Final ID: MP2316
Estimating CardioMEMS Pulmonary Artery Diastolic Pressure With a Non-invasive Cardiac Hemodynamic Artificial Intelligence monitoring System (CHAIS)
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
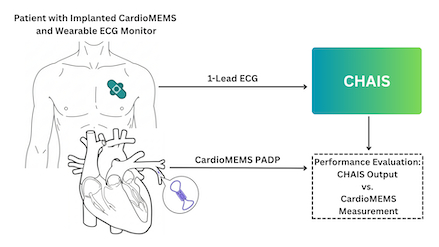
The implantable CardioMEMS Heart Failure (HF) system, which monitors pulmonary arterial pressures in an outpatient setting, has been shown to reduce HF hospitalizations and improve functional status in patients with chronic heart failure. However, implantation is invasive and entails risk. Recent evidence suggests that a Cardiac Hemodynamic Artificial Intelligence System (CHAIS) can non-invasively identify when the mean pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (mPCWP) is elevated using ECG Lead-I signals. In this pilot study, we test whether CHAIS, without any retraining, can identify when the pulmonary artery diastolic pressure (PADP) – a correlate of the mPCWP – is elevated using ECG Lead-I signals obtained from a wearable ECG monitor.
Hypothesis
CHAIS can determine when CardioMEMS-derived PADP is elevated.
Methods
Ten adults (1 female, age 72 ± 11 years) with chronic HF and CardioMEMS implants were enrolled at Boston Medical Center (BMC, n=6, IRB H-44263) and Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH, n=4, IRB 2023P001291). Participants wore a single-lead ECG patch for up to 14 days. ECG data was segmented into 10 second windows, pre-processed, and input to CHAIS, which returned the probability of mPCWP > 18 mmHg. CHAIS probabilities were matched to CardioMEMS-derived PADP, producing N=76 contemporaneous pairs across all 10 patients.
Results
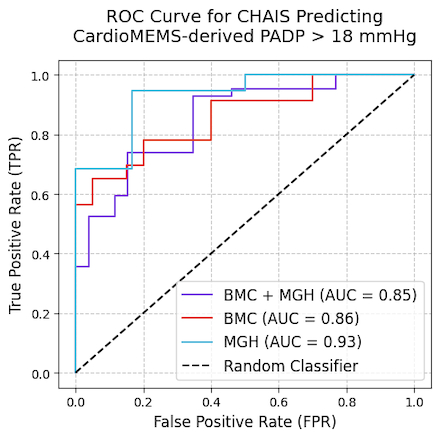
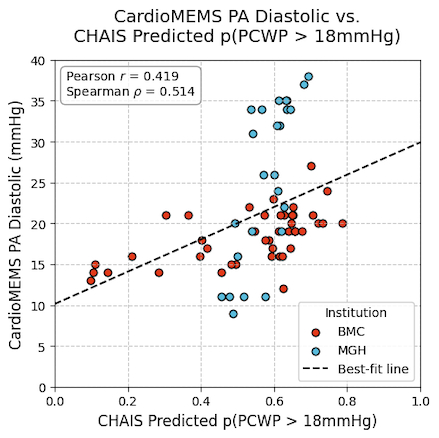
CHAIS showed strong discriminatory ability for identifying when CardioMEMS PADP > 18 mmHg, yielding an overall AUC of 0.82 (BMC 0.85; MGH 0.81). After excluding eight ECG signals with poor signal quality (resulting in N=68 ECG-PADP pairs), the overall AUC rose to 0.85 (BMC 0.86; MGH 0.93). Moreover, CHAIS output was positively associated with contemporaneous CardioMEMS PADP (Pearson r=0.36, Spearman ρ=0.45 with N=76 and Pearson r=0.42, ρ=0.51 with N=68; all p < 0.001). P-values were computed via permutation testing using 25,000 resamples.
Conclusion
This is the first study to demonstrate that a deep-learning model (CHAIS) can discriminate for elevated PADP using ECG signals obtained from a wearable ECG monitor. This non-invasive low-cost methodology for hemodynamic monitoring could expand HF surveillance, especially for patients who are ineligible to receive an invasive device. Fine-tuning CHAIS on wearable ECG data would improve its ability to non-invasively identify patients at risk for a HF exacerbation.
The implantable CardioMEMS Heart Failure (HF) system, which monitors pulmonary arterial pressures in an outpatient setting, has been shown to reduce HF hospitalizations and improve functional status in patients with chronic heart failure. However, implantation is invasive and entails risk. Recent evidence suggests that a Cardiac Hemodynamic Artificial Intelligence System (CHAIS) can non-invasively identify when the mean pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (mPCWP) is elevated using ECG Lead-I signals. In this pilot study, we test whether CHAIS, without any retraining, can identify when the pulmonary artery diastolic pressure (PADP) – a correlate of the mPCWP – is elevated using ECG Lead-I signals obtained from a wearable ECG monitor.
Hypothesis
CHAIS can determine when CardioMEMS-derived PADP is elevated.
Methods
Ten adults (1 female, age 72 ± 11 years) with chronic HF and CardioMEMS implants were enrolled at Boston Medical Center (BMC, n=6, IRB H-44263) and Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH, n=4, IRB 2023P001291). Participants wore a single-lead ECG patch for up to 14 days. ECG data was segmented into 10 second windows, pre-processed, and input to CHAIS, which returned the probability of mPCWP > 18 mmHg. CHAIS probabilities were matched to CardioMEMS-derived PADP, producing N=76 contemporaneous pairs across all 10 patients.
Results
CHAIS showed strong discriminatory ability for identifying when CardioMEMS PADP > 18 mmHg, yielding an overall AUC of 0.82 (BMC 0.85; MGH 0.81). After excluding eight ECG signals with poor signal quality (resulting in N=68 ECG-PADP pairs), the overall AUC rose to 0.85 (BMC 0.86; MGH 0.93). Moreover, CHAIS output was positively associated with contemporaneous CardioMEMS PADP (Pearson r=0.36, Spearman ρ=0.45 with N=76 and Pearson r=0.42, ρ=0.51 with N=68; all p < 0.001). P-values were computed via permutation testing using 25,000 resamples.
Conclusion
This is the first study to demonstrate that a deep-learning model (CHAIS) can discriminate for elevated PADP using ECG signals obtained from a wearable ECG monitor. This non-invasive low-cost methodology for hemodynamic monitoring could expand HF surveillance, especially for patients who are ineligible to receive an invasive device. Fine-tuning CHAIS on wearable ECG data would improve its ability to non-invasively identify patients at risk for a HF exacerbation.
More abstracts on this topic:
9-Year Longitudinal Assessment of the 12-lead Electrocardiogram of Volunteer Firefighters
Bae Alexander, Dzikowicz Dillon, Lai Chi-ju, Brunner Wendy, Krupa Nicole, Carey Mary, Tam Wai Cheong, Yu Yichen
A Deep Learning Topic Analysis Approach for Enhancing Risk Assessment in Heart Failure Using Unstructured Clinical NotesAdejumo Philip, Pedroso Aline, Khera Rohan