Final ID: MP920
c-Rel–Mediated Lipid Accumulation and Inflammatory Activation in Monocytes in Hypertriglyceridemia
Hypertriglyceridemia (HTG), with elevated triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TRLs) and remnants, increases atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk, but the mechanisms remain unclear. Monocyte infiltration from the circulation into arterial walls, differentiation into macrophages, and transformation into foam cells are key steps for atherogenesis. We showed that HTG in mice and humans increases lipid accumulation and inflammation in circulating monocytes, particularly intermediate/nonclassical monocytes (int/ncMo). However, the specific roles and mechanisms of TRLs in monocyte lipid accumulation and inflammation are not known.
Methods:
Ldlr–/– mice with or without human Apoc3-transgenic expression (A3LDLRKO, LDLRKO) and human subjects with or without severe HTG (TG: 1441.4 ± 485.7 vs. 112.0 ± 11.4 mg/dL in controls; n = 5/group) were studied. Monocytes were analyzed by flow cytometry, automated quantitative confocal microscopy, and single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq). In vitro, primary monocytes from humans and mice and THP-1 monocytes were treated with very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) from HTG subjects at 3.6 nM of apoB. Lipid droplets (LDs) and gene expression were assessed by flow cytometry and bulk RNA-seq.
Results:
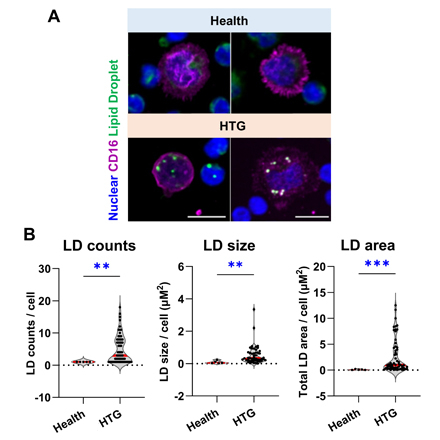
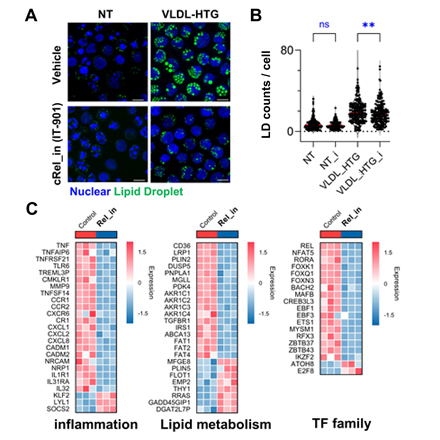
Compared to LDLRKO mice or healthy humans, A3LDLRKO mice and humans with HTG exhibited increased LD accumulation in Ly6ClowCD36+ (mouse) and CD16+ (human) int/ncMo. scRNA-seq of mouse monocytes revealed an HTG-responsive int/ncMo cluster enriched for genes involved in lipid metabolism and inflammatory pathways, including the transcription factor Rel. In vitro, compared to vehicle controls, VLDL treatment increased LD accumulation in primary and THP-1 monocytes and upregulated inflammatory markers including c-Rel examined by flow cytometry. RNA-seq revealed that VLDL treatment upregulated gene expression related to lipid uptake (Cd36, Scarb1, Lrp1) and inflammation (Il1b, Tnfα) in THP1 monocytes. Pharmacologic inhibition of c-Rel with IT-901 (3 mM) reduced VLDL-induced lipid accumulation in primary and THP-1 monocytes and downregulated the expression of genes involved in lipid uptake and inflammation (Plin2, Dgat2l7p, Tnf, Il1r1, Rel) in THP-1 monocytes.
Summary:
VLDL from HTG subjects drives lipid accumulation and inflammatory activation mainly in int/ncMo, with c-Rel playing a crucial role, thereby highlighting c-Rel as a potential therapeutic target for monocyte inflammation and ASCVD in HTG.
- Xiao, Jing ( Baylor College of Medicine , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Alagirova, Tamara ( MONCYTE Health , Helsinki , Finland )
- Lahdeniemi, Iris ( Moncyte Health , Helsinki , Finland )
- Hoogeveen, Ron ( Baylor College of Medicine , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Ballantyne, Christie ( Baylor College of Medicine , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Pfisterer, Simon ( MONCYTE Health , Helsinki , Finland )
- Wu, Huaizhu ( Baylor College of Medicine , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Obrien, Veronica ( Baylor College of Medicine , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Litchfield, Benjamin ( Baylor College of Medicine , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Gao, Feng ( Baylor College of Medicine , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Hamid, Arsalan ( Baylor College of Medicine , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Chao, Cheng ( Baylor College of Medicine , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Li, Yanming ( Baylor College of Medicine , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Shen, Ying ( Baylor College of Medicine , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Pi, Xinchun ( Baylor College of Medicine , Houston , Texas , United States )
Meeting Info:
Session Info:
Medical Therapies in Vascular Disease
Saturday, 11/08/2025 , 01:45PM - 02:35PM
Moderated Digital Poster Session
More abstracts on this topic:
Iverson Leslie, Knight Stacey, May Heidi, Le Viet, Bair Tami, Knowlton Kirk, Anderson Jeffrey
Investigating Transcriptomic Profiles of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Moyamoya Disease Using Single-Cell RNAseqDemirag Zeynep, Uchino Haruto, Tokairin Kikutaro, Rao Shailaja, Chiang Terrance, Morton Gabriella, Lee Alex, Cheng Michelle, Steinberg Gary
More abstracts from these authors:
Zhou Peidi, Yang Yueh-ning, Schlosser Pascal, Hoogeveen Ron, Ballantyne Christie, Yu Bing
Linking variability of leukocyte lipid metabolism to circulating lipids, lipoprotein composition and cardiovascular risk in the Finnish adult populationHlushchenko Iryna, Pamilo Siina, Islam Mohammad Majharul, Lahdeniemi Iris, Tamlander Max, Ripatti Samuli, Pfisterer Simon