Final ID: Mo1011
Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors Reduce Dementia Risk in Type 2 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2is) are cardioprotective glucose-lowering therapies, but their impact on dementia risk in type 2 diabetes remains underexplored.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Scopus, and Embase from inception to May 1, 2025, for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing GLP-1RAs or SGLT2is with controls, reporting dementia or cognitive score changes. Included trials featured guideline-recommended drugs for cardiovascular risk reduction. A Bayesian network meta-analysis estimated risk ratios (RR) with 95% credible intervals (CrI) using Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods, with Gelman-Rubin diagnostics for convergence. Surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) ranked treatments.
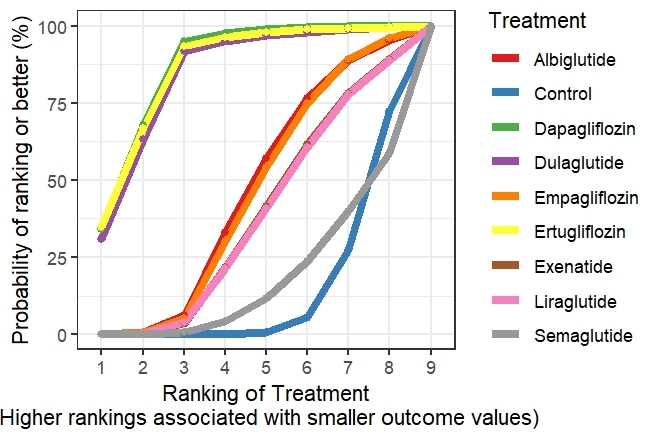
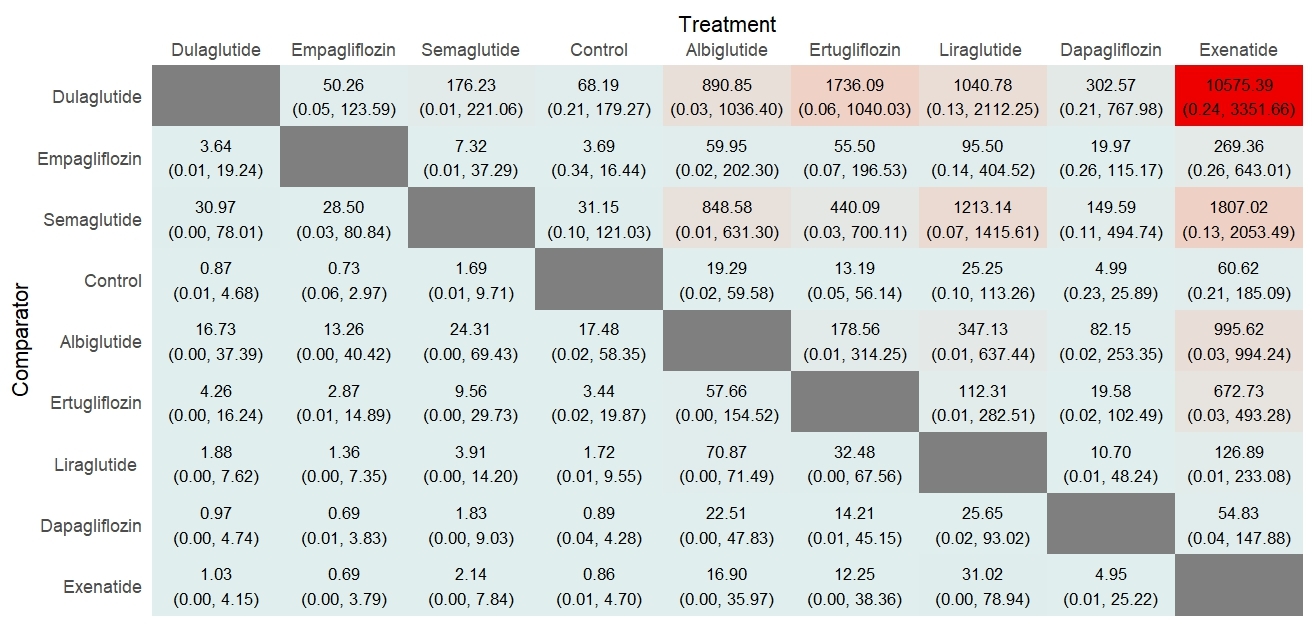
Results: From 22 RCTs with 156,697 patients, therapies showed varied dementia risk reductions. For all-cause dementia versus control according to the SUCRA: albiglutide (RR: 0.03, 95% CrI: 0.00 to 0.08; SUCRA: 94.4%), lixisenatide (RR: 0.08, 95% CrI: 0.00 to 0.20; SUCRA: 93.62%), efpeglenatide (RR: 0.24, 95% CrI: 0.00 to 1.38; SUCRA: 70.09%), canagliflozin (RR: 0.31, 95% CrI: 0.01 to 1.47; SUCRA: 61.81%), semaglutide (RR: 0.50, 95% CrI: 0.03 to 1.98; SUCRA: 50.06%), liraglutide (RR: 2.12, 95% CrI: 0.02 to 9.89; SUCRA: 41.91%), empagliflozin (RR: 0.68, 95% CrI: 0.05 to 2.35; SUCRA: 39.63%), exenatide (RR: 4.13, 95% CrI: 0.02 to 20.28; SUCRA: 35.41%), dulaglutide (RR: 3.38, 95% CrI: 0.03 to 15.72; SUCRA: 32.89%), dapagliflozin (RR: 1.19, 95% CrI: 0.09 to 4.96; SUCRA: 30.37%), ertugliflozin (RR: 6.79, 95% CrI: 0.02 to 29.23; SUCRA: 30.1%), control (SUCRA: 19.67%). For vascular dementia versus control: dapagliflozin (RR: 0.01, 95% CrI: 0.00 to 0.08; SUCRA: 86.65%), ertugliflozin (RR: 0.03, 95% CrI: 0.00 to 0.16; SUCRA: 85.98%), dulaglutide (RR: 0.05, 95% CrI: 0.00 to 0.32; SUCRA: 84.35%), while semaglutide (RR: 3.83, 95% CrI: 0.05 to 21.72; SUCRA: 17.4%), and control (SUCRA: 13.2%). For Alzheimer’s dementia versus control: dulaglutide showed the lowest (RR: 0.87, 95% CrI: 0.01 to 4.68; SUCRA: 77.64%), while exenatide the highest (RR: 60.62, 95% CrI: 0.21 to 185.09; SUCRA: 23.36%), and control (SUCRA: 50.29%).
