Final ID: Su2103
A 50% or Greater Reduction in LDL-Cholesterol Is Associated with Improved Long-Term Outcomes and Lower Health Care Utilization After Myocardial Infarction - a SWEDEHEART study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Numerous clinical trials have established that low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) is among the strongest causal modifiable risk factors for cardiovascular (CV) events. However, large-scale real-world studies examining the relationship between LDL-C reduction following acute events and subsequent HCRU are lacking.
Research Question
What is the association between degree of LDL-C reduction post–myocardial infarction (MI) and subsequent clinical and economic burden?
Methods
Patients with a first-time MI who had LDL-C levels measured during hospitalization and again after 6–10 weeks were identified from the nationwide Swedish SWEDEHEART registry between January 2012 and January 2022 and followed through November 2024. Patients were stratified based on LDL-C reduction (≥50% vs <50%) at 6-10 weeks post-MI and their risk of subsequent major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) was estimated using multivariable adjusted Cox regression. MACE was defined as cardiovascular (CV)-related death, MI, ischemic stroke (IS), limb ischemia (LI), or urgent arterial revascularization. HCRU and costs were estimated using diagnosis-related group weights and national price lists and analyzed using two-part models adjusted for baseline characteristics.
Results
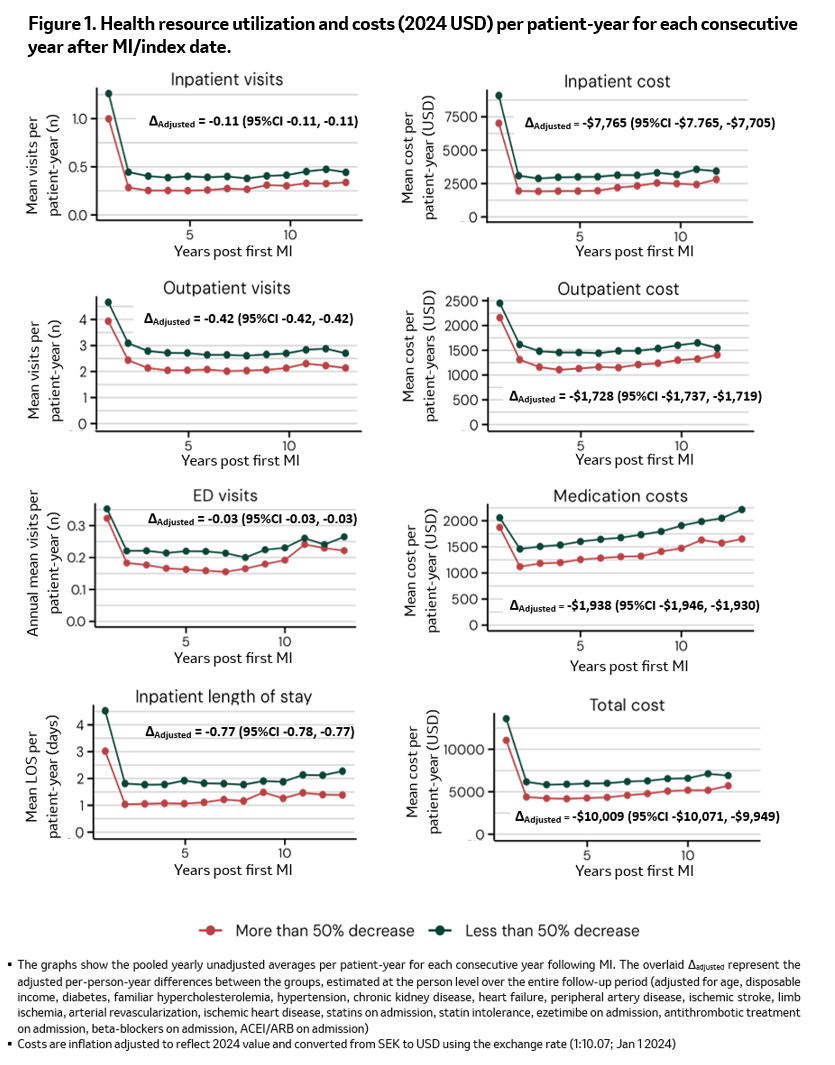
A total of 49,966 patients with a median follow up of 6.9 years was identified among who, 20,644 patients (41%) achieved a ≥50% LDL-C reduction at 6–10 weeks (Table 1). Those who achieved ≥50% LDL-C reduction were similar in age but had fewer comorbidities compared with those with <50% LDL-C reduction. They were also associated with significantly lower risk of MACE and its individual components compared to those with a <50% LDL-C reduction. This association was more pronounced for components of CV-related death, MI, IS, and limb ischemia (34-66% reduced hazards, all p<0.001), (and less pronounced, 14% hazards reduction, for risk of urgent arterial revascularization). Additionally, patients with a ≥50% LDL-C reduction had fewer hospitalizations, shorter hospital stays, and lower healthcare costs compared to those with a <50% reduction (Figure 1). These differences persisted throughout the observation period.
