Final ID: Mo1001
Pharmacological Inhibition of GPR39 Markedly Reduces Brain Infarction in a Mouse Model of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: GPR39 is abundantly expressed in all brain regions. We have previuosly demonstrated that it is present in vascular smooth muscle cells and pericytes where its activation increases cytosolic Ca++ resulting in cell contraction, causing reduction in perfusion. We, therefore, hypothesized inhibition of GPR39 with VC108, a selective GPR39 blocker, would reduce brain infarct size after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). Since VC108 does not cross the blood brain barrier (BBB) it was administered drug directly into the brain.
Methods: To understand the biodistribution of drug after direct brain injection, 15 wild-type mice underwent cerebral ventricular injection of 0.05 mg/kg of VC108 a selective GPR39 inhibitor. This dose is 5% of the intravenous dose that results in >90% of receptor occupancy. Five mice each were then euthanized 30 min, 24 h, and 48 h later for measuring brain tissue drug levels. Based on these results mice received either vehicle (n=5) or VC108 (n=6) similalry administered and 24 hr later underwent 45 min of MCAO. They were euhanized 24 hr after MCAO and brain sectioned in 4 slices and stained with triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) for infarct size estimation. Both sides of the brain slices were imaged.
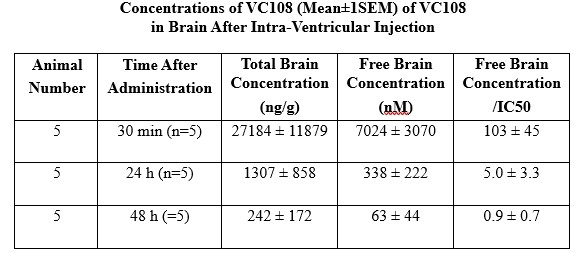
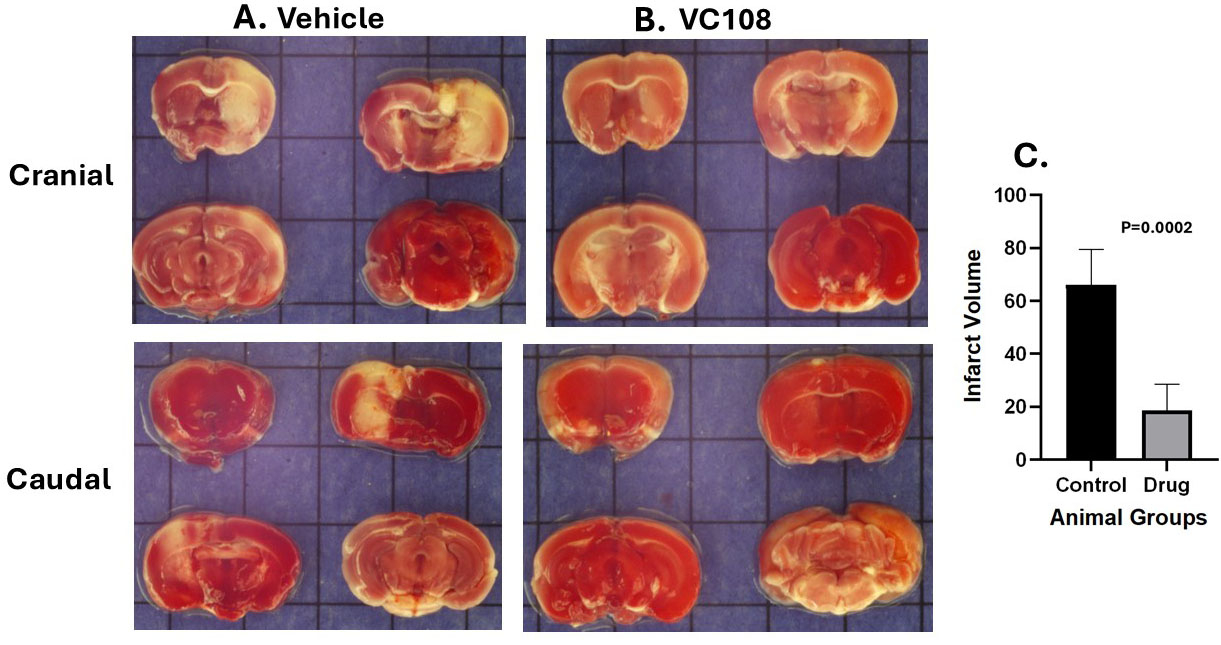
Results: Mean total and free (25.84% of total) drug levels in brain from the 15 animals are depicted in Figure 1. There is considerable variability in drug levels between animals and between different regions of the brain. The free concentration of VC108 exceeds the IC50 (64.8 nM) of the drug at 30 min and 24h but not 48 h after injection. Panels A and B in Figure 2 illustrate the cranial and caudal aspects of brain slices from vehicle and VC108 treated animals, respectively. A markedly different extent of infarction is seen between the two with negligible infarction in the drug versus vehicle treated animal. Aggregate data show a markedly smaller IS in VC108 versus vehicle treated animals (Panel C).
