Final ID: MP799
The Chinese Medicine Xinfuli Granules in Chronic Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Single-Center, Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Objective: As an integral component of complementary and alternative medicine systems, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has presented novel therapeutic possibilities for the clinical management of chronic heart failure (HF). This trial investigates the clinical efficacy and safety profile of Xinfuli Granules (XFLG), a Chinese herbal formulation, in patients diagnosed with HF with reduced ejection fraction.
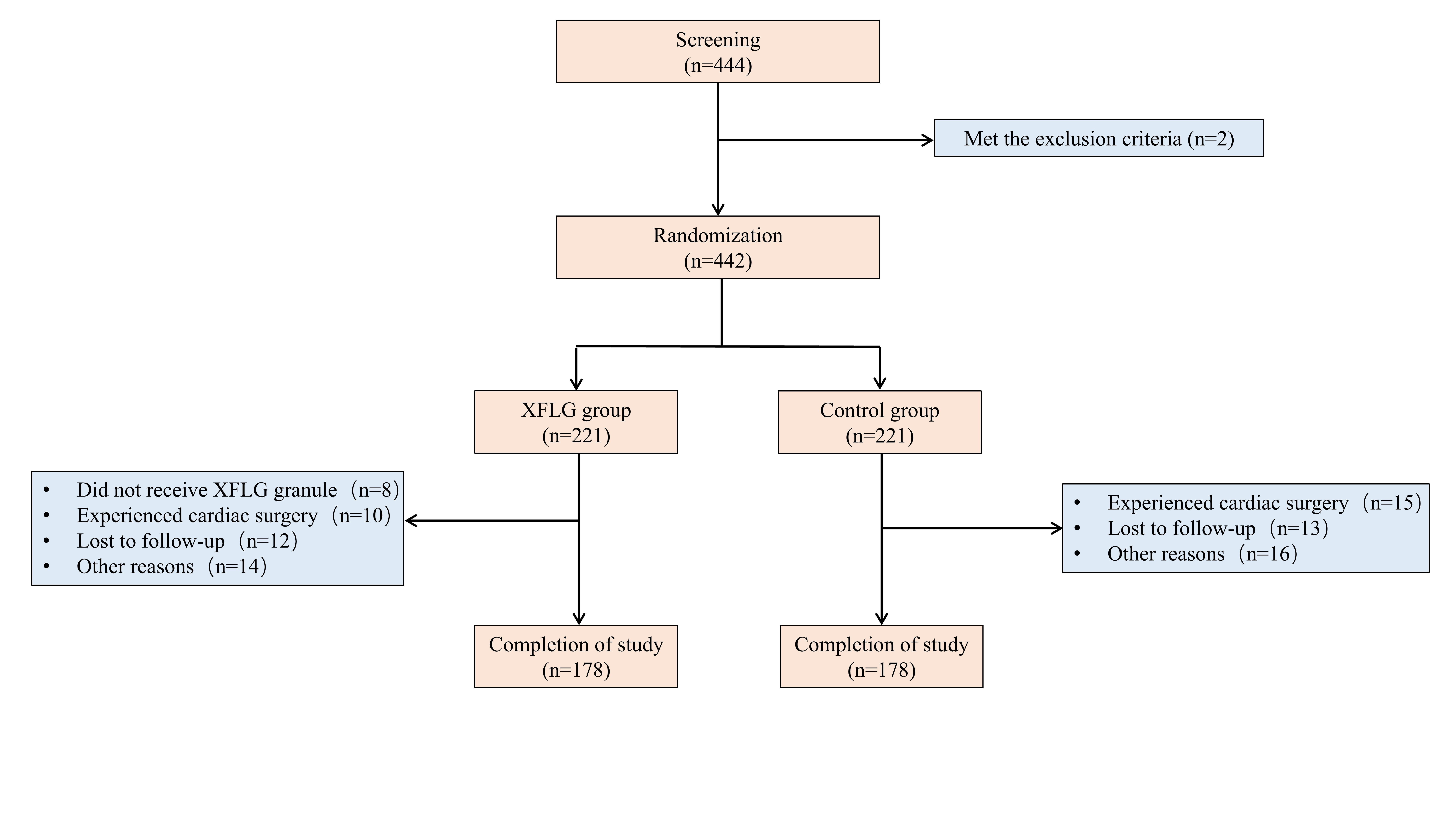
Methods: This single-center, randomized controlled trial enrolled 444 HF patients (NT-pro BNP ≥ 450 pg/mL and LVEF ≤ 45%) at Fuwai Hospital between October 2021 and December 2024. Participants were randomized (1:1) to receive either XFLG plus standard care or standard care alone. The primary endpoint was the composite of all-cause mortality and HF-related hospitalization. Secondary outcomes included changes in LVEF, NT-pro BNP, NYHA functional class, Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire (MLHFQ) score, TCM syndrome score, Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) and Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) scores.
