Final ID: Sa4167
Targeting GPR39 for Hypoxia-induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Mice
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Primary pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a disease affecting young subjects. It has very poor prognosis and optimal treatment is not available. 15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (15-HETE), a potent vasoconstrictor, has been implicated in the pathogenesis of PAH. Elevated levels of 15-HETE have been shown to be associated with worse prognosis in patients with PAH. Oral ingestion of 15-HETE leads to development of PAH in rodents. We recently showed that 15-HETE is the endogenous agonist for the G-protein coupled receptor 39 (GPR39) present in vascular smooth muscle cells.
Hypothesis: We, therefore, hypothesized that global deletion of GPR39 (knock-out [KO] mice) would protect from PAH by removing the receptor through which 15-HETE causes vasoconstriction.
Methods: Accordingly, 13 wild-type (WT) and 16 KO mice were placed in a hypoxia chamber (10% O2). Litter-mate controls (7 WT and 13 KO) were subjected to normoxia (room air, 21% O2). At the end of 4 weeks heart rate as well as aortic and right ventricular (RV) pressures were measured (latter using micromanometer-tipped catheter), and the animals were then euthanized for measurement of RV wall thickness and RV size from which RV wall stress was calculated.
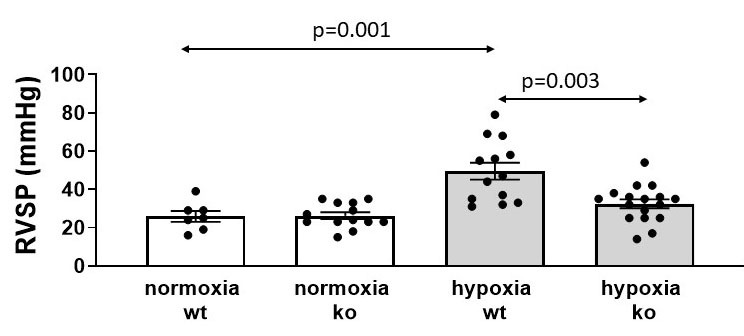
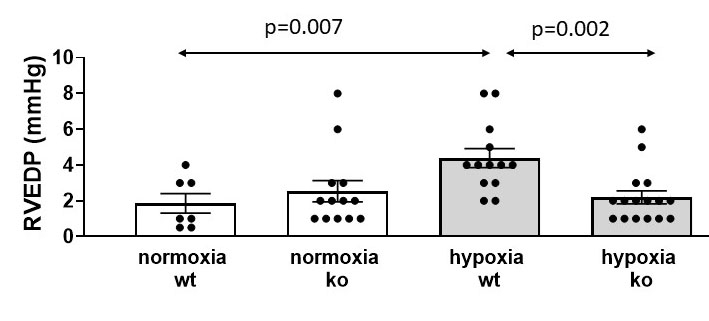
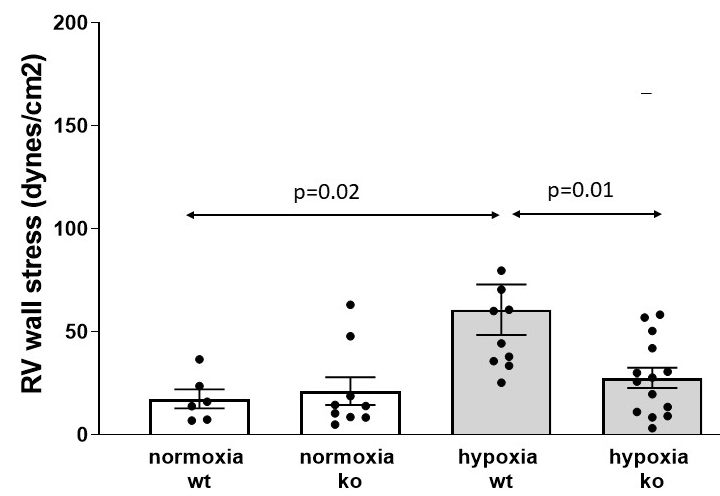
Results: Heart rate and systolic blood pressure were not different between the 4 groups. WT hypoxic animals developed PAH with peak RV systolic pressures (RVSP) being significantly higher than normoxic WT and hypoxic WT and hypoxic KO mice. (Figure 1) Similar results were noted for RV end-diastolic pressure (Figure 2) and RV wall stress (Figure 3).
Conclusions: By deleting GPR39, the target for 15-HETE, we were able to prevent hypoxia induced PAH and RV dysfunction. Pharmacological inhibition of GPR39 may open new frontiers in the treatment of PAH.
Hypothesis: We, therefore, hypothesized that global deletion of GPR39 (knock-out [KO] mice) would protect from PAH by removing the receptor through which 15-HETE causes vasoconstriction.
Methods: Accordingly, 13 wild-type (WT) and 16 KO mice were placed in a hypoxia chamber (10% O2). Litter-mate controls (7 WT and 13 KO) were subjected to normoxia (room air, 21% O2). At the end of 4 weeks heart rate as well as aortic and right ventricular (RV) pressures were measured (latter using micromanometer-tipped catheter), and the animals were then euthanized for measurement of RV wall thickness and RV size from which RV wall stress was calculated.
Results: Heart rate and systolic blood pressure were not different between the 4 groups. WT hypoxic animals developed PAH with peak RV systolic pressures (RVSP) being significantly higher than normoxic WT and hypoxic WT and hypoxic KO mice. (Figure 1) Similar results were noted for RV end-diastolic pressure (Figure 2) and RV wall stress (Figure 3).
Conclusions: By deleting GPR39, the target for 15-HETE, we were able to prevent hypoxia induced PAH and RV dysfunction. Pharmacological inhibition of GPR39 may open new frontiers in the treatment of PAH.
More abstracts on this topic:
Bile Acid Dysregulation in Response to Right Heart Failure and Hepatic Congestion
Park Arick, Yang Bin, Parvathaneni Adeesh, Fu Christina, Byrnes Kathleen, Haeusler Rebecca, Schilling Joel
Chronic Suppression of the Renin-Angiotensin System Induces Renal Vascular Remodeling, Hypoxia, and Metabolic ReprogrammingAlmeida Lucas, Medrano Silvia, Smith Jason, Yamaguchi Hiroki, Yamaguchi Manako, Sequeira Maria Luisa, Gomez Ariel