Conclusions: Direct Intracerebroventricular injection of VC108 in the brain can achieve adequate drug tissue levels for efficacy for upto 48 h later. Pre-treatment with VC108 can markedly reduce infarct size in a MCAO mouse model. In addition to vasodilation, inhibition of GPR39 could also have direct cellular effects enabling reduction in ischemic injury. GPR39 appears to be an appropriate target for treatment of stroke and development of molecules that cross the BBB is warrented.
Methods: To understand the biodistribution of drug after direct brain injection, 15 wild-type mice underwent cerebral ventricular injection of 0.05 mg/kg of VC108 a selective GPR39 inhibitor. This dose is 5% of the intravenous dose that results in >90% of receptor occupancy. Five mice each were then euthanized 30 min, 24 h, and 48 h later for measuring brain tissue drug levels. Based on these results mice received either vehicle (n=5) or VC108 (n=6) similalry administered and 24 hr later underwent 45 min of MCAO. They were euhanized 24 hr after MCAO and brain sectioned in 4 slices and stained with triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) for infarct size estimation. Both sides of the brain slices were imaged.
Results: Mean total and free (25.84% of total) drug levels in brain from the 15 animals are depicted in Figure 1. There is considerable variability in drug levels between animals and between different regions of the brain. The free concentration of VC108 exceeds the IC50 (64.8 nM) of the drug at 30 min and 24h but not 48 h after injection. Panels A and B in Figure 2 illustrate the cranial and caudal aspects of brain slices from vehicle and VC108 treated animals, respectively. A markedly different extent of infarction is seen between the two with negligible infarction in the drug versus vehicle treated animal. Aggregate data show a markedly smaller IS in VC108 versus vehicle treated animals (Panel C).
Conclusions: Direct Intracerebroventricular injection of VC108 in the brain can achieve adequate drug tissue levels for efficacy for upto 48 h later. Pre-treatment with VC108 can markedly reduce infarct size in a MCAO mouse model. In addition to vasodilation, inhibition of GPR39 could also have direct cellular effects enabling reduction in ischemic injury. GPR39 appears to be an appropriate target for treatment of stroke and development of molecules that cross the BBB is warrented.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of fixed dose combination therapy use with blood pressure control and cardiovascular outcomes in the Systolic Blood Pressure Reduction Intervention (SPRINT) Trial: A post-hoc analysis
Rao Shreya, Pandey Ambarish, Segar Matthew, Agarwal Anubha, Keshvani Neil, Vongpatanasin Wanpen, Hsue Priscilla, Huffman Mark, Wang Thomas, Prabhakaran Dorairaj
Automated Assessment of Intracerebral Hemorrhage Volumes using the VIOLA tool Performs Similarly to ABC/2 in Predictive ModellingPotter Thomas, Aamodt Eva, Borei Karim, Khan Osman, Bako Abdulaziz, Pan Alan, Liu Qinghui, Macintosh Bradley, Vahidy Farhaan