Final ID: MP1857
Oridonin alleviates sunitinib-induced cardiac fibrosis by targeting the fibroblast growth factor receptor 1/extracellular regulated protein kinases 1/2/ fatty acid transporter family 4 axis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Sunitinib, a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is approved for the treating several advanced solid tumors. However, its clinical application is severely limited by cardiotoxicity, particularly myocardial fibrosis. Oridonin, a natural diterpenoid compound, has emerged as a promising candidate due to its potential antifibrotic properties.
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the protective effects of oridonin against sunitinib-induced cardiotoxicity and elucidate its potential mechanism for inhibiting myocardial fibrosis.
Methods: A mouse model of sunitinib-induced cardiotoxicity was established by oral gavage administration of sunitinib (40 mg/kg/day) for 8 weeks. Concurrently, oridonin (2.5, 5, or 10 mg/kg/day) was administered via intraperitoneal injection. Cardiac function was assessed using echocardiography. Untargeted metabolomic profiling was performed using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry . Heart tissues underwent single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq) for transcriptomic analysis. Protein expression was analyzed using Western blotting.
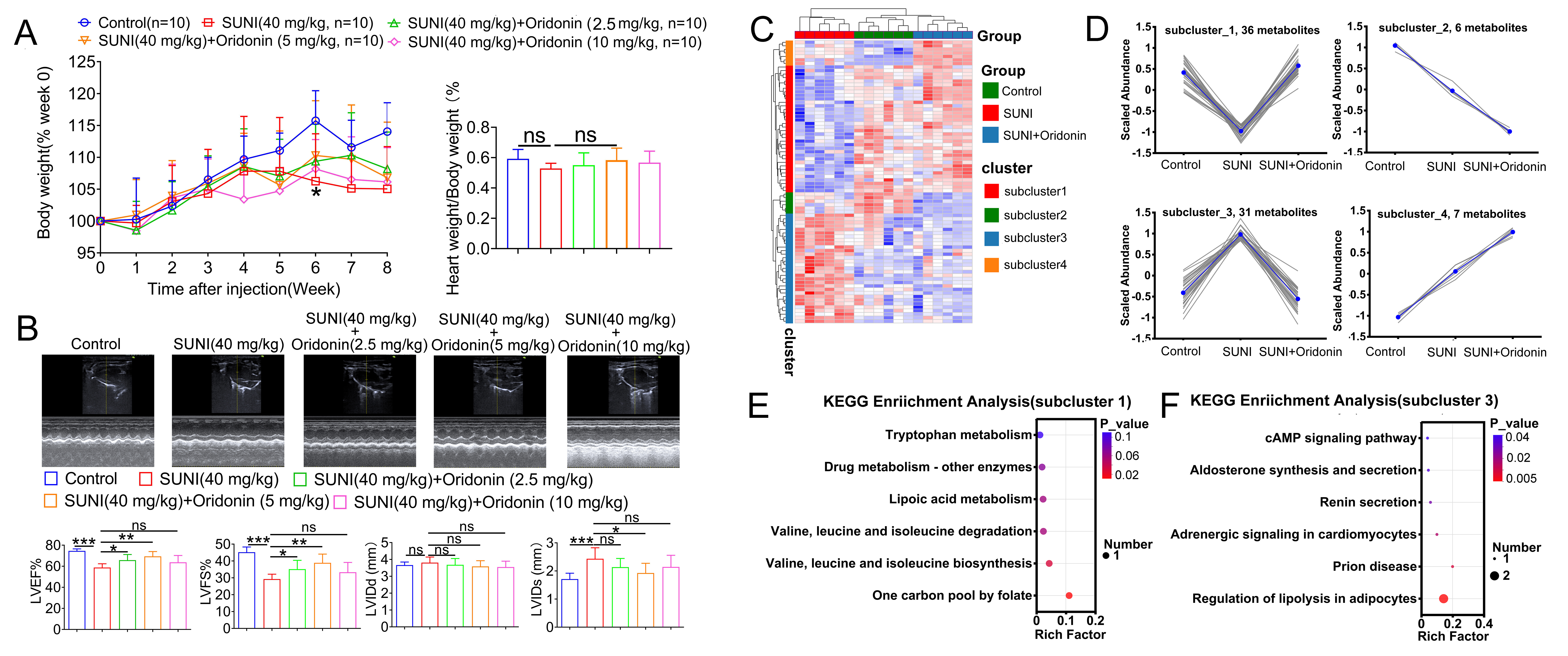
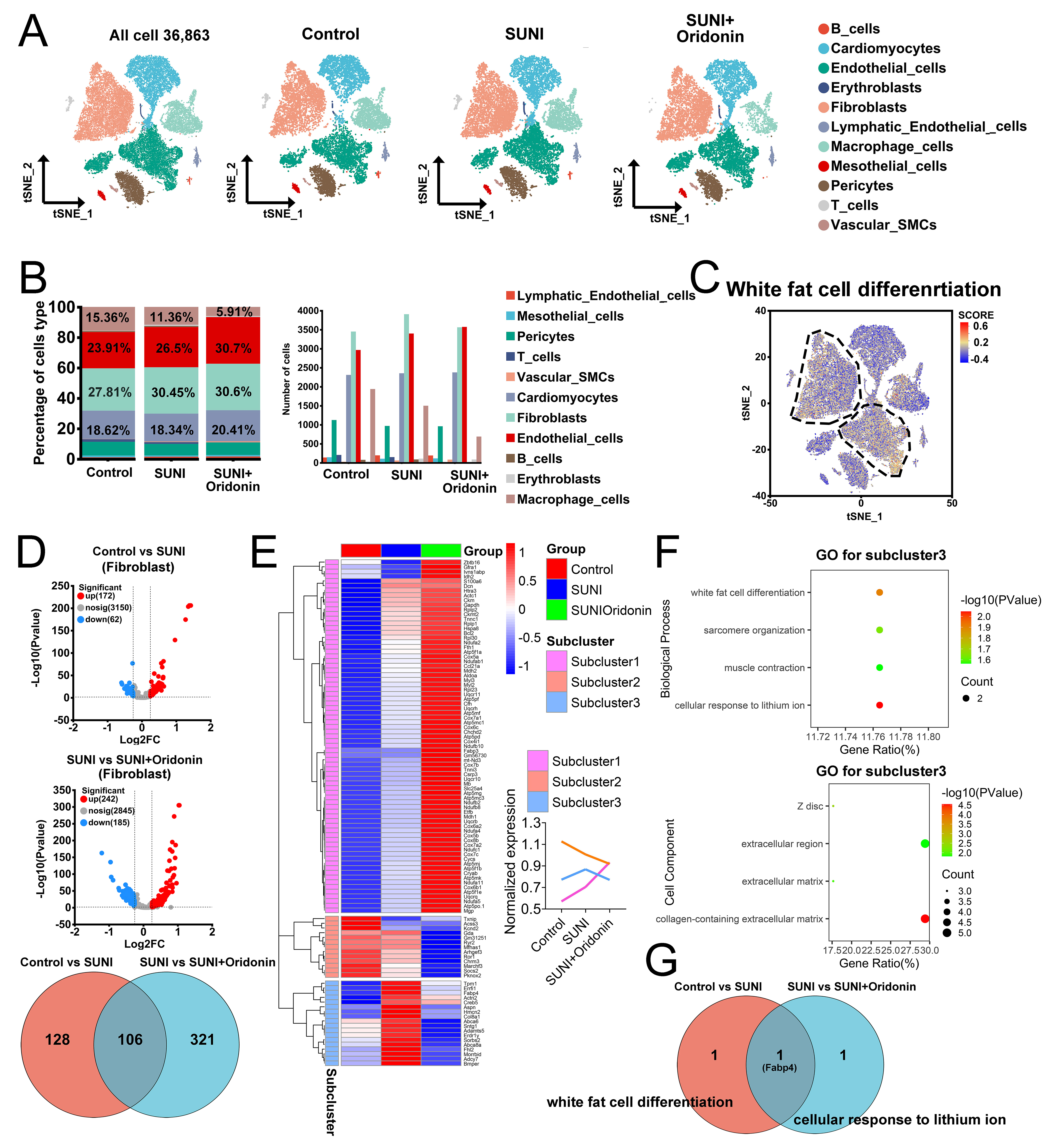
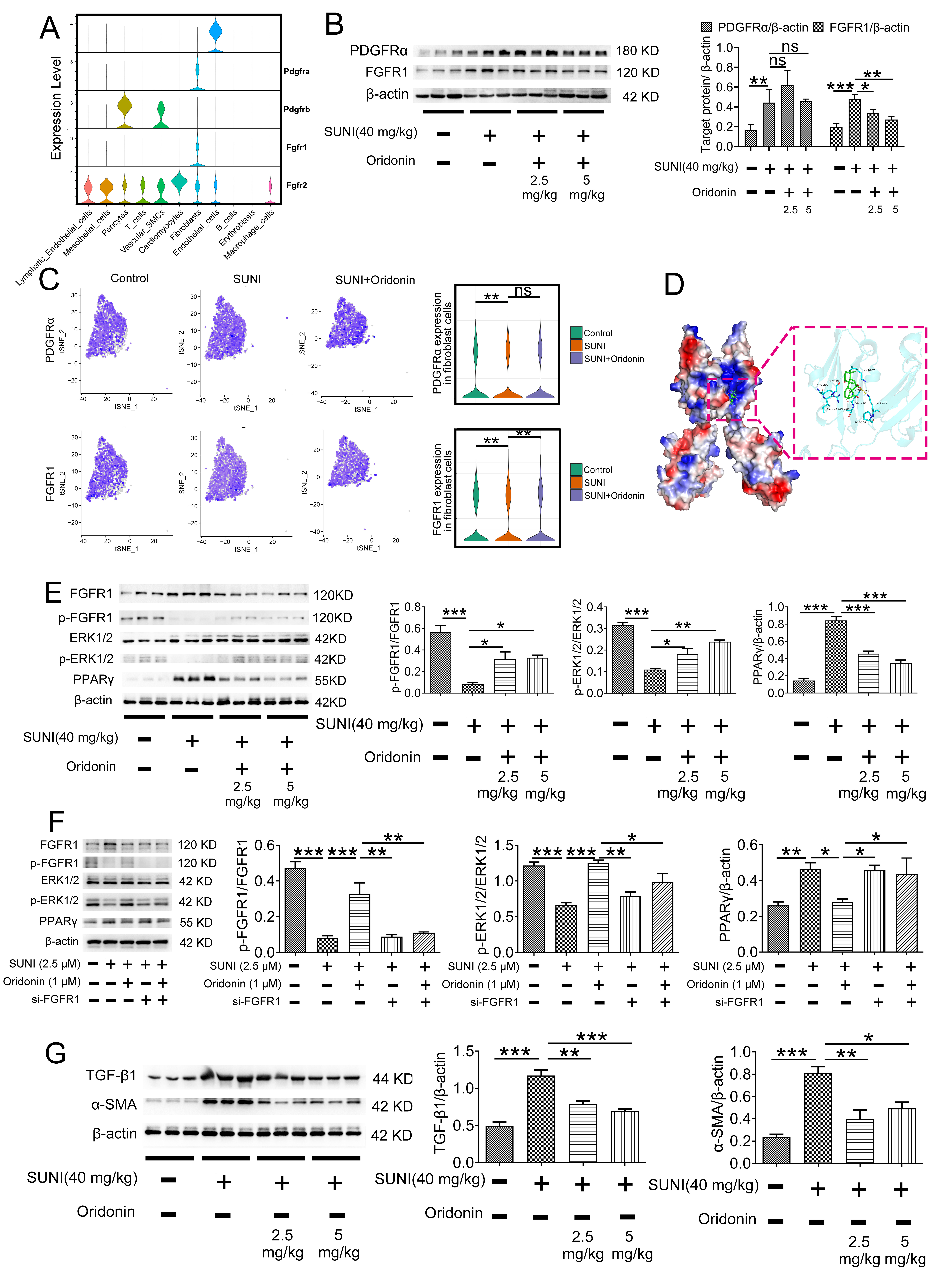
