Final ID: P3041
Association of Urine Metabolites with All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study
Abstract Body: Introduction. Circulating metabolites are associated with all-cause and cause-specific mortality. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) and cancer are two leading causes of mortality, providing complementary assessment of disease burden in addition to all-cause mortality. However, the role of urine markers in predicting the risk of mortality is understudied.
Hypothesis. We hypothesize that urine metabolites are associated with all-cause, CVD, and cancer mortality.
Methods. Using the Nightingale platform, urine metabolite profiling was performed at the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study visit 5 (2011-13). Urine metabolite levels were probability quotient normalized. We conducted Cox proportional models on 42 urine metabolites with all-cause, CVD, and cancer mortality, adjusting for traditional risk factors and kidney function. A metabolite risk score (MRS) was constructed using weights obtained from least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression. Harrell’s C statistics was calculated to estimate the models’ predictive performance.
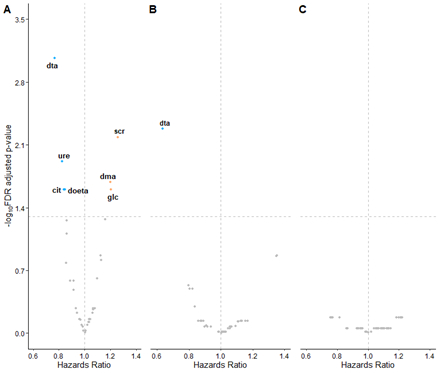
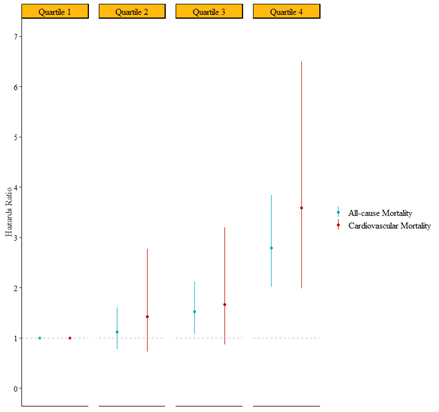
Results. Over an average of 5 years of follow-up, 372, 113, and 85 all-cause, CVD, and cancer mortality cases were developed among 1,350 participants (mean age: 75 years, 74% women, 35% Blacks). Seven and one urine metabolites were associated with all-cause and CVD mortality (FDR<0.05, Figure.1). 4-deoxythreonate, a carboxylic acid found in foods, was associated with a decreased risk of all-cause (HR per SD: 0.77, 95% CI: 0.68-0.87) and CVD (HR per SD: 0.63, 95% CI: 0.50-0.80) mortality. The highest quartile of MRS, consisting of 13 and 5 selected urine metabolites, had about a three-fold and four-fold risk of all-cause and CVD mortality compared to the lowest quartile, respectively, and a graded effect across quartiles was observed (p for trend: p<0.001, Figure.2). Adding seven significant urine metabolites improved all-cause mortality prediction by 4% over a traditional risk model (p<0.05).
Conclusions. We identified urine metabolites associated with all-cause and CVD mortality, suggesting the potential of considering urine markers in clinical practice and for at-risk population identification.
Hypothesis. We hypothesize that urine metabolites are associated with all-cause, CVD, and cancer mortality.
Methods. Using the Nightingale platform, urine metabolite profiling was performed at the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study visit 5 (2011-13). Urine metabolite levels were probability quotient normalized. We conducted Cox proportional models on 42 urine metabolites with all-cause, CVD, and cancer mortality, adjusting for traditional risk factors and kidney function. A metabolite risk score (MRS) was constructed using weights obtained from least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression. Harrell’s C statistics was calculated to estimate the models’ predictive performance.
Results. Over an average of 5 years of follow-up, 372, 113, and 85 all-cause, CVD, and cancer mortality cases were developed among 1,350 participants (mean age: 75 years, 74% women, 35% Blacks). Seven and one urine metabolites were associated with all-cause and CVD mortality (FDR<0.05, Figure.1). 4-deoxythreonate, a carboxylic acid found in foods, was associated with a decreased risk of all-cause (HR per SD: 0.77, 95% CI: 0.68-0.87) and CVD (HR per SD: 0.63, 95% CI: 0.50-0.80) mortality. The highest quartile of MRS, consisting of 13 and 5 selected urine metabolites, had about a three-fold and four-fold risk of all-cause and CVD mortality compared to the lowest quartile, respectively, and a graded effect across quartiles was observed (p for trend: p<0.001, Figure.2). Adding seven significant urine metabolites improved all-cause mortality prediction by 4% over a traditional risk model (p<0.05).
Conclusions. We identified urine metabolites associated with all-cause and CVD mortality, suggesting the potential of considering urine markers in clinical practice and for at-risk population identification.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acetylation of Electron Transfer Flavoprotein Alpha Is a Possible Regulatory Mechanism of Fatty Acid Oxidation in Diabetic Hearts
Tatekoshi Yuki, Yano Masaki, Hosoda Ryusuke, Saga Yukika, Kuno Atsushi
Accelerometer-Measured Sedentary Behavior and Future Cardiovascular DiseaseAjufo Ezimamaka, Kany Shinwan, Ramo Joel, Churchill Timothy, Guseh James, Aragam Krishna, Ellinor Patrick, Khurshid Shaan