Final ID: MP1761
Pulmonary Hypertension is associated with higher In-Hospital Complications After WATCHMANTM Implantation - A Nationwide Analysis of 198,000 Patients
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction Left atrial appendage occlusion (WATCHMANTM) device has gained popularity in atrial fibrillation(AF) patients not suitable for systemic anticoagulation. Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is common in this population and may increase risks, particularly during transseptal puncture. The impact of PH on in-hospital outcomes following WATCHMANTM implantation remains undefined.
Methods We conducted a retrospective study using the 2016–2022 National Inpatient Sample. WATCHMANTM recipients were stratified by PH status via ICD-10-CM codes. Inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) was used on propensity scores (PS). Logistic regression was used to obtain adjusted odds ratios (aORs) for in-hospital primary (all-cause mortality) and secondary outcomes (including stroke, cardiac arrhythmias, acute kidney injury, procedural complications and major adverse cardiovascular events). P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
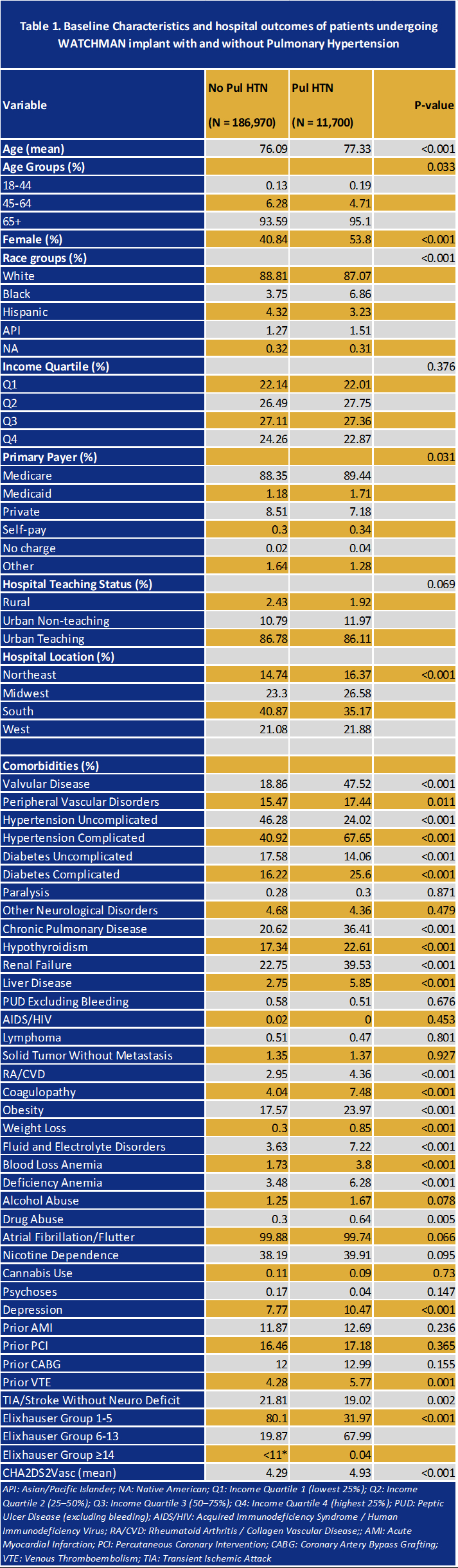
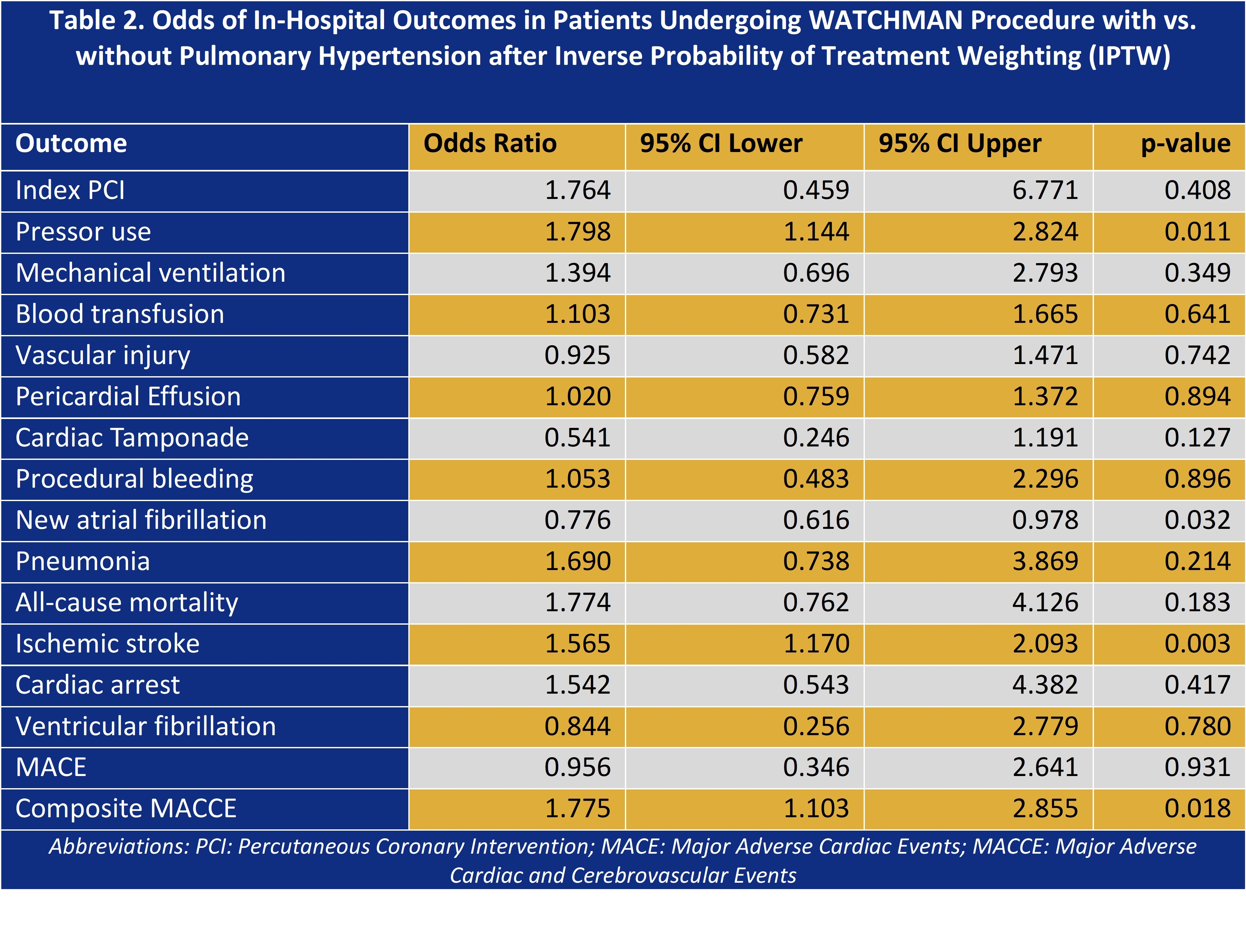
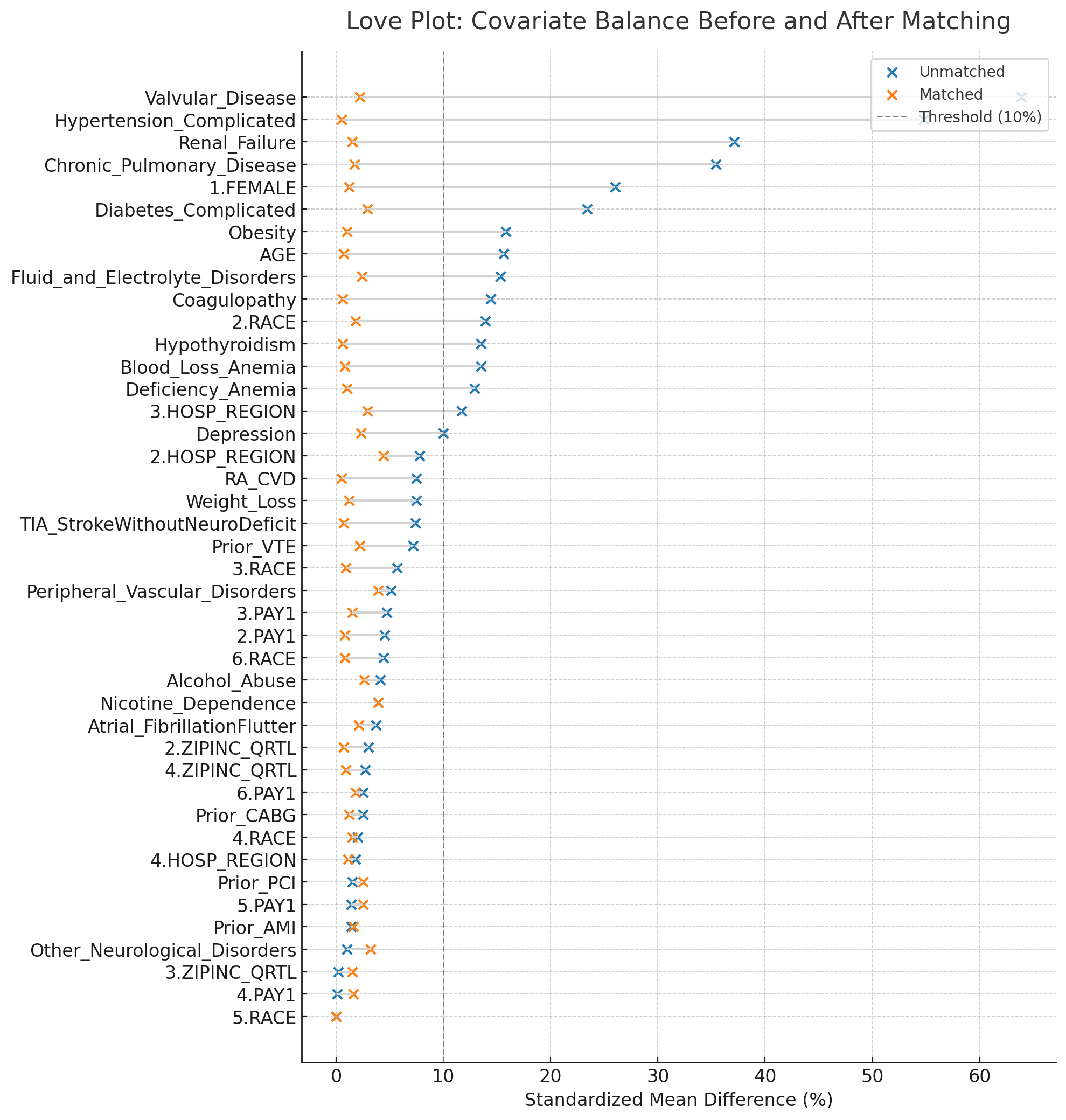
Results Of the 198,670 patients undergoing WATCHMANTM implantation, 6.26% had PH (mean age 77 years). In the unadjusted cohort, PH patients were more often female, Black, and had higher rates of comorbidity(Table 1). After PS and IPTW, all excellent covariate balance was achieved (Figure 1). On multivariate regression analysis, PH was independently associated with higher odds of