Final ID: LBMP4
Prognostic Value of Serum Bilirubin and Therapeutic Potential of the Bilirubin-based Nanoparticle for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) remains the leading cause of death globally. Despite well-controlled low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) level, a subset of patients still suffered from major adverse cardiac events (MACE), highlighting the need to identify biomarkers for risk stratification and to develop novel treatment for reducing this residual risk.
Recent growing evidence supports bilirubin, the endogenous metabolite of heme catabolism, may exert potential cardiovascular protective effect due to its anti-inflammatory properties. However, its role as a prognostic biomarker in ASCVD and the direct therapeutic effect on atherosclerosis remain unclear.
Hypothesis
Elevated bilirubin level within normal range predicted reduced MACE risk in ASCVD patients, and bilirubin treatment reduced plaque formation in mouse model of atherosclerosis.
Methods
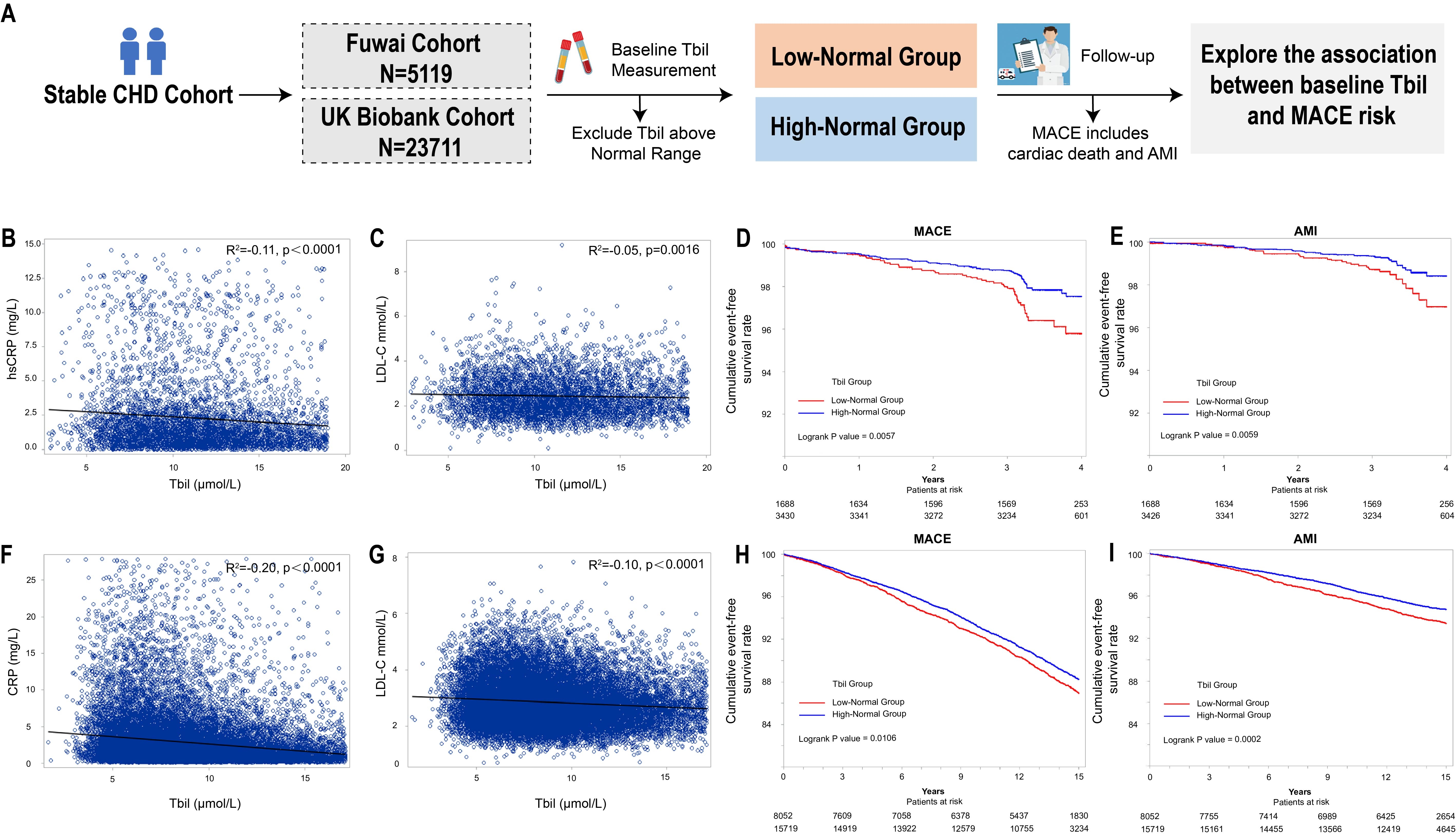
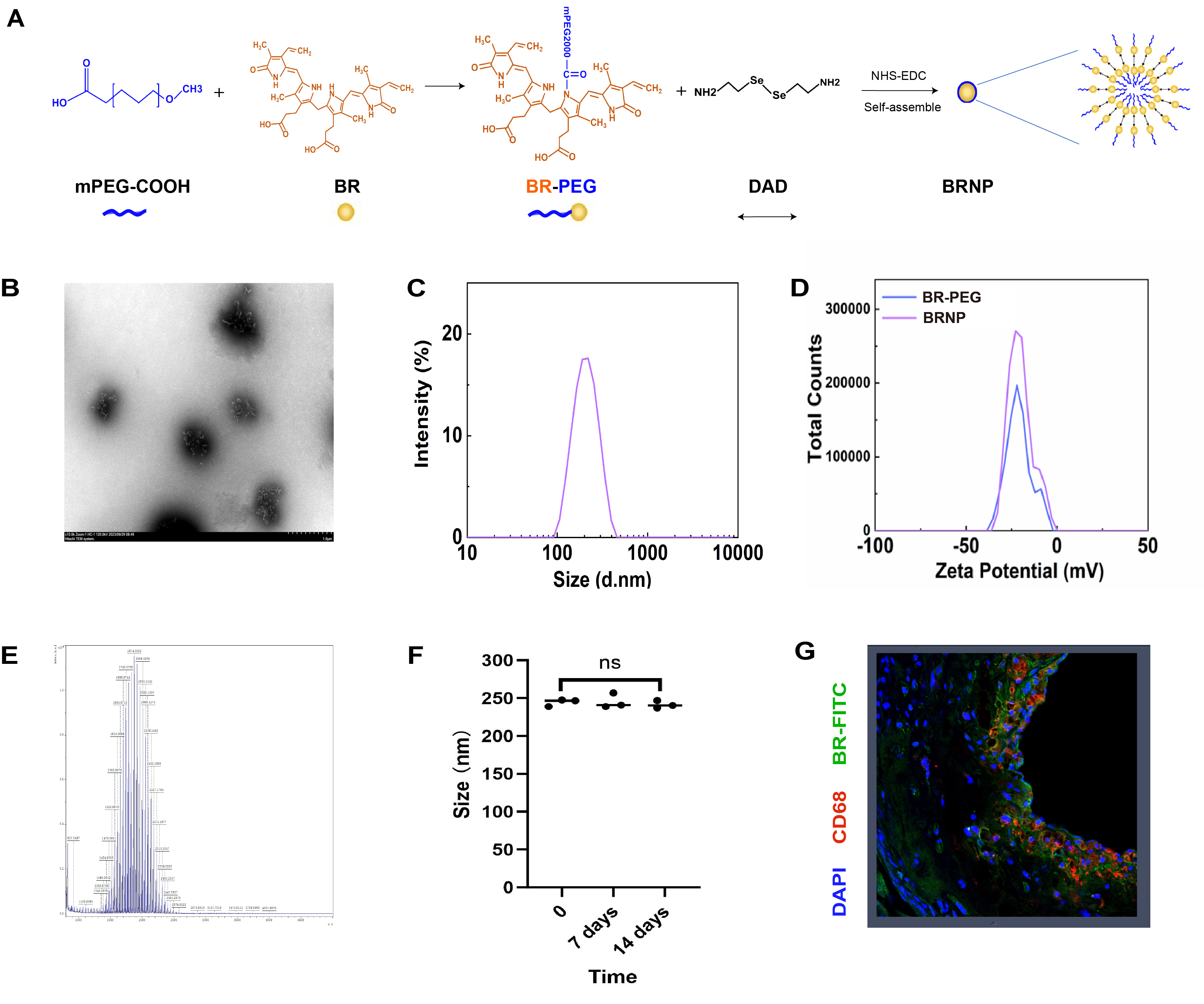
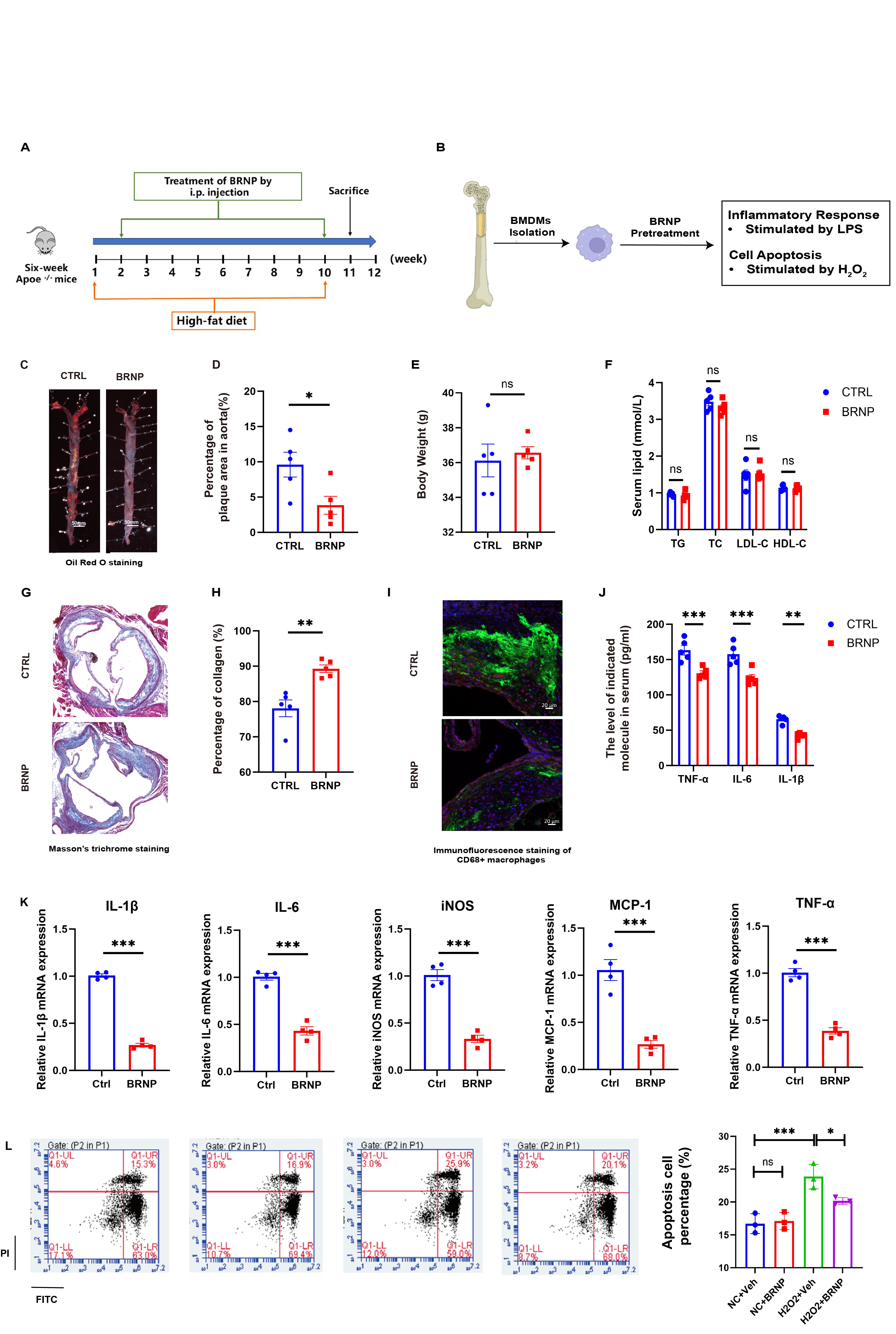
The association between baseline serum total bilirubin (Tbil) level and MACE risk, a composite endpoint of cardiac death and acute myocardial infarction, was explored in two large-scale cohorts of patients with stable coronary heart disease (CHD), the Fuwai cohort and the UK biobank cohort. Patients with Tbil above normal range were excluded and the included patients were categorized into the low-normal group and the high-normal group based on Tbil. A bilirubin-based nanoparticle (BRNP), composed of the biocompatible material polyethylene glycol and the ROS responsive diselenide bond, was developed to improve the solubility and stability of bilirubin. The Apoe-/- mouse fed with high-fat diet was used as model of atherosclerosis, and the bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) were used to examine the effect of BRNP in vitro.
