Final ID: MP1954
Impella Support for Refractory Ventricular Tachycardia Storm in the Context of Severe Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease: A Case Report
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Unstable ventricular tachycardia (VT) in the setting of multivessel coronary artery disease (MVCAD) poses significant clinical and hemodynamic challenges. This case highlights the use of Impella CP for circulatory support in a patient with VT storm, cardiogenic shock, and severe metabolic acidosis, enabling high-risk PCI.
Case description:
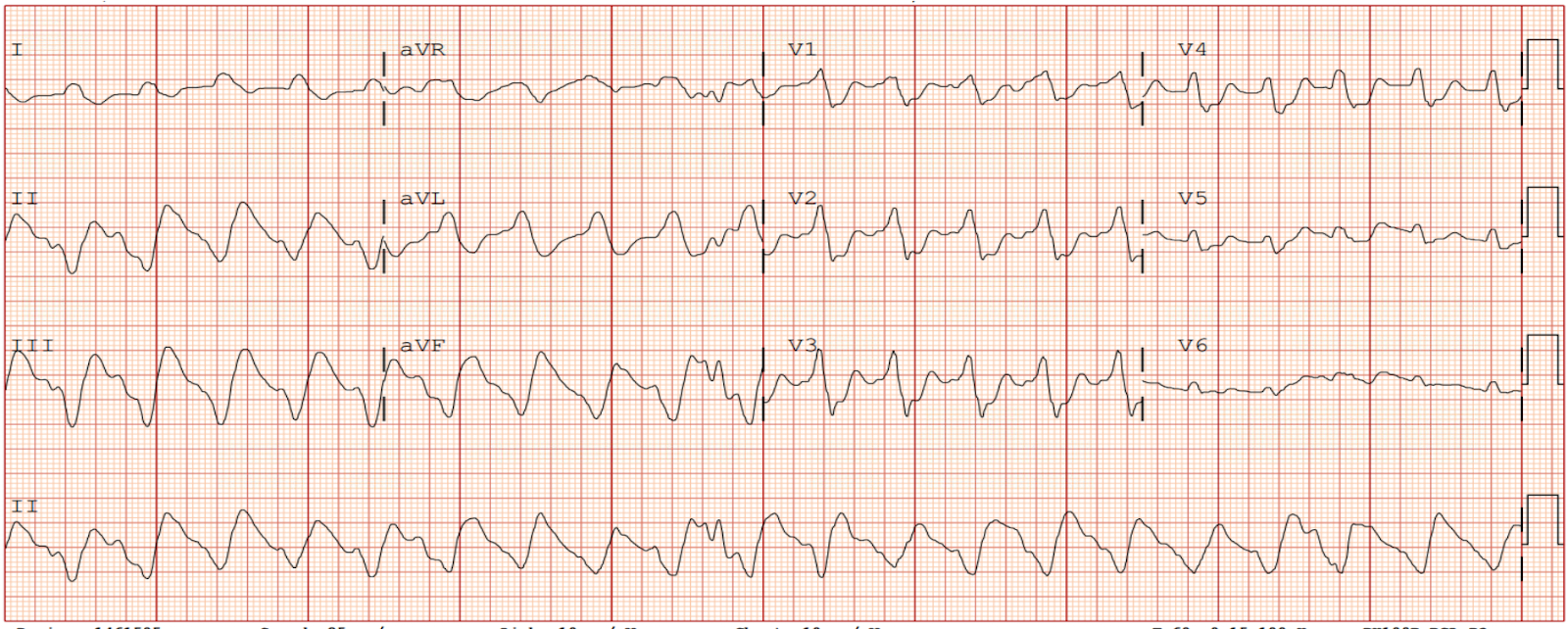
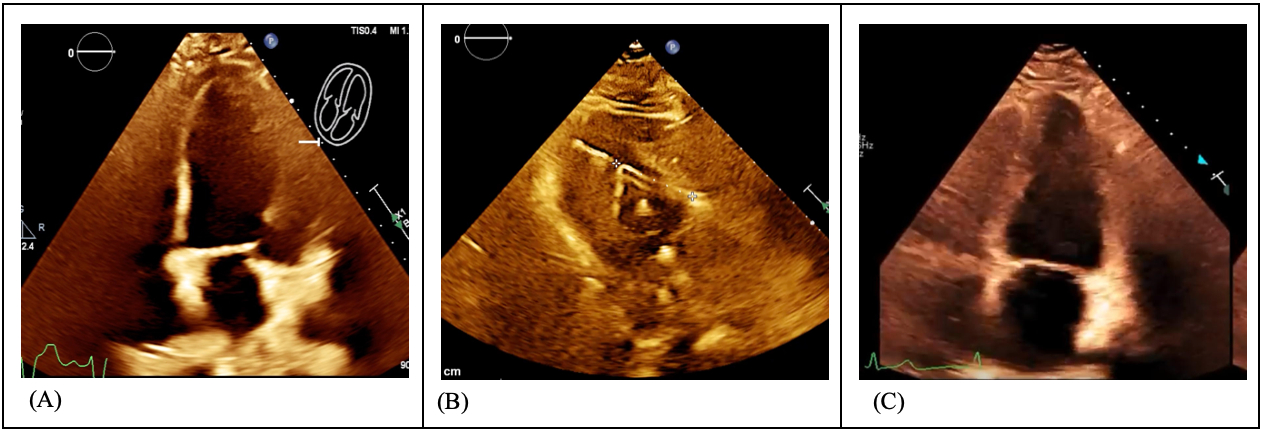
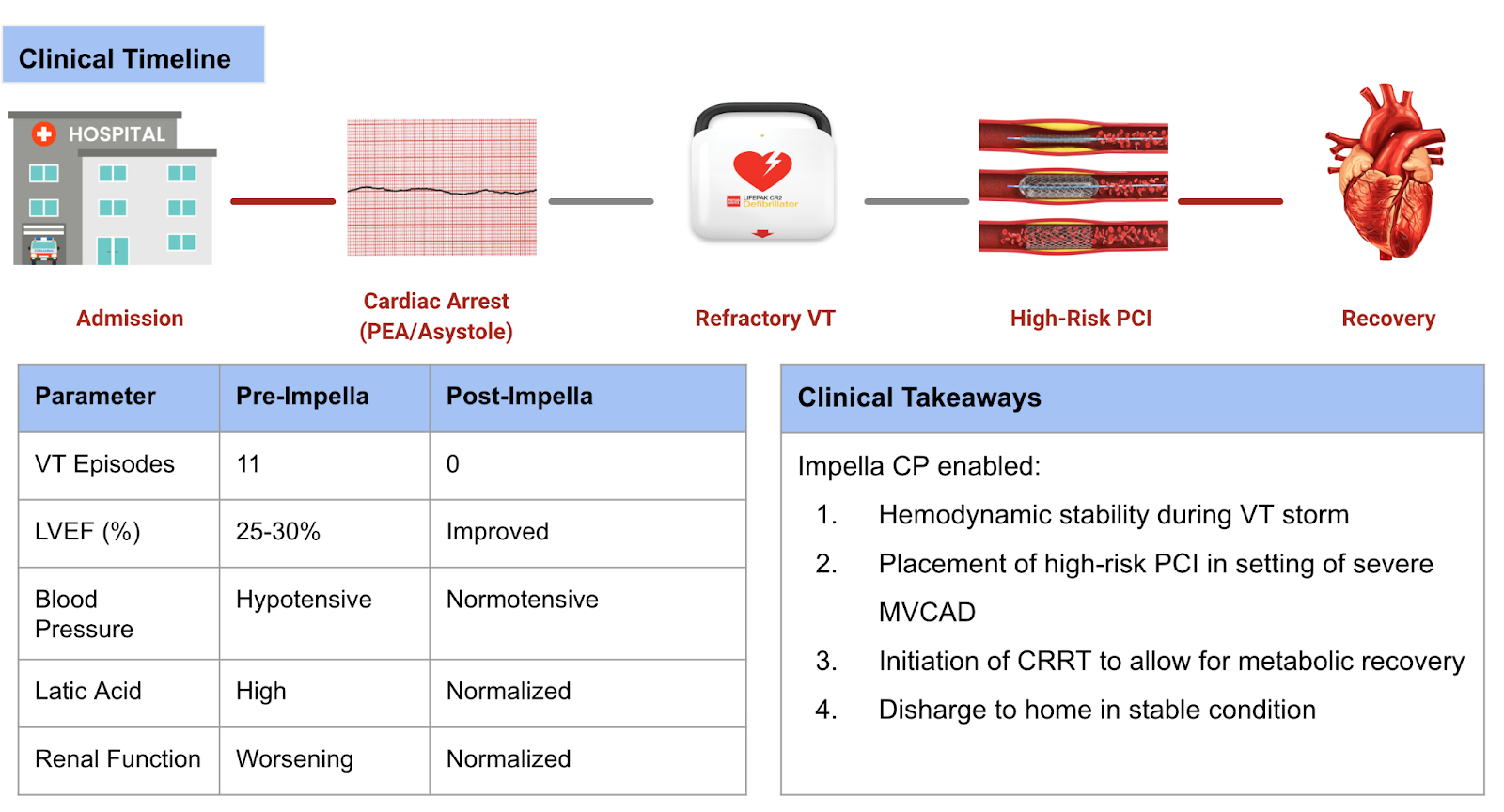
A 72-year-old male with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, peripheral artery disease, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (25–30%), diabetes, hypertension, and stage III chronic kidney disease presented with acute hypoxic respiratory failure. Initial labs showed severe acidosis. He experienced pulseless electrical activity arrest followed by asystole, requiring resuscitation and intubation. After return of spontaneous circulation, complete heart block developed, requiring transvenous pacemaker (TP) placement. The patient had multiple episodes of unstable VT, needing five defibrillations before catheterization and maximal pressor support (Figure 1). Right heart catheterization revealed cardiogenic shock; left heart catheterization showed severe three-vessel coronary artery disease, including critical left main stenosis. VT recurred during catheterization, requiring six more shocks despite amiodarone and lidocaine. Due to refractory VT and acidosis, an Impella CP was placed. VT resolved post-placement with no further cardioversion. Hemodynamic stability enabled continuous renal replacement therapy. Bypass surgery was deemed unsuitable. High-risk PCI with rotational atherectomy and drug-eluting stents was performed