Final ID: MP980
Artificial-Intelligence Based Smart Catheter Guidance for Atrial Fibrillation Ablation: Large Registry Validation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Ablation of atrial fibrillation (AF) by pulmonary vein (PV) isolation has limited success in some patients. However, identifying additional ablation targets in such patients currently requires mapping the entire atrium, which is time-consuming and poorly accounts for real-time changes.
Objectives:
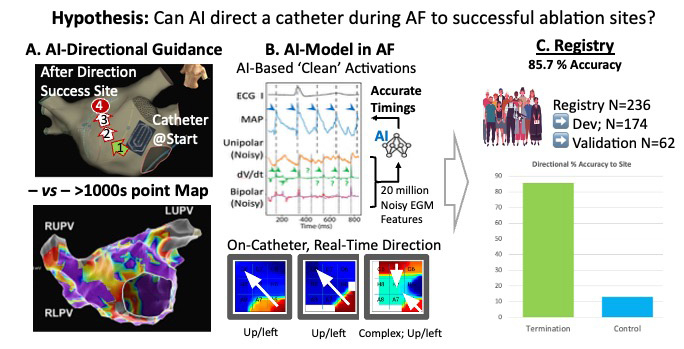
We developed an Artificial-Intelligence (AI) based system that can guide an electrophysiology catheter in real-time (i.e. left/right, superior/inferior) during AF from an arbitrary location directly to sites leading to AF termination or 1Y success (fig. A). We validated the system in a large registry, and evaluated projected time savings from this approach.
Methods:
coPilot is an AI-system developed and tested in separate cohorts on ~20 million electrograms in a N=236 patient registry with physiological and clinical ground truth labels. First, we trained recurrent neural network (RNN) models to estimate AF activation times using unipolar and bipolar electrogram features (first derivative dV/dt, shape), tuned in a random forest classifier to experts informed by monophasic action potential (MAP) tracings (fig. B; top). Second, we applied this AI-model to multi-electrode catheters (e.g. local HDGrid, global Basket), to calculate predominant AF wave direction (fig. B bottom). Third, we validated if moving a catheter in AI-indicated directions reached successful AF ablation sites in a hold-out set not used for training.
Results:
The validation cohort was 69.0±8.3 years’ and 72.6% had non-paroxysmal AF. In Fig. B, AF activation times by traditional electrogram features were noisy versus MAPs (arrows). Fig. B (bottom) shows AI-activation times on a multi-electrode array in a 67Y woman in persistent AF, showing predominantly up/left activity over time. The array was moved accordingly and analysis repeated (steps 1-4 in fig. A, top), until the AF termination site was reached. coPilot pointed to 85.7% of AF termination versus 13.1% of control sites (p<0.01, fig. C). coPilot also reached sites ablated in cases of long-term success (68.8% at 1Y). Time to the successful region was 4.2±1.1 movements (estimated <5 minutes) that was shorter than atrial mapping time (>10-15 minutes).
Conclusions:
A novel AI-based system trained to physiological and clinical gold standards can rapidly steer a clinical catheter during AF to successful ablation sites. This approach has promise for improving the success of AF ablation while reducing case time over existing strategies.
Ablation of atrial fibrillation (AF) by pulmonary vein (PV) isolation has limited success in some patients. However, identifying additional ablation targets in such patients currently requires mapping the entire atrium, which is time-consuming and poorly accounts for real-time changes.
Objectives:
We developed an Artificial-Intelligence (AI) based system that can guide an electrophysiology catheter in real-time (i.e. left/right, superior/inferior) during AF from an arbitrary location directly to sites leading to AF termination or 1Y success (fig. A). We validated the system in a large registry, and evaluated projected time savings from this approach.
Methods:
coPilot is an AI-system developed and tested in separate cohorts on ~20 million electrograms in a N=236 patient registry with physiological and clinical ground truth labels. First, we trained recurrent neural network (RNN) models to estimate AF activation times using unipolar and bipolar electrogram features (first derivative dV/dt, shape), tuned in a random forest classifier to experts informed by monophasic action potential (MAP) tracings (fig. B; top). Second, we applied this AI-model to multi-electrode catheters (e.g. local HDGrid, global Basket), to calculate predominant AF wave direction (fig. B bottom). Third, we validated if moving a catheter in AI-indicated directions reached successful AF ablation sites in a hold-out set not used for training.
Results:
The validation cohort was 69.0±8.3 years’ and 72.6% had non-paroxysmal AF. In Fig. B, AF activation times by traditional electrogram features were noisy versus MAPs (arrows). Fig. B (bottom) shows AI-activation times on a multi-electrode array in a 67Y woman in persistent AF, showing predominantly up/left activity over time. The array was moved accordingly and analysis repeated (steps 1-4 in fig. A, top), until the AF termination site was reached. coPilot pointed to 85.7% of AF termination versus 13.1% of control sites (p<0.01, fig. C). coPilot also reached sites ablated in cases of long-term success (68.8% at 1Y). Time to the successful region was 4.2±1.1 movements (estimated <5 minutes) that was shorter than atrial mapping time (>10-15 minutes).
Conclusions:
A novel AI-based system trained to physiological and clinical gold standards can rapidly steer a clinical catheter during AF to successful ablation sites. This approach has promise for improving the success of AF ablation while reducing case time over existing strategies.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Deep Learning Digital Biomarker for Mitral Valve Prolapse using Echocardiogram Videos
Al-alusi Mostafa, Khurshid Shaan, Sanborn Danita, Picard Michael, Ho Jennifer, Maddah Mahnaz, Ellinor Patrick, Lau Emily, Small Aeron, Reeder Christopher, Shnitzer Dery Tal, Andrews Carl, Kany Shinwan, Ramo Joel, Haimovich Julian
Ablation versus Anti-arrhythmic Drug Therapy for Ventricular Tachycardia in Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled TrialsKhan Ubaid, Chaudhry Kashif, Amin Ahmed Mazen, A. Ibrahim Ahmed, Imran Muhammad, Rakab Mohamed, Iltaf Arej, M. Albarakat Majd, Ranabhat Chet, Brilliant Justin