Conclusions: GLP-1RAs and SGLT2is reduce dementia risk, with albiglutide and lixisenatide excelling for all-cause dementia, dapagliflozin and ertugliflozin for vascular dementia, and dulaglutide for Alzheimer’s. Higher risks with some drugs highlight tailored therapy needs.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Scopus, and Embase from inception to May 1, 2025, for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing GLP-1RAs or SGLT2is with controls, reporting dementia or cognitive score changes. Included trials featured guideline-recommended drugs for cardiovascular risk reduction. A Bayesian network meta-analysis estimated risk ratios (RR) with 95% credible intervals (CrI) using Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods, with Gelman-Rubin diagnostics for convergence. Surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) ranked treatments.
Results: From 22 RCTs with 156,697 patients, therapies showed varied dementia risk reductions. For all-cause dementia versus control according to the SUCRA: albiglutide (RR: 0.03, 95% CrI: 0.00 to 0.08; SUCRA: 94.4%), lixisenatide (RR: 0.08, 95% CrI: 0.00 to 0.20; SUCRA: 93.62%), efpeglenatide (RR: 0.24, 95% CrI: 0.00 to 1.38; SUCRA: 70.09%), canagliflozin (RR: 0.31, 95% CrI: 0.01 to 1.47; SUCRA: 61.81%), semaglutide (RR: 0.50, 95% CrI: 0.03 to 1.98; SUCRA: 50.06%), liraglutide (RR: 2.12, 95% CrI: 0.02 to 9.89; SUCRA: 41.91%), empagliflozin (RR: 0.68, 95% CrI: 0.05 to 2.35; SUCRA: 39.63%), exenatide (RR: 4.13, 95% CrI: 0.02 to 20.28; SUCRA: 35.41%), dulaglutide (RR: 3.38, 95% CrI: 0.03 to 15.72; SUCRA: 32.89%), dapagliflozin (RR: 1.19, 95% CrI: 0.09 to 4.96; SUCRA: 30.37%), ertugliflozin (RR: 6.79, 95% CrI: 0.02 to 29.23; SUCRA: 30.1%), control (SUCRA: 19.67%). For vascular dementia versus control: dapagliflozin (RR: 0.01, 95% CrI: 0.00 to 0.08; SUCRA: 86.65%), ertugliflozin (RR: 0.03, 95% CrI: 0.00 to 0.16; SUCRA: 85.98%), dulaglutide (RR: 0.05, 95% CrI: 0.00 to 0.32; SUCRA: 84.35%), while semaglutide (RR: 3.83, 95% CrI: 0.05 to 21.72; SUCRA: 17.4%), and control (SUCRA: 13.2%). For Alzheimer’s dementia versus control: dulaglutide showed the lowest (RR: 0.87, 95% CrI: 0.01 to 4.68; SUCRA: 77.64%), while exenatide the highest (RR: 60.62, 95% CrI: 0.21 to 185.09; SUCRA: 23.36%), and control (SUCRA: 50.29%).
Conclusions: GLP-1RAs and SGLT2is reduce dementia risk, with albiglutide and lixisenatide excelling for all-cause dementia, dapagliflozin and ertugliflozin for vascular dementia, and dulaglutide for Alzheimer’s. Higher risks with some drugs highlight tailored therapy needs.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of Delayed Diagnosis of Transthyretin Cardiomyopathy with Heart Failure Hospitalizations and Mortality
Spencer-bonilla Gabriela, Huang Joanna, Witteles Ronald, Heidenreich Paul, Sandhu Alexander, Alexander Kevin, Fan Jun, Cheng Paul, Din Natasha, Rodriguez Fatima, Varshney Anubodh, Davies Marie, Venditto John, Papas Mia
Add-on Therapy with Dantrolene, a RyR2 Stabilizer, Terminates Ventricular Tachycardia Storm refractory to Intravenous Amiodarone in Heart Failure.Nawata Junya, Omuro Ayumi, Fukuda Masakazu, Suetomi Takeshi, Miyazaki Yosuke, Fujimura Tatsuhiro, Mochizuki Mamoru, Sano Motoaki, Kobayashi Shigeki, Ishikawa Maho, Nakata Yuki, Murakawa Kaori, Nakashima Yusuke, Hisaoka Masahiro, Matsuyama Tetsuya, Nakamura Yoshihide