Final ID: Sa3083
Pulmonary Hypertension Due to Fibrous Mediastinitis Treated Successfully with Stenting of Pulmonary Artery Stenoses
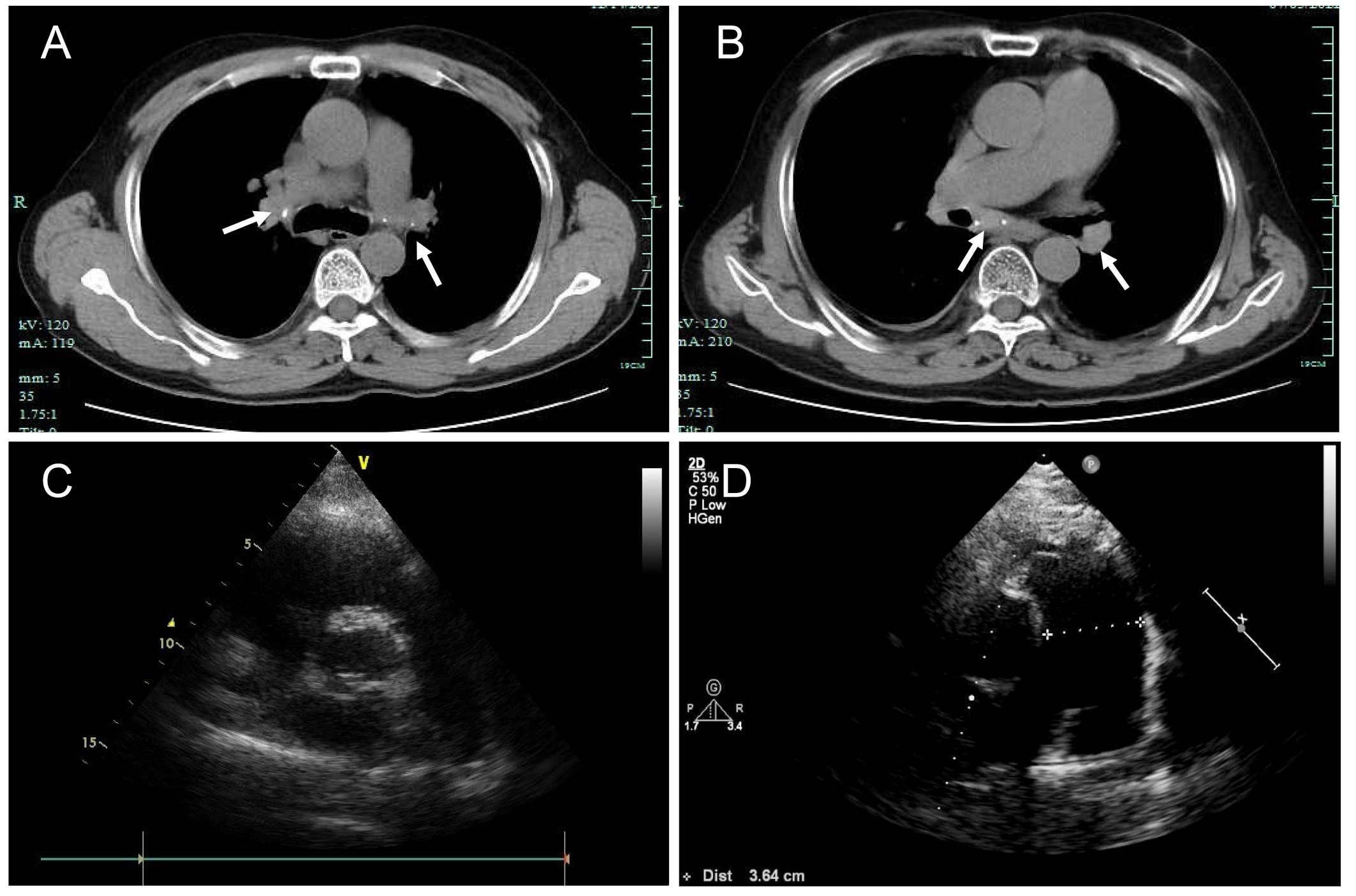
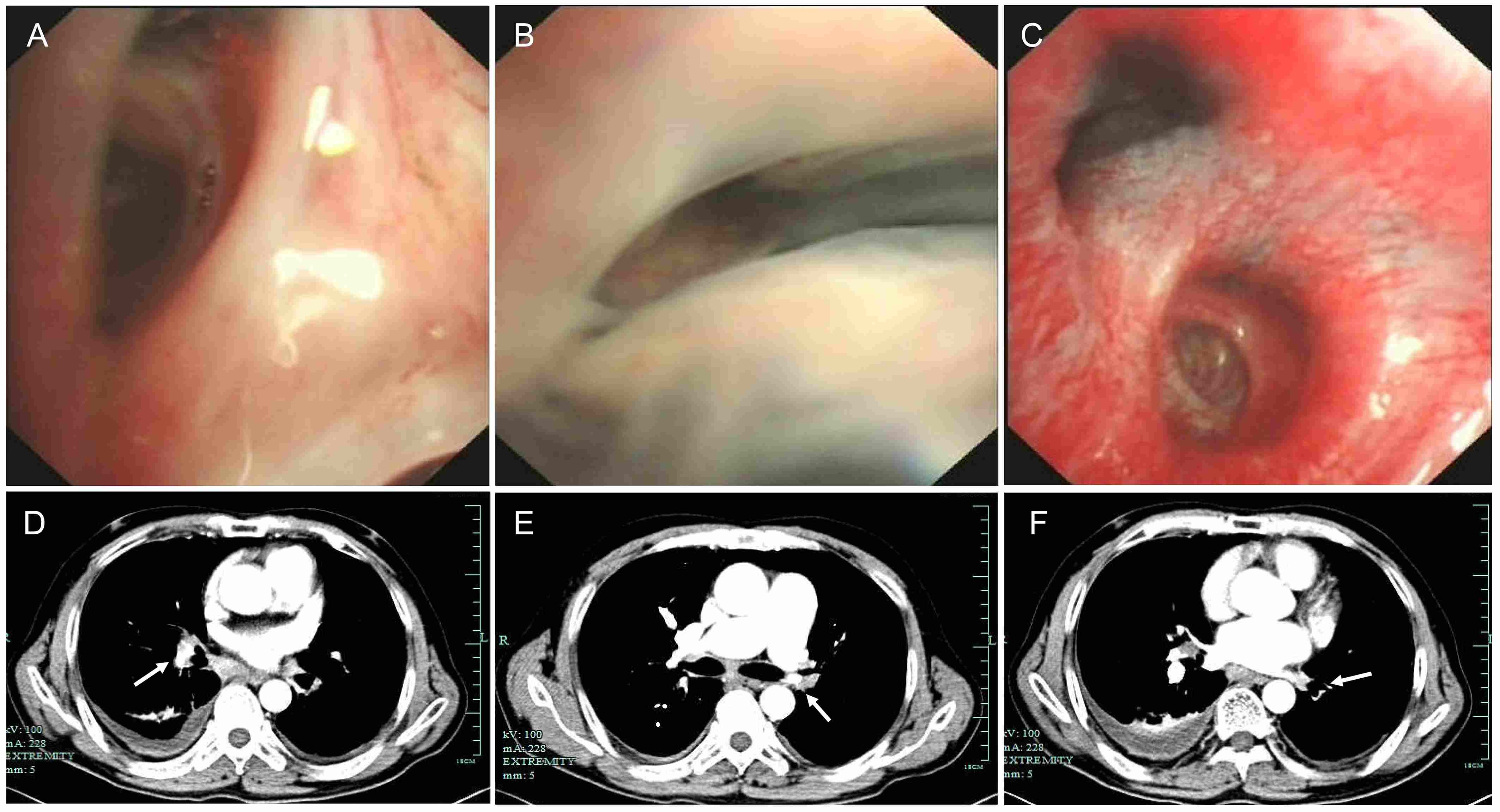
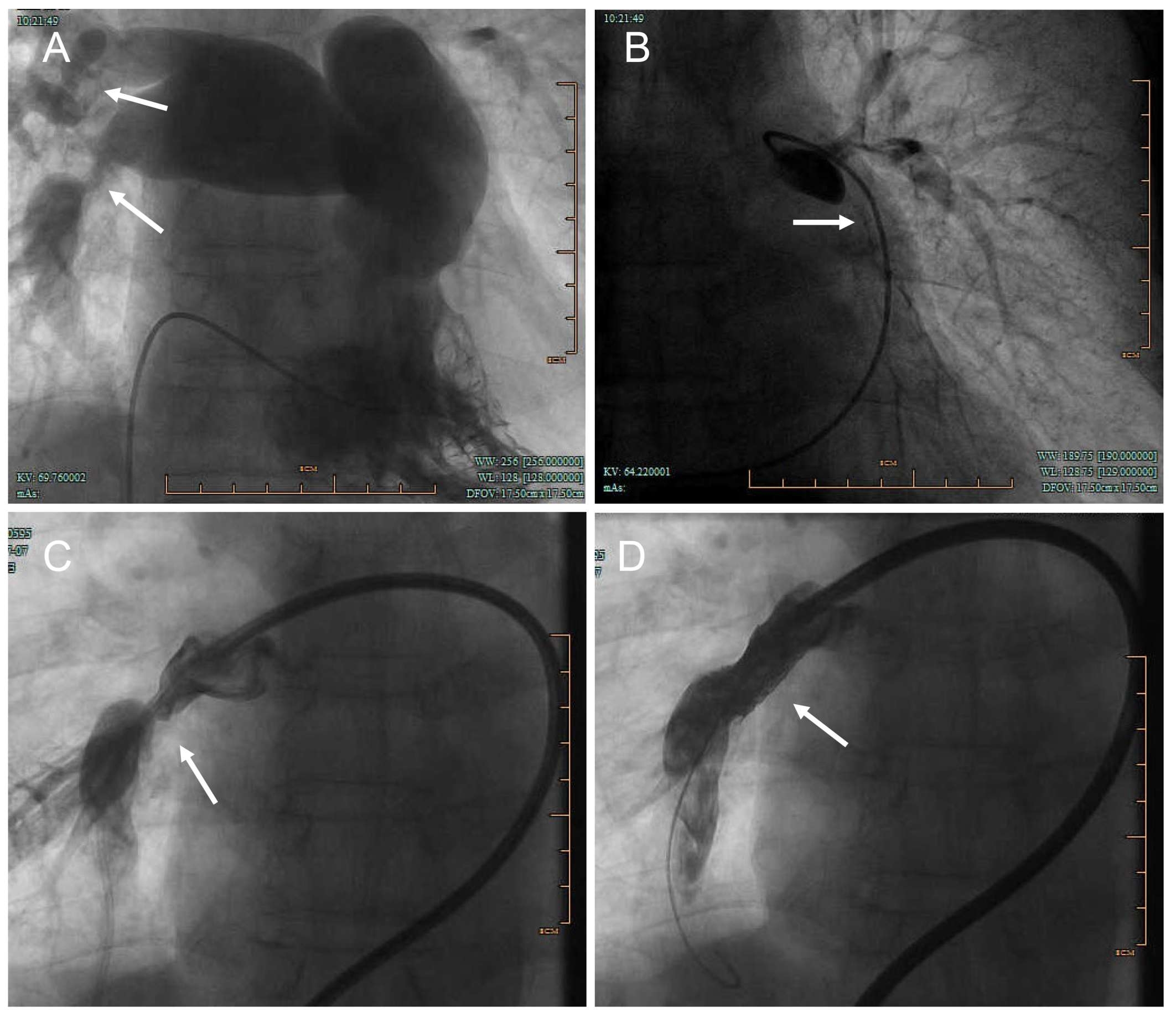
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:Fibrosing mediastinitis is a rare condition characterized by excessive fibrous tissue proliferation in the mediastinum, leading to compression of vital structures. We present a case of idiopathic fibrosing mediastinitis with progressive pulmonary hypertension and multi-vessel stenosis, highlighting diagnostic challenges and management strategies. Research Questions: The case explores the clinical and imaging features of fibrosing mediastinitis, its differentiation from other causes of pulmonary hypertension, and the potential treatment options for fibrosing mediastinitis-related vascular obstruction. Aims: This case aims to (1) describe the clinical course and diagnostic pitfalls in a patient