Final ID: MP2732
Machine Learning For Precision Phenotyping and Genomic Discovery for Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) affects over 32 million people globally, and has a 30% mortality within one year of first hospitalization. Currently there are no HFpEF medications that are disease modifying or reduce mortality. As genomic-led drug discovery has demonstrated a 2.6-fold improvement in successful drug development, there have been ‘urgent’ calls to understand the genetic architecture of HFpEF. Despite this, our understanding remains poor; the two dedicated genome-wide association studies (GWAS) discovered only two, marginally significant loci. The primary limitation is imprecise phenotyping in genetic biobanks. For example, the most common heart failure code in the UK Biobank (UKB) is “heart failure, unspecified”)
Aim: To use machine learning to decipher the full genetic architecture of HFpEF.
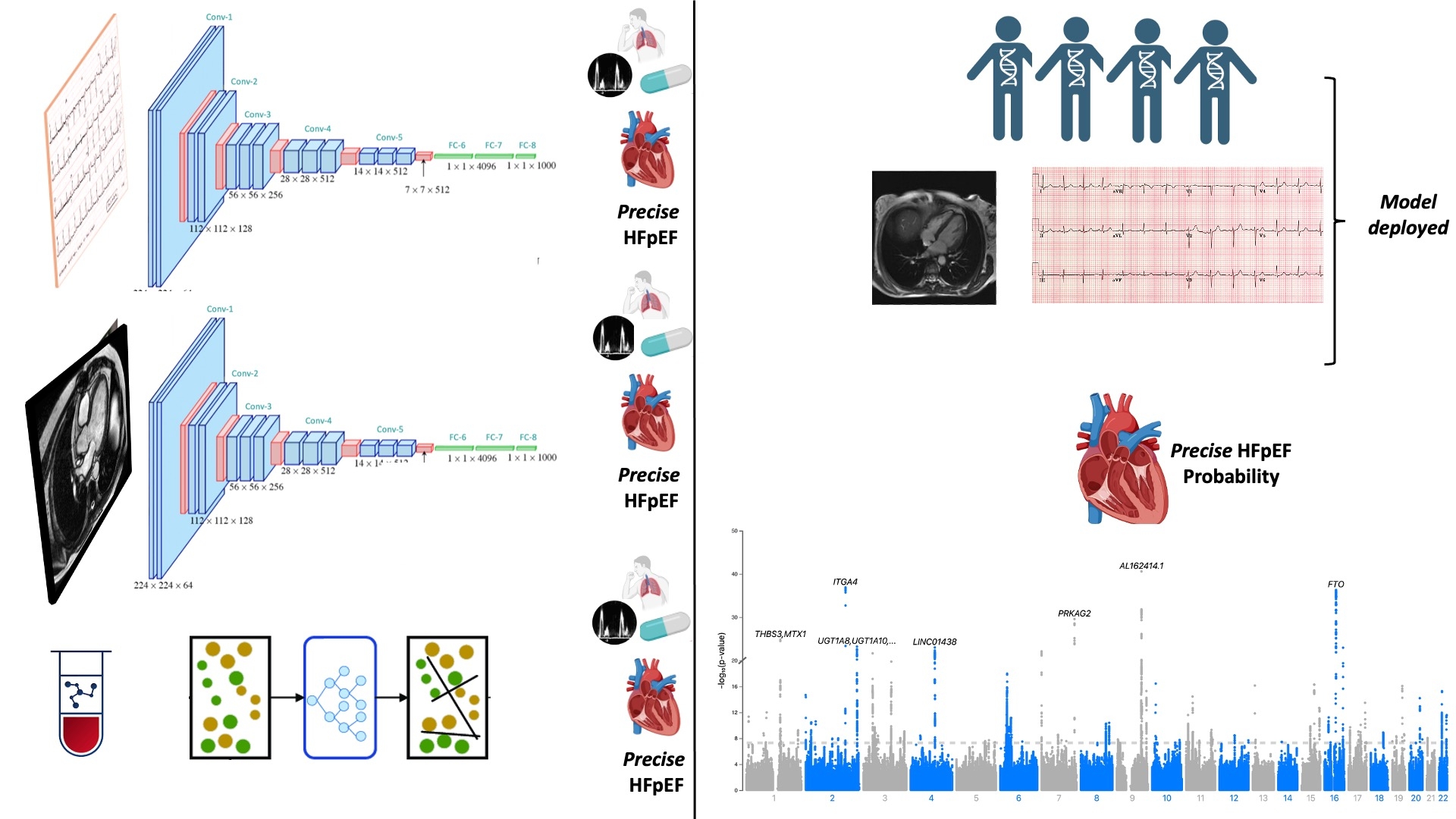
Methods: To uncover the full genetic architecture of HFpEF, we performed the following: a) Trained ML models to predict a precise HFpEF phenotype, b) Deployed models in UKB and assigned participants a HFpEF probability and c) Conducted GWAS on these predicted HFpEF probabilities. We trained 3 separate ML models to predict HFpEF: 1) Prediction from 40 biomarkers using XGBoost 2) Prediction from ECGs using neural networks, and 3) Prediction from Cardiac MRIs using neural networks. We deployed these 3 models on UKB participants which generated a HFpEF probability from which we conducted 3 GWAS. We then conducted proteomic analysis to identify proteins highly expressed in participants with high probability of HFpEF in UKB.