Results: Sunitinib administration significantly decreased left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), an effect rescued by oridonin treatment. Untargeted metabolomics revealed increased levels of lipid-related metabolites in the sunitinib group, which were reduced by oridonin. snRNA-seq analysis demonstrated a significant increase in fibroblasts within the SUNI group, correlating with alterations in lipid metabolism regulation. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of fibroblasts identified elevated expression of fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4) in the SUNI group, which was attenuated by oridonin. Molecular docking indicated that oridonin binds to fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1), potentially activating extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) and subsequently suppressing the proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARγ)/FABP4/transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) signaling pathway. Crucially, FGFR1 knockdown using siRNA abolished oridonin's suppressive effect on FABP4 expression.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that oridonin mitigates sunitinib-induced myocardial fibrosis by selectively inhibiting the PPARγ/FABP4/TGF-β1 axis. These findings provide a novel strategy for managing cardiotoxicity during cancer therapy and suggest that natural compound-based combination therapies represent a viable approach to balancing antitumor efficacy and cardiovascular safety.
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the protective effects of oridonin against sunitinib-induced cardiotoxicity and elucidate its potential mechanism for inhibiting myocardial fibrosis.
Methods: A mouse model of sunitinib-induced cardiotoxicity was established by oral gavage administration of sunitinib (40 mg/kg/day) for 8 weeks. Concurrently, oridonin (2.5, 5, or 10 mg/kg/day) was administered via intraperitoneal injection. Cardiac function was assessed using echocardiography. Untargeted metabolomic profiling was performed using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry . Heart tissues underwent single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq) for transcriptomic analysis. Protein expression was analyzed using Western blotting.
Results: Sunitinib administration significantly decreased left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), an effect rescued by oridonin treatment. Untargeted metabolomics revealed increased levels of lipid-related metabolites in the sunitinib group, which were reduced by oridonin. snRNA-seq analysis demonstrated a significant increase in fibroblasts within the SUNI group, correlating with alterations in lipid metabolism regulation. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of fibroblasts identified elevated expression of fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4) in the SUNI group, which was attenuated by oridonin. Molecular docking indicated that oridonin binds to fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1), potentially activating extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) and subsequently suppressing the proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARγ)/FABP4/transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) signaling pathway. Crucially, FGFR1 knockdown using siRNA abolished oridonin's suppressive effect on FABP4 expression.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that oridonin mitigates sunitinib-induced myocardial fibrosis by selectively inhibiting the PPARγ/FABP4/TGF-β1 axis. These findings provide a novel strategy for managing cardiotoxicity during cancer therapy and suggest that natural compound-based combination therapies represent a viable approach to balancing antitumor efficacy and cardiovascular safety.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Retrospective Analysis of Measured Versus Estimated Resting Oxygen Uptake for Derivation of Fick Cardiac Output in Patients in the Cardiac Intensive Care Unit
Minasian Alexandra, Dudzinski David, Shelton Ken, Malhotra Rajeev, Lewis Gregory, Mcginnis Shaina, Rouvina Jennifer, Newlands Chloe, Griskowitz Catharine, Kowal Alyssa, Kelly Katherine, Oloughlin Joseph, Wallace Dayquan
A Meta-analysis of the Right Ventricle Changes in Cancer Therapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity - The Forgotten Ventricle in Cardio-OncologyDe Oliveira Fischer Bacca Caroline, Huntermann Ramon, Gomes Rodrigo, Alexandrino Francisco, Yoshie Sato Mariane, De Sant Anna Melo Edielle