Conclusion
In a nationwide registry, an initial ≥50% reduction in LDL-C following MI was linked to a lower long-term risk of recurrent MACE and reduced HCRU and costs. This highlights the importance of optimizing LDL-C to mitigate the risk of both initial and subsequent ASCVD events.
Numerous clinical trials have established that low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) is among the strongest causal modifiable risk factors for cardiovascular (CV) events. However, large-scale real-world studies examining the relationship between LDL-C reduction following acute events and subsequent HCRU are lacking.
Research Question
What is the association between degree of LDL-C reduction post–myocardial infarction (MI) and subsequent clinical and economic burden?
Methods
Patients with a first-time MI who had LDL-C levels measured during hospitalization and again after 6–10 weeks were identified from the nationwide Swedish SWEDEHEART registry between January 2012 and January 2022 and followed through November 2024. Patients were stratified based on LDL-C reduction (≥50% vs <50%) at 6-10 weeks post-MI and their risk of subsequent major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) was estimated using multivariable adjusted Cox regression. MACE was defined as cardiovascular (CV)-related death, MI, ischemic stroke (IS), limb ischemia (LI), or urgent arterial revascularization. HCRU and costs were estimated using diagnosis-related group weights and national price lists and analyzed using two-part models adjusted for baseline characteristics.
Results
A total of 49,966 patients with a median follow up of 6.9 years was identified among who, 20,644 patients (41%) achieved a ≥50% LDL-C reduction at 6–10 weeks (Table 1). Those who achieved ≥50% LDL-C reduction were similar in age but had fewer comorbidities compared with those with <50% LDL-C reduction. They were also associated with significantly lower risk of MACE and its individual components compared to those with a <50% LDL-C reduction. This association was more pronounced for components of CV-related death, MI, IS, and limb ischemia (34-66% reduced hazards, all p<0.001), (and less pronounced, 14% hazards reduction, for risk of urgent arterial revascularization). Additionally, patients with a ≥50% LDL-C reduction had fewer hospitalizations, shorter hospital stays, and lower healthcare costs compared to those with a <50% reduction (Figure 1). These differences persisted throughout the observation period.
Conclusion
In a nationwide registry, an initial ≥50% reduction in LDL-C following MI was linked to a lower long-term risk of recurrent MACE and reduced HCRU and costs. This highlights the importance of optimizing LDL-C to mitigate the risk of both initial and subsequent ASCVD events.
More abstracts on this topic:
Ability of Composite Magnetic Resonance Brain Imaging Scores to Predict Functional Outcomes in Survivors of Cardiac Arrest
Nguyen Thuhien, Town James, Wahlster Sarah, Johnson Nicholas, Poilvert Nicolas, Lin Victor, Ukatu Hope, Matin Nassim, Davis Arielle, Taylor Breana, Thomas Penelope, Sharma Monisha
A Randomized Clinical Trial Evaluating Vitamin D Normalization on Major Adverse Cardiovascular-Related Events Among Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients: The TARGET-D TrialMay Heidi, Colipi Dominique, Whiting Tyler, Muhlestein Joseph, Le Viet, Anderson Jeffrey, Babcock Daniel, Wayman Libby, Bair Tami, Knight Stacey, Knowlton Kirk, Iverson Leslie