Final ID: MP2674
Circulating extracellular vesicle-derived CAPG as a novel molecule associated with pathophysiology and outcomes in heart failure
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) facilitate the transportation of active biomolecules, including proteins, and play crucial roles in intercellular and interorgan communications under both physiological and pathological conditions. However, the proteome or clinical relevance of the circulating EVs in heart failure has yet to be elucidated.
Aims:
We sought to illustrate the distinct proteomic profile of circulating EVs and to identify the clinical significance in patients with heart failure.
Methods:
We isolated and purified circulating EVs from patient serum using size-exclusion chromatography. Quantitative proteomic analysis of the EVs was conducted through mass spectrometry in a discovery cohort comprising 15 hospitalized patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and 8 non-heart failure control subjects. Associations between EV-derived molecules and clinical outcomes were examined in a cohort of 95 consecutive HFrEF patients with dilated cardiomyopathy.
Results:
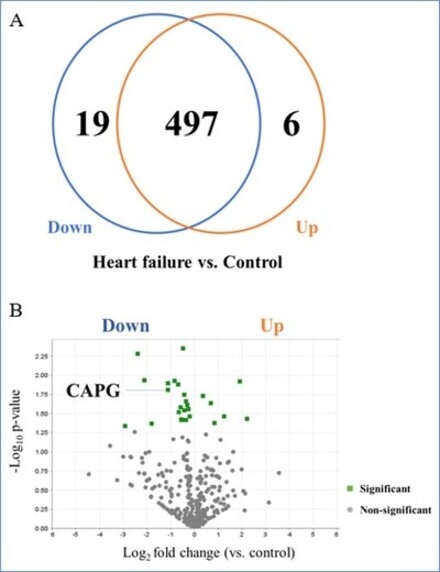
In the discovery cohort, quantitative proteomics identified a total of 522 proteins within circulating EVs. Among these, 19 molecules were significantly down-regulated and 6 were up-regulated in patients with HFrEF compared to controls (Figure 1). Notably, macrophage-capping protein (CAPG) emerged as one of the most down-regulated molecules in HFrEF. CAPG is known to regulate cytoplasmic and nuclear structures through potential interactions with actin, suggesting a role in gene regulation and cellular remodeling. In the validation cohort (mean age, 56.9 years: 66.3% male), we assessed the levels of EV-derived CAPG (EV-CAPG) and found that patients with lower EV-CAPG showed more enlarged left ventricular dimensions and higher BNP levels. During a median follow-up period of 1313 days, patients with decreased EV-CAPG exhibited significantly lower event-free survival from the composite outcomes of cardiac death and worsening heart failure (Figure 2). In a multivariable Cox proportional hazard model, low EV-CAPG was independently associated with increased risks of the cardiac events (hazard ratio, 2.73; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-7.36; P = 0.04).
Conclusion:
Reduced levels of circulating EV-CAPG are associated with adverse clinical outcomes in patients with HFrEF. EV-CAPG may represent a novel molecular target involved in the pathogenesis of heart failure.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) facilitate the transportation of active biomolecules, including proteins, and play crucial roles in intercellular and interorgan communications under both physiological and pathological conditions. However, the proteome or clinical relevance of the circulating EVs in heart failure has yet to be elucidated.
Aims:
We sought to illustrate the distinct proteomic profile of circulating EVs and to identify the clinical significance in patients with heart failure.
Methods:
We isolated and purified circulating EVs from patient serum using size-exclusion chromatography. Quantitative proteomic analysis of the EVs was conducted through mass spectrometry in a discovery cohort comprising 15 hospitalized patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and 8 non-heart failure control subjects. Associations between EV-derived molecules and clinical outcomes were examined in a cohort of 95 consecutive HFrEF patients with dilated cardiomyopathy.
Results:
In the discovery cohort, quantitative proteomics identified a total of 522 proteins within circulating EVs. Among these, 19 molecules were significantly down-regulated and 6 were up-regulated in patients with HFrEF compared to controls (Figure 1). Notably, macrophage-capping protein (CAPG) emerged as one of the most down-regulated molecules in HFrEF. CAPG is known to regulate cytoplasmic and nuclear structures through potential interactions with actin, suggesting a role in gene regulation and cellular remodeling. In the validation cohort (mean age, 56.9 years: 66.3% male), we assessed the levels of EV-derived CAPG (EV-CAPG) and found that patients with lower EV-CAPG showed more enlarged left ventricular dimensions and higher BNP levels. During a median follow-up period of 1313 days, patients with decreased EV-CAPG exhibited significantly lower event-free survival from the composite outcomes of cardiac death and worsening heart failure (Figure 2). In a multivariable Cox proportional hazard model, low EV-CAPG was independently associated with increased risks of the cardiac events (hazard ratio, 2.73; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-7.36; P = 0.04).
Conclusion:
Reduced levels of circulating EV-CAPG are associated with adverse clinical outcomes in patients with HFrEF. EV-CAPG may represent a novel molecular target involved in the pathogenesis of heart failure.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Biomarker Based on Aneurysm Wall Enhancement and Blood Gene Expression to Identify Symptomatic Intracranial Aneurysms
Veeturi Sricharan, Poppenberg Kerry, Jaikumar Vinay, Pinter Nandor, Levy Elad, Siddiqui Adnan, Tutino Vincent
A Case Presentation of Severe Left Ventricular Dysfunction from Focal Myocarditis due to Immune Checkpoint InhibitorPatel Romil, Hussain Kifah, Gordon Robert