Final ID: MP310
Redefining Cardiotoxicity Surveillance in Targeted Immunotherapy: Cytokine Release Syndrome as a High-Yield Trigger for Detecting Cancer Therapy-Related Cardiac Dysfunction After CAR-T Therapy
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy offers durable remissions in hematologic malignancies but carries a substantial risk of cancer therapy–related cardiac dysfunction (CTRCD). Current imaging strategies are predominantly event-driven, initiated after overt cardiovascular deterioration, leading to underdiagnosis of subclinical or evolving dysfunction. Cytokine release syndrome (CRS), a near-universal CAR-T complication, represents a biologically and temporally linked trigger for cardiac injury. We hypothesized that CRS-guided echocardiography, independent of MACE, would improve CTRCD detection and enable earlier intervention.
Methods:
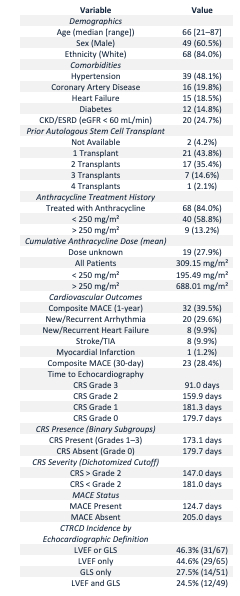
We retrospectively analyzed 81 CAR-T recipients with pre- and post-treatment echocardiograms. CTRCD was defined by: (1) LVEF <50% or >10% decline, (2) >15% GLS reduction, or (3) either (LVEF or GLS). Surveillance performance was compared between CRS- and MACE-triggered imaging. Univariable and stratified logistic regression assessed associations between CRS grade and CTRCD risk. ROC analysis evaluated GLS reduction as a predictor of LVEF-defined CTRCD.
Results:
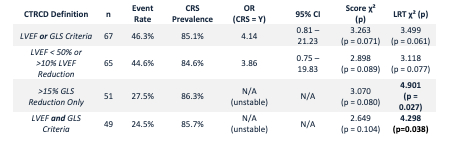
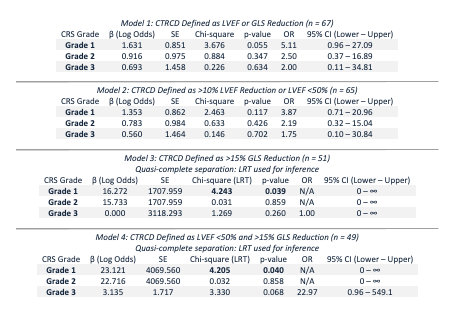
CTRCD occurred in 46.3% of patients based on the composite “LVEF or GLS” definition; LVEF-defined CTRCD occurred in 44.6%, GLS-defined CTRCD in 27.5%, and dual-criteria CTRCD (both LVEF and GLS abnormalities) in 24.5%. CRS occurred in 85.1%, mostly Grades 1–2. CRS-based surveillance detected 93.5% of all CTRCD cases and 100% of GLS-only and dual-criteria cases, compared to 48.4–58.3% detection via MACE-based imaging. MACE-based surveillance missed over 50% of affected patients across all CTRCD definitions. Logistic regression models revealed elevated CTRCD risk with any CRS exposure; Grade 1 CRS conferred the strongest odds (OR 5.11, p = 0.055). Quasi-complete separation occurred in GLS-only and dual-criteria models, as all CTRCD cases occurred in patients with CRS. ROC analysis showed that GLS reduction >8.63% predicted LVEF-defined CTRCD with an AUC of 0.766 (sensitivity 66.7%, specificity 87.5%).
Conclusion:
CRS is a powerful and reproducible trigger for detecting CTRCD defined by LVEF and/or GLS. Compared to MACE-driven imaging, CRS-based surveillance offers greater sensitivity and earlier detection of subclinical dysfunction. Event-triggered imaging misses over half of cases. Our findings support integrating CRS-based surveillance into post-CAR-T care to improve early detection, risk stratification, and cardioprotection.
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy offers durable remissions in hematologic malignancies but carries a substantial risk of cancer therapy–related cardiac dysfunction (CTRCD). Current imaging strategies are predominantly event-driven, initiated after overt cardiovascular deterioration, leading to underdiagnosis of subclinical or evolving dysfunction. Cytokine release syndrome (CRS), a near-universal CAR-T complication, represents a biologically and temporally linked trigger for cardiac injury. We hypothesized that CRS-guided echocardiography, independent of MACE, would improve CTRCD detection and enable earlier intervention.
Methods:
We retrospectively analyzed 81 CAR-T recipients with pre- and post-treatment echocardiograms. CTRCD was defined by: (1) LVEF <50% or >10% decline, (2) >15% GLS reduction, or (3) either (LVEF or GLS). Surveillance performance was compared between CRS- and MACE-triggered imaging. Univariable and stratified logistic regression assessed associations between CRS grade and CTRCD risk. ROC analysis evaluated GLS reduction as a predictor of LVEF-defined CTRCD.
Results:
CTRCD occurred in 46.3% of patients based on the composite “LVEF or GLS” definition; LVEF-defined CTRCD occurred in 44.6%, GLS-defined CTRCD in 27.5%, and dual-criteria CTRCD (both LVEF and GLS abnormalities) in 24.5%. CRS occurred in 85.1%, mostly Grades 1–2. CRS-based surveillance detected 93.5% of all CTRCD cases and 100% of GLS-only and dual-criteria cases, compared to 48.4–58.3% detection via MACE-based imaging. MACE-based surveillance missed over 50% of affected patients across all CTRCD definitions. Logistic regression models revealed elevated CTRCD risk with any CRS exposure; Grade 1 CRS conferred the strongest odds (OR 5.11, p = 0.055). Quasi-complete separation occurred in GLS-only and dual-criteria models, as all CTRCD cases occurred in patients with CRS. ROC analysis showed that GLS reduction >8.63% predicted LVEF-defined CTRCD with an AUC of 0.766 (sensitivity 66.7%, specificity 87.5%).
Conclusion:
CRS is a powerful and reproducible trigger for detecting CTRCD defined by LVEF and/or GLS. Compared to MACE-driven imaging, CRS-based surveillance offers greater sensitivity and earlier detection of subclinical dysfunction. Event-triggered imaging misses over half of cases. Our findings support integrating CRS-based surveillance into post-CAR-T care to improve early detection, risk stratification, and cardioprotection.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Multicenter Friedreich Ataxia Registry Identifies Posterior Wall Thickness as a Predictor of Major Adverse Cardiac Events
A Case of Possible IgG4-Related Constrictive Pericarditis Masquerading as Idiopathic Pericarditis: A Rare and Elusive Diagnosis
Lin Kimberly, Johnson Jonathan, Mccormack Shana, Lynch David, Tate Barbara, Feng Yixuan, Huang Jing, Mercer-rosa Laura, Dedio Anna, Mcsweeney Kara, Fournier Anne, Yoon Grace, Payne Ronald, Cripe Linda, Patel Aarti, Niaz Talha
A Case of Possible IgG4-Related Constrictive Pericarditis Masquerading as Idiopathic Pericarditis: A Rare and Elusive Diagnosis
Nandyal Shreyas, Sharma Bharosa, Gajjar Rohan, Varma Revati, Ezegwu Olisa, Amdetison Gedion Yilma, Tottleben Jon