with long-standing fibrosing mediastinitis, (2) evaluate the role of imaging and invasive testing in diagnosis, and (3) assess the efficacy of endovascular stenting in symptomatic relief. Methods: A 58-year-old male with a 5-year history of recurrent dyspnea and chest tightness underwent serial evaluations, including CT angiography, echocardiography, pulmonary function tests, bronchoscopy, and right heart catheterization. After failing medical therapy, he underwent percutaneous pulmonary artery stenting. Results: Imaging revealed mediastinal lymphadenopathy with calcification, pulmonary artery stenosis, and tracheobronchial compression. Pulmonary arteriography confirmed severe stenosis in multiple pulmonary arteries. Stent implantation improved exercise capacity (6-minute walk distance: 360m to 485m) and oxygen saturation. Conclusions: Fibrosing mediastinitis is a rare but treatable cause of pulmonary hypertension. A high index of suspicion is needed in patients with progressive dyspnea and mediastinal fibrosis. Endovascular stenting may provide symptomatic relief in select cases, though long-term outcomes require further study.
More abstracts on this topic:
2 Dimensional Echocardiography versus 3 Dimentional Echocardiography to Assess Right Ventricular Function in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Systematic Review
Chaudhry Waleed Razzaq, Hajj Fatima, Bathula Satyamedha, Meghji Mohammed Askari, Pasupuleti Hemalatha, Kiyani Madiha, Shah Syeda Simrah, Neelakantan Ramaswamy Sanathanan, Mirzaeidizaji Nakisa, St. Jacques Jahnoy, Khan Khalil Ullah, Veluchamy Elakkiya, Jesse Joshanna
Asymmetric Pulmonary Artery Geometry Drives Branch-Specific Shear Stress Patterns in Repaired Tetralogy of Fallot: A Substudy of the Single Center Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Outcomes Registry – Tetralogy of FallotBhattacharya Anindro, Thompson Elizabeth, Hu Fengling, Shinohara Russell, Perdikaris Paris, Whitehead Kevin, Goldmuntz Elizabeth, Fogel Mark, Witschey Walter