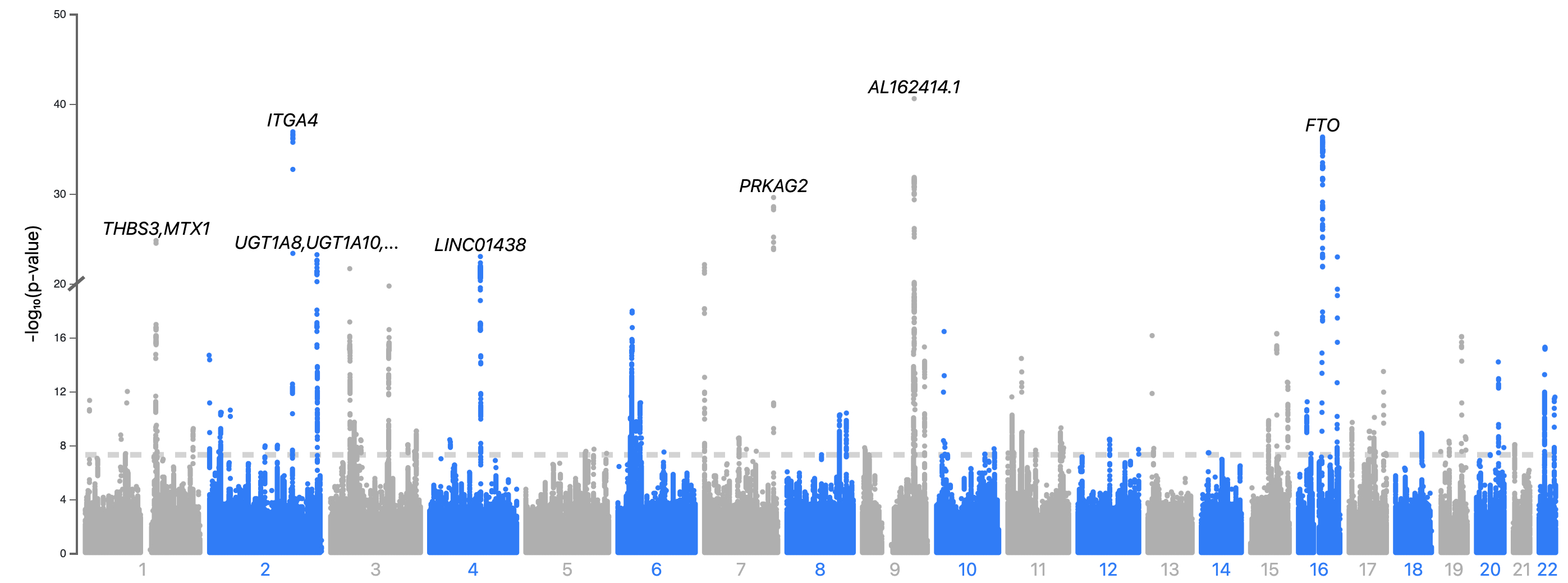
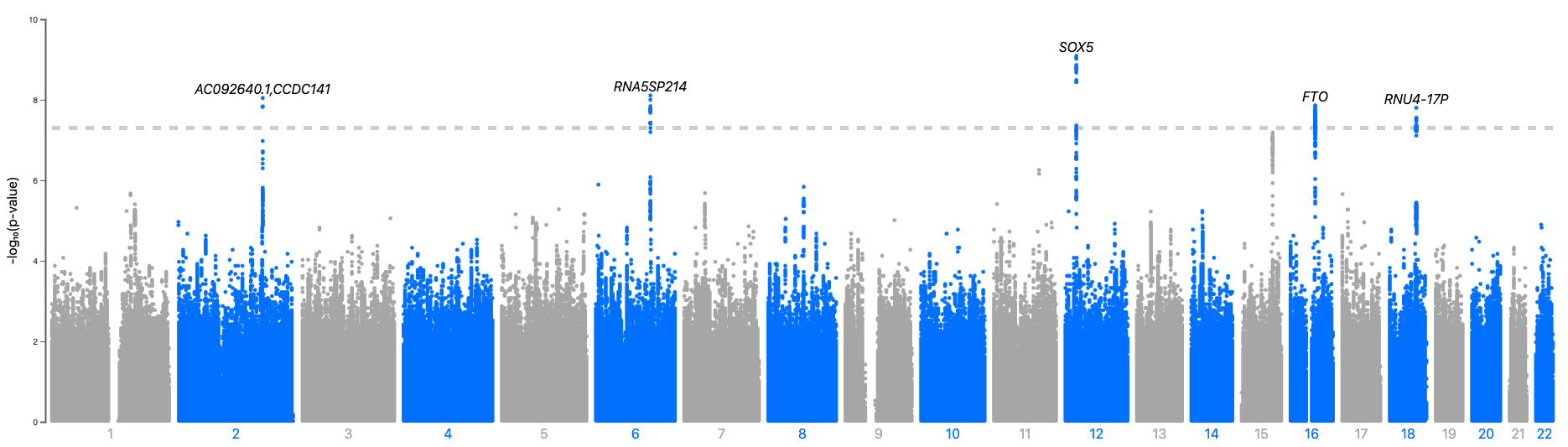
Results: Our 3 ML models predicted HFpEF with acceptable accuracy (AUC for biomarker XGBoost model: 0.85 (95%CI: 0.84-0.86), AUC for ECG neural network: 0.79 (0.78-0.80), and AUC for cardiac MRI: 0.75 (0.74-0.76). Our genome-wide association studies reveal 47 novel loci for HFpEF, with leading loci including: FTO, PRKAG2, AL162414, ITGA4, CAPN8, and HABP4. Proteomic analysis revealing a mixture of known associated proteins (e.g. NT-proBNP, Renin, and Leptin) and novel proteins associated with HFpEF, such as: Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4, Synuclein Gamma, and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1.
Conclusion: Machine learning facilitates the prediction of precise HFpEF phenotypes, which in turn reveals the full genetic architecture of HFpEF. Our genetic and proteomic data can serve as therapeutic targets for future research to create truly disease modifying HFpEF medications.
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) affects over 32 million people globally, and has a 30% mortality within one year of first hospitalization. Currently there are no HFpEF medications that are disease modifying or reduce mortality. As genomic-led drug discovery has demonstrated a 2.6-fold improvement in successful drug development, there have been ‘urgent’ calls to understand the genetic architecture of HFpEF. Despite this, our understanding remains poor; the two dedicated genome-wide association studies (GWAS) discovered only two, marginally significant loci. The primary limitation is imprecise phenotyping in genetic biobanks. For example, the most common heart failure code in the UK Biobank (UKB) is “heart failure, unspecified”)
Aim: To use machine learning to decipher the full genetic architecture of HFpEF.
