Final ID: Sa4036
The Effects of Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases on the Development of Clonal Hematopoiesis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Observational studies have proposed that genetic susceptibility to autoimmune rheumatic disease predisposes to the development of clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP), which may exacerbate cardiovascular risk associated with both conditions. However, it remains unknown if these two distinct conditions are causally related or stem from risk factors common to both etiologies.
Purpose: We aimed to determine the causal association between three rheumatic diseases – rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and ankylosing spondylitis (AS) - and CHIP.
Approach: Two-sample Mendelian randomization using publicly available summary statistics from genome-wide association studies allows for the investigation of causal relationships between variables, if all assumptions are sufficiently met. We selected 3 rheumatic disease exposures – RA (5427 cases; 479171 controls), SLE (647 cases; 482264 controls), and AS (1296 cases; 461637 controls). Our primary outcome was overall CHIP (10203 cases; 173918 controls). We additionally assessed CHIP gene subtypes, namely DNMT3A (5185 cases; 173918 controls) and TET2 (2042 cases; 173918 controls). Analyses were conducted with inverse-weighted variance methods. Additional sensitivity analyses used weighted median and Mendelian Randomization Pleiotropy RESidual Sum and Outlier (MR-PRESSO) methods. Results are presented as odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (95%CI).
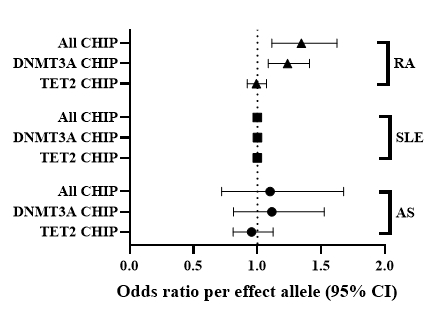
Results: Of the three selected rheumatic diseases, only RA was associated with a greater risk of overall CHIP (OR 1.34, 95%CI: 1.11-1.62, p=0.002). This finding was robustly supported by weighted median (p<0.001) and MR-PRESSO (p=0.013) results. Similar results were observed in analyses specific to DNMT3A CHIP (Figure). Only RA was significantly associated with an increased risk (OR 1.24, 95%CI: 1.09-1.41, p=0.001), again supported by weighted median (p=0.011) and MR-PRESSO analyses (p=0.011). Conversely, SLE was associated with a reduced risk of TET2 CHIP in inverse-variance weighted (p=0.028) and MR-PRESSO (p=0.015) models.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that RA, one of the most common rheumatic diseases in the U.S., is associated with greater risk for overall CHIP and the DNMT3A CHIP subtype. The development of CHIP in the RA population may contribute to their greater cardiovascular disease risk. Further investigation is needed to understand the clinical implications of CHIP in rheumatic diseases.
Purpose: We aimed to determine the causal association between three rheumatic diseases – rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and ankylosing spondylitis (AS) - and CHIP.
Approach: Two-sample Mendelian randomization using publicly available summary statistics from genome-wide association studies allows for the investigation of causal relationships between variables, if all assumptions are sufficiently met. We selected 3 rheumatic disease exposures – RA (5427 cases; 479171 controls), SLE (647 cases; 482264 controls), and AS (1296 cases; 461637 controls). Our primary outcome was overall CHIP (10203 cases; 173918 controls). We additionally assessed CHIP gene subtypes, namely DNMT3A (5185 cases; 173918 controls) and TET2 (2042 cases; 173918 controls). Analyses were conducted with inverse-weighted variance methods. Additional sensitivity analyses used weighted median and Mendelian Randomization Pleiotropy RESidual Sum and Outlier (MR-PRESSO) methods. Results are presented as odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (95%CI).
Results: Of the three selected rheumatic diseases, only RA was associated with a greater risk of overall CHIP (OR 1.34, 95%CI: 1.11-1.62, p=0.002). This finding was robustly supported by weighted median (p<0.001) and MR-PRESSO (p=0.013) results. Similar results were observed in analyses specific to DNMT3A CHIP (Figure). Only RA was significantly associated with an increased risk (OR 1.24, 95%CI: 1.09-1.41, p=0.001), again supported by weighted median (p=0.011) and MR-PRESSO analyses (p=0.011). Conversely, SLE was associated with a reduced risk of TET2 CHIP in inverse-variance weighted (p=0.028) and MR-PRESSO (p=0.015) models.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that RA, one of the most common rheumatic diseases in the U.S., is associated with greater risk for overall CHIP and the DNMT3A CHIP subtype. The development of CHIP in the RA population may contribute to their greater cardiovascular disease risk. Further investigation is needed to understand the clinical implications of CHIP in rheumatic diseases.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Multi-Population-First Approach Leveraging UK Biobank (UKBB) and All of Us (AoU) Datasets Reveals Higher Cardiomyopathy Variant Burden in Individuals with Myocarditis
Gurumoorthi Manasa, Khanji Mohammed, Munroe Patricia, Petersen Steffen, Landstrom Andrew, Chahal Anwar, Hesse Kerrick, Asatryan Babken, Shah Ravi, Sharaf Dabbagh Ghaith, Wolfe Rachel, Shyam Sundar Vijay, Mohiddin Saidi, Aung Nay
Autoimmunity and Sex Inform Clinical Outcomes of Non-Aortic Arterial DissectionsGonzalez Moret Yurilu, Chacin Suarez Audry, Musri M. Carolina, Yanamandala Mounica, Lo Kevin, Loscalzo Joseph, Gerhard-herman Marie, Pandey Arvind