all-cause mortality (ACM), aOR 2.74 acute kidney injury (AKI), aOR 1.30, pressor use, aOR 1.91, and composite MACCE, aOR 1.51. In IPTW analyses, PH groups had higher odds of pressor use (aOR 1.80; 1.14 - 2.82; P=0.01), ischemic stroke (aOR 1.56; 1.17 - 2.09; P=0.003 and composite MACCE (aOR 1.77; 1.10-2.85; P=0.02). However, mortality (aOR 1.77; 0.76-4.13; P=0.18), pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade did not reach significance . PH was however protective for new atrial fibrillation(AF) (aOR 0.78; 0.62-0.99; P=0.032) (Table 2).
Conclusion In this largest to-date inpatient analysis, PH was independently associated with significantly higher pressor use, stroke events and composite MACCE following WATCHMANTM implantation but had a protective effect from new onset AF. These findings warrant the need for close monitoring and hemodynamic optimization in PH patients prior to undergoing WATCHMANTM implantation.
Methods We conducted a retrospective study using the 2016–2022 National Inpatient Sample. WATCHMANTM recipients were stratified by PH status via ICD-10-CM codes. Inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) was used on propensity scores (PS). Logistic regression was used to obtain adjusted odds ratios (aORs) for in-hospital primary (all-cause mortality) and secondary outcomes (including stroke, cardiac arrhythmias, acute kidney injury, procedural complications and major adverse cardiovascular events). P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results Of the 198,670 patients undergoing WATCHMANTM implantation, 6.26% had PH (mean age 77 years). In the unadjusted cohort, PH patients were more often female, Black, and had higher