to the left main, anterior descending, and circumflex arteries. Intravascular ultrasound optimized stent deployment. TP was maintained during PCI. Following the procedure, Impella was weaned, and left ventricular function improved significantly (Figure 2). He was discharged in stable condition. This course is outlined in Figure 3.
Discussion:
Refractory VT storms in severe MVCAD with cardiogenic shock may not respond to antiarrhythmics or defibrillation alone. Mechanical support with pLVADs can offload the left ventricle, enhance coronary perfusion, and allow time for metabolic correction. This case illustrates Impella’s value in bridging patients to revascularization while stabilizing VT storms. Though pLVADs are well established in acute coronary syndromes and high-risk PCI, their role in VT storm remains underexplored. Further studies are needed to clarify their utility in this setting.
Unstable ventricular tachycardia (VT) in the setting of multivessel coronary artery disease (MVCAD) poses significant clinical and hemodynamic challenges. This case highlights the use of Impella CP for circulatory support in a patient with VT storm, cardiogenic shock, and severe metabolic acidosis, enabling high-risk PCI.
Case description:
A 72-year-old male with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, peripheral artery disease, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (25–30%), diabetes, hypertension, and stage III chronic kidney disease presented with acute hypoxic respiratory failure. Initial labs showed severe acidosis. He experienced pulseless electrical activity arrest followed by asystole, requiring resuscitation and intubation. After return of spontaneous circulation, complete heart block developed, requiring transvenous pacemaker (TP) placement. The patient had multiple episodes of unstable VT, needing five defibrillations before catheterization and maximal pressor support (Figure 1). Right heart