Final ID: Sa3027
Safety and Efficacy of Antisense Oligonucleotides On Triglyceride and Apolipoprotein C-III Levels in Hypertriglyceridemia; A Network Meta-Analysis Of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Hypertriglyceridemia is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Apolipoprotein C-III (APOC3) inhibition through the antisense oligonucleotides volanesorsen, olezarsen, and plozasiran, reduced triglycerides in the previous trials. However, the safety and efficacy of the three medications have not been compared yet.
Methods
A network meta-analysis was performed to compare multiple doses of the three medications to each other through the placebo. Nine randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were retrieved by searching PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, SCOPUS, and Cochrane. The mean difference (MD) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were used for continuous outcomes. The risk ratio (RR) and 95% CI were used for dichotomous outcomes.
Results
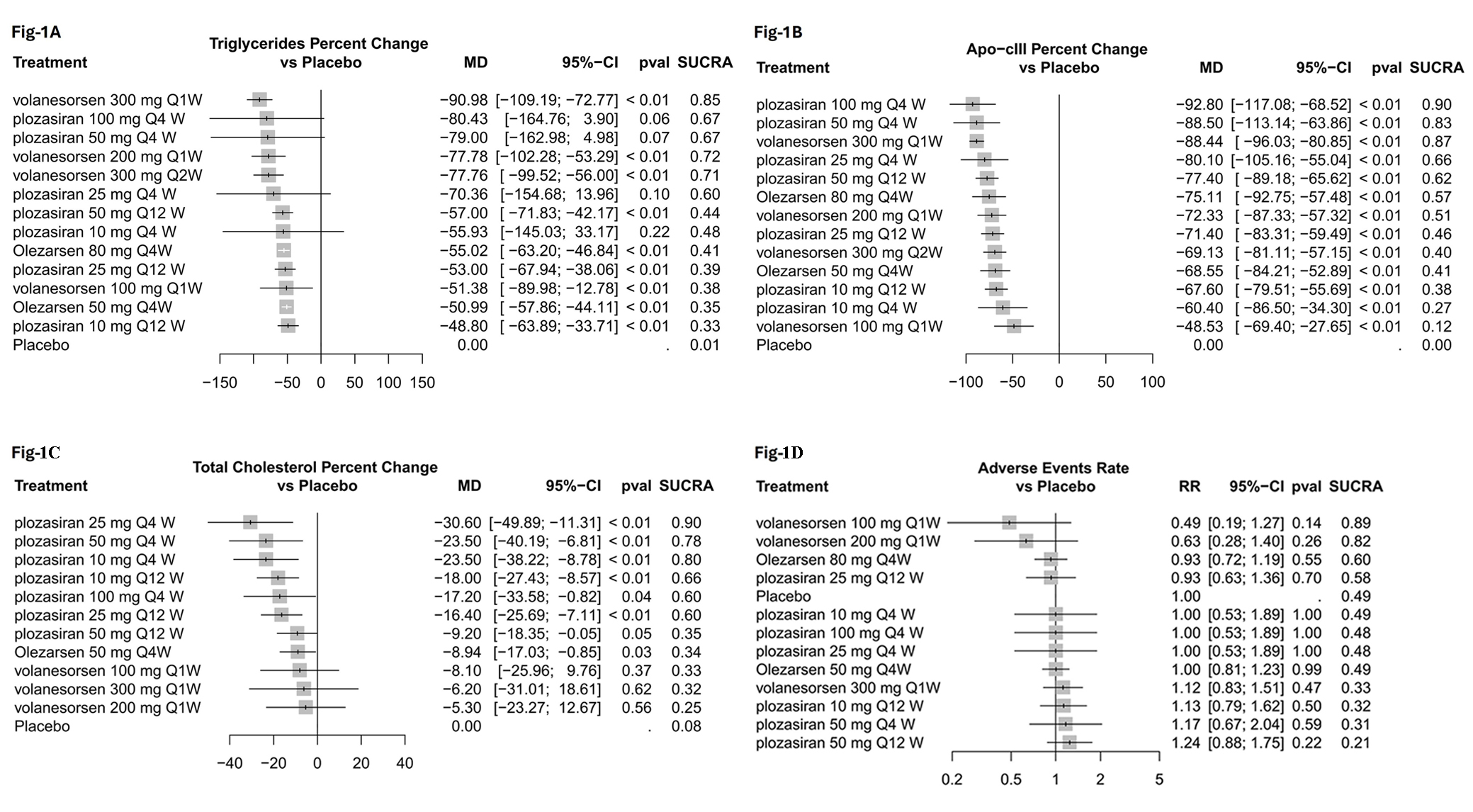
A total of 782 patients were included. Volanesorsen 300 mg once weekly showed the most significant reduction in triglyceride levels (MD = -90.98%, 95% CI: [-109.2%; -72.8%]; p<0.01). Only plozasiran once monthly, regardless of the dose, showed a non-significant reduction in triglycerides, which should be taken with caution as the data were derived from a phase 1 trial with a small sample size. All the regimens significantly reduced APOC3 levels compared to placebo with plozasiran 100 mg and 50 mg once monthly and volanesorsen 300 mg once weekly, showing the most significant reduction (MD range: -92.8% to -88.4%; p<0.01). Plozasiran regimens, especially the 25 mg, 50 mg, and 10 mg once monthly dosages, respectively, reduced total cholesterol levels the most compared to placebo (MD range: -30.6% to -23.5%; p<0.01). Only volanesorsen, regardless of the dose, did not significantly reduce total cholesterol compared to placebo. None of the treatments showed a statistically significant difference in the adverse events rate compared to placebo.