Methods: To uncover the full genetic architecture of HFpEF, we performed the following: a) Trained ML models to predict a precise HFpEF phenotype, b) Deployed models in UKB and assigned participants a HFpEF probability and c) Conducted GWAS on these predicted HFpEF probabilities. We trained 3 separate ML models to predict HFpEF: 1) Prediction from 40 biomarkers using XGBoost 2) Prediction from ECGs using neural networks, and 3) Prediction from Cardiac MRIs using neural networks. We deployed these 3 models on UKB participants which generated a HFpEF probability from which we conducted 3 GWAS. We then conducted proteomic analysis to identify proteins highly expressed in participants with high probability of HFpEF in UKB.
Results: Our 3 ML models predicted HFpEF with acceptable accuracy (AUC for biomarker XGBoost model: 0.85 (95%CI: 0.84-0.86), AUC for ECG neural network: 0.79 (0.78-0.80), and AUC for cardiac MRI: 0.75 (0.74-0.76). Our genome-wide association studies reveal 47 novel loci for HFpEF, with leading loci including: FTO, PRKAG2, AL162414, ITGA4, CAPN8, and HABP4. Proteomic analysis revealing a mixture of known associated proteins (e.g. NT-proBNP, Renin, and Leptin) and novel proteins associated with HFpEF, such as: Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4, Synuclein Gamma, and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1.
Conclusion: Machine learning facilitates the prediction of precise HFpEF phenotypes, which in turn reveals the full genetic architecture of HFpEF. Our genetic and proteomic data can serve as therapeutic targets for future research to create truly disease modifying HFpEF medications.
More abstracts on this topic:
9-Year Longitudinal Assessment of the 12-lead Electrocardiogram of Volunteer Firefighters
Bae Alexander, Dzikowicz Dillon, Lai Chi-ju, Brunner Wendy, Krupa Nicole, Carey Mary, Tam Wai Cheong, Yu Yichen
A Predictive Tool and Diagnostic Screening Algorithm for the Identification of Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy in High-Risk Patient PopulationsChai Jocelyn, Sathananthan Janarthanan, Fine Nowell, Davis Margot, Starovoytov Andrew, Campbell Christine, Hawkins Nathaniel, Virani Sean, Luong Michael, Straatman Lynn, Kiess Marla, Worsley Daniel