Results: A total of 356 participants (178 per group) completed the trial, with median ages of 58 years (IQR: 50-67) in the XFLG group and 60 years (IQR: 52.75-69) in controls. At 12 weeks, the XFLG group demonstrated a significantly lower incidence of the primary composite outcome compared to the control group (11.24% vs. 18.54%; HR, 0.566; 95%CI: 0.325-0.988; P=0.042). In secondary endpoint analyses, the XFLG group demonstrated superior improvement in LVEF compared with controls (4% vs 3%; P=0.047). For NT-pro BNP levels, XFLG group showed significantly greater median absolute reductions (413 pg/mL vs 256 pg/mL; P=0.048) and relative reductions (42.02% vs 25.84%; P=0.01). NT-pro BNP reduction (>30%) was achieved by more patients in the XFLG arm (59.5% vs 44.1%; P=0.008). Significant advantages were observed in NYHA class improvement (efficacy rate: 53.8% vs 41.4%, P=0.031) and TCM syndrome scores (efficacy rate: 74.05% vs 37.24%, P<0.001). Quality of life assessments showed marked improvements in the MLHFQ, PHQ-9, and GAD-7 scores (differences: -15 vs -4; -2 vs 0; -1 vs 0 respectively; P<0.001), with comparable safety profiles between groups.
Conclusions: XFLG combined with standard HF therapy significantly reduced the risk of all-cause mortality and HF-related hospitalization composite outcome, improved cardiac function, and quality of life, alleviated depressive and anxiety states in HF patients, with a favorable safety profile.
Methods: This single-center, randomized controlled trial enrolled 444 HF patients (NT-pro BNP ≥ 450 pg/mL and LVEF ≤ 45%) at Fuwai Hospital between October 2021 and December 2024. Participants were randomized (1:1) to receive either XFLG plus standard care or standard care alone. The primary endpoint was the composite of all-cause mortality and HF-related hospitalization. Secondary outcomes included changes in LVEF, NT-pro BNP, NYHA functional class, Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire (MLHFQ) score, TCM syndrome score, Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) and Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) scores.
Results: A total of 356 participants (178 per group) completed the trial, with median ages of 58 years (IQR: 50-67) in the XFLG group and 60 years (IQR: 52.75-69) in controls. At 12 weeks, the XFLG group demonstrated a significantly lower incidence of the primary composite outcome compared to the control group (11.24% vs. 18.54%; HR, 0.566; 95%CI: 0.325-0.988; P=0.042). In secondary endpoint analyses, the XFLG group demonstrated superior improvement in LVEF compared with controls (4% vs 3%; P=0.047). For NT-pro BNP levels, XFLG group showed significantly greater median absolute reductions (413 pg/mL vs 256 pg/mL; P=0.048) and relative reductions (42.02% vs 25.84%; P=0.01). NT-pro BNP reduction (>30%) was achieved by more patients in the XFLG arm (59.5% vs 44.1%; P=0.008). Significant advantages were observed in NYHA class improvement (efficacy rate: 53.8% vs 41.4%, P=0.031) and TCM syndrome scores (efficacy rate: 74.05% vs 37.24%, P<0.001). Quality of life assessments showed marked improvements in the MLHFQ, PHQ-9, and GAD-7 scores (differences: -15 vs -4; -2 vs 0; -1 vs 0 respectively; P<0.001), with comparable safety profiles between groups.
Conclusions: XFLG combined with standard HF therapy significantly reduced the risk of all-cause mortality and HF-related hospitalization composite outcome, improved cardiac function, and quality of life, alleviated depressive and anxiety states in HF patients, with a favorable safety profile.
More abstracts on this topic:
Documentation Time, System Integration, and Workflow Challenges in Cardiology: A Clinician Survey
Tiosano Samuel, Elkin Peter, Koppel Ross
A novel Urocortin-2 analog COR-1167 corrects cardiac and renal dysfunction on top of Empagliflozin in a rat model of acute decompensated heart failureStephan Yohan, Corruble Clement, Charrier Lucie, Nicol Lionel, Kowala Mark, Ozoux Marie-laure, Lawson Francesca, Janiak Philip, Mulder Paul