <19 μmol/L (P < 0.05). Mediation analysis suggested that the protective effect of serum iron was partially mediated through reduced erythrocyte sedimentation rate (15.5%) and increased bilirubin (19.4%).
Conclusions: Serum iron predicts long-term outcomes in diabetic CAD patients irrespective of iron storage status. A clinically significant threshold of 19 μmol/L was identified for risk stratification, with its protective effects potentially mediated through anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
Objective: To evaluate the prognostic value of iron markers in predicting major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCEs) in diabetic CAD patients.
Research Design and Methods: Serum iron, ferritin, transferrin, transferrin saturation, and soluble transferrin receptor were measured in 416 prospectively enrolled diabetic CAD patients. The primary endpoint was 1-year MACCEs, including cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stroke, revascularization, and heart failure.
Results: During a median follow-up of 1.13 years, 38 MACCEs were observed (9.1%). Serum iron was an independent predictor of 1-year MACCEs (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.92; 95% CI: 0.88–0.97; P = 0.003), remaining significant after adjusting for baseline variables, hemoglobin, inflammation, lipid profiles, and iron storage markers (HR: 0.88; 95% CI: 0.81–0.96; P = 0.001). A decreasing exponential relationship was observed, identifying a clinically relevant threshold of 19 μmol/L. Patients with serum iron ≥19 μmol/L had significantly lower MACCEs compared to those with <19 μmol/L (P < 0.05). Mediation analysis suggested that the protective effect of serum iron was partially mediated through reduced erythrocyte sedimentation rate (15.5%) and increased bilirubin (19.4%).
Conclusions: Serum iron predicts long-term outcomes in diabetic CAD patients irrespective of iron storage status. A clinically significant threshold of 19 μmol/L was identified for risk stratification, with its protective effects potentially mediated through anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Real-world Evaluation of Longitudinal Healthcare Expenses in a Health System Registry of Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease Enabled by the 21st Century Cures Act
A Longitudinal 20-year Analysis Indicates Acceleration of Cardiometabolic Comorbidities on Dementia Risk
Dhingra Lovedeep, Aminorroaya Arya, Pedroso Aline, Rajpura Jigar, Mehanna Sherif, Tonnu-mihara Ivy, Khera Rohan
A Longitudinal 20-year Analysis Indicates Acceleration of Cardiometabolic Comorbidities on Dementia Risk
Lihua Huang, Danish Muhammad, Auyeung Tw, Jenny Lee, Kwok Timothy, Abrigo Jill, Wei Yingying, Lo Cecilia, Fung Erik