catheterization revealed cardiogenic shock; left heart catheterization showed severe three-vessel coronary artery disease, including critical left main stenosis. VT recurred during catheterization, requiring six more shocks despite amiodarone and lidocaine. Due to refractory VT and acidosis, an Impella CP was placed. VT resolved post-placement with no further cardioversion. Hemodynamic stability enabled continuous renal replacement therapy. Bypass surgery was deemed unsuitable. High-risk PCI with rotational atherectomy and drug-eluting stents was performed to the left main, anterior descending, and circumflex arteries. Intravascular ultrasound optimized stent deployment. TP was maintained during PCI. Following the procedure, Impella was weaned, and left ventricular function improved significantly (Figure 2). He was discharged in stable condition. This course is outlined in Figure 3.
Discussion:
Refractory VT storms in severe MVCAD with cardiogenic shock may not respond to antiarrhythmics or defibrillation alone. Mechanical support with pLVADs can offload the left ventricle, enhance coronary perfusion, and allow time for metabolic correction. This case illustrates Impella’s value in bridging patients to revascularization while stabilizing VT storms. Though pLVADs are well established in acute coronary syndromes and high-risk PCI, their role in VT storm remains underexplored. Further studies are needed to clarify their utility in this setting.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Myocardial Infarction with Non-obstructive Coronary Arteries (MINOCA) Complicated by a Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
Thai Theresa, Lipinski Jerry, Sola Michael, El Rafei Abdelghani, Desai Aken, Sailer Christine
A First-in-Class EV-miRNA Diagnostic System for Early Identification of IVIG-Resistant Kawasaki DiseaseNakaoka Hideyuki, Hirono Keiichi, Hara Akane, Tsuboi Kaori, Ibuki Keijiro, Ozawa Sayaka, Ichida Fukiko