Results
In the Fuwai cohort, elevated Tbil level within normal range was negatively associated with inflammatory biomarker (r2=-0.11, p<0.01), and predicted reduced MACE risk during follow-up (adjusted HR:0.56, 95%CI: 0.39-0.82). These findings were validated in the UK biobank cohort. The BRNP could target atherosclerotic lesions in vivo, with good solubility and stability. BRNP treatment significantly decreased plaque formation and plaque vulnerability in Apoe-/- mice, as shown by the reduced plaque area, reduced macrophage infiltration, increased collagen content, and inhibited inflammatory response and apoptosis in BMDMs in vitro.
Conclusions
Our study provided novel insights into the prognostic value of serum bilirubin and therapeutic potential of BRNP in ASCVD.
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) remains the leading cause of death globally. Despite well-controlled low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) level, a subset of patients still suffered from major adverse cardiac events (MACE), highlighting the need to identify biomarkers for risk stratification and to develop novel treatment for reducing this residual risk.
Recent growing evidence supports bilirubin, the endogenous metabolite of heme catabolism, may exert potential cardiovascular protective effect due to its anti-inflammatory properties. However, its role as a prognostic biomarker in ASCVD and the direct therapeutic effect on atherosclerosis remain unclear.
Hypothesis
Elevated bilirubin level within normal range predicted reduced MACE risk in ASCVD patients, and bilirubin treatment reduced plaque formation in mouse model of atherosclerosis.
Methods
The association between baseline serum total bilirubin (Tbil) level and MACE risk, a composite endpoint of cardiac death and acute myocardial infarction, was explored in two large-scale cohorts of patients with stable coronary heart disease (CHD), the Fuwai cohort and the UK biobank cohort. Patients with Tbil above normal range were excluded and the included patients were categorized into the low-normal group and the high-normal group based on Tbil. A bilirubin-based nanoparticle (BRNP), composed of the biocompatible material polyethylene glycol and the ROS responsive diselenide bond, was developed to improve the solubility and stability of bilirubin. The Apoe-/- mouse fed with high-fat diet was used as model of atherosclerosis, and the bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) were used to examine the effect of BRNP in vitro.
Results
In the Fuwai cohort, elevated Tbil level within normal range was negatively associated with inflammatory biomarker (r2=-0.11, p<0.01), and predicted reduced MACE risk during follow-up (adjusted HR:0.56, 95%CI: 0.39-0.82). These findings were validated in the UK biobank cohort. The BRNP could target atherosclerotic lesions in vivo, with good solubility and stability. BRNP treatment significantly decreased plaque formation and plaque vulnerability in Apoe-/- mice, as shown by the reduced plaque area, reduced macrophage infiltration, increased collagen content, and inhibited inflammatory response and apoptosis in BMDMs in vitro.
Conclusions
Our study provided novel insights into the prognostic value of serum bilirubin and therapeutic potential of BRNP in ASCVD.
More abstracts on this topic:
A hepatic steatosis-mediated metabolite reprograms macrophage lipid metabolism and aggravates atherosclerosis
Long Ting, Feng Ruijia, Feng Weiqi, Peng Guiyan, Yang Wenchao, Li Zilun, Huang Kan, Chang Guangqi
ApoB-100 peptide nanoparticles inhibit established atherosclerosis progression in female HLA-A*0201 transgenic miceZhou Jianchang, Zhao Xiaoning, Dimayuga Paul, Lio Nicole, Cercek Bojan, Trac Noah, Chung Eun Ji, Shah Prediman, Chyu Kuang-yuh