rates of comorbidity(Table 1). After PS and IPTW, all excellent covariate balance was achieved (Figure 1). On multivariate regression analysis, PH was independently associated with higher odds of all-cause mortality (ACM), aOR 2.74 acute kidney injury (AKI), aOR 1.30, pressor use, aOR 1.91, and composite MACCE, aOR 1.51. In IPTW analyses, PH groups had higher odds of pressor use (aOR 1.80; 1.14 - 2.82; P=0.01), ischemic stroke (aOR 1.56; 1.17 - 2.09; P=0.003 and composite MACCE (aOR 1.77; 1.10-2.85; P=0.02). However, mortality (aOR 1.77; 0.76-4.13; P=0.18), pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade did not reach significance . PH was however protective for new atrial fibrillation(AF) (aOR 0.78; 0.62-0.99; P=0.032) (Table 2).
Conclusion In this largest to-date inpatient analysis, PH was independently associated with significantly higher pressor use, stroke events and composite MACCE following WATCHMANTM implantation but had a protective effect from new onset AF. These findings warrant the need for close monitoring and hemodynamic optimization in PH patients prior to undergoing WATCHMANTM implantation.
More abstracts on this topic:
A novel deep learning framework identified associated genes and Interpretable deep learning translation of GWAS findings for drug repurposing in Atrial Fibrillation
Tonegawa-kuji Reina, Xu Jielin, Guntupalli Suman, Barnard John, Chung Mina, Cheng Feixiong
A comparison of the efficacy of initial high energy versus initial low energy biphasic shocks for cardioversion of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter – a real-life experienceAlampoondi Venkataramanan Sai Vikram, Vunnam Ramarao, Voruganti Dinesh, Tsai Shane