Conclusion
APOC3 antisense oligonucleotide inhibitors effectively reduced triglyceride, APOC3, and total cholesterol levels in hypertriglyceridemia, with an acceptable safety profile. However, due to the relatively small sample size, the results should be interpreted with caution. Further research is needed to confirm the beneficial effects of APOC3 inhibitors and provide strong evidence on the effects of each medication regimen.
Hypertriglyceridemia is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Apolipoprotein C-III (APOC3) inhibition through the antisense oligonucleotides volanesorsen, olezarsen, and plozasiran, reduced triglycerides in the previous trials. However, the safety and efficacy of the three medications have not been compared yet.
Methods
A network meta-analysis was performed to compare multiple doses of the three medications to each other through the placebo. Nine randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were retrieved by searching PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, SCOPUS, and Cochrane. The mean difference (MD) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were used for continuous outcomes. The risk ratio (RR) and 95% CI were used for dichotomous outcomes.
Results
A total of 782 patients were included. Volanesorsen 300 mg once weekly showed the most significant reduction in triglyceride levels (MD = -90.98%, 95% CI: [-109.2%; -72.8%]; p<0.01). Only plozasiran once monthly, regardless of the dose, showed a non-significant reduction in triglycerides, which should be taken with caution as the data were derived from a phase 1 trial with a small sample size. All the regimens significantly reduced APOC3 levels compared to placebo with plozasiran 100 mg and 50 mg once monthly and volanesorsen 300 mg once weekly, showing the most significant reduction (MD range: -92.8% to -88.4%; p<0.01). Plozasiran regimens, especially the 25 mg, 50 mg, and 10 mg once monthly dosages, respectively, reduced total cholesterol levels the most compared to placebo (MD range: -30.6% to -23.5%; p<0.01). Only volanesorsen, regardless of the dose, did not significantly reduce total cholesterol compared to placebo. None of the treatments showed a statistically significant difference in the adverse events rate compared to placebo.
Conclusion
APOC3 antisense oligonucleotide inhibitors effectively reduced triglyceride, APOC3, and total cholesterol levels in hypertriglyceridemia, with an acceptable safety profile. However, due to the relatively small sample size, the results should be interpreted with caution. Further research is needed to confirm the beneficial effects of APOC3 inhibitors and provide strong evidence on the effects of each medication regimen.
More abstracts on this topic:
Olezarsen for Hypertriglyceridemia in Patients at High Cardiovascular Risk - A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis
Raja Sandesh, Salman Madiha, Raja Adarsh, Asghar Muhammad Sohaib, Shafique Muhammad Ashir, Mustafa Muhammad Saqlain, Alim Ur Rahman Hafsah, Ahmed Muhammad, Fahim Muhammad Ahmed Ali, Azeem Bazil
Association between Elevated Lipoprotein(a) and Cardiovascular Events and Mortality in a Nationally Representative Sample of US Medicare, Medicaid, and Commercial Enrollees with ASCVDHu Xingdi, Lozama Tony, Petrilla Allison, Agatep Barnabie, Mcmorrow Donna, Mohammadi Iman, Reisman Lonny, Wong Nathan