Final ID: MP1487
Enhancing Lipid Management in Veterans: Integrating Whole Health Principles through the VALOR-QI Program and Veterans Health Administration
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality among U.S. Veterans, with uncontrolled low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) contributing to adverse outcomes. The Louis A. Johnson VA Medical Center (LAJVAMC) VA is one of 50 VA sites participating in a national quality improvement initiative called the VALOR QI: VA Lipid Optimization Reimagined Quality Improvement Project. VALOR-QI is a collaborative project between the VA and the American Heart Association (AHA) with the goal of positively impacting Veterans’ cardiovascular (CV) health. As part of the program, VA sites work with AHA QI Consultants to develop and deploy a local quality improvement plan to help overcome site specific barriers preventing Veterans from achieving optimal cholesterol levels.
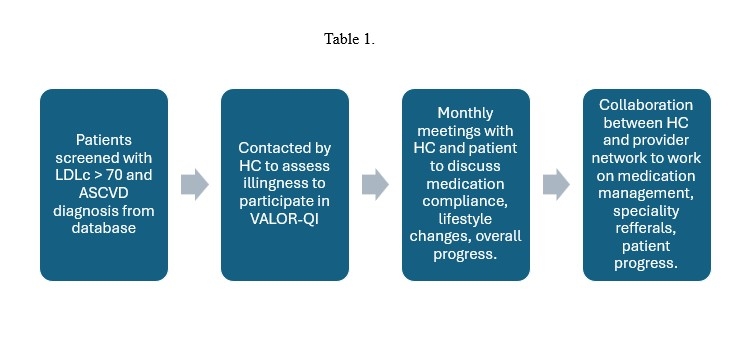
Veterans with ASCVD and baseline LDL-C >70 mg/dL were identified across primary care, cardiology, and pharmacy-led clinics. The intervention integrated health coaching, routine follow-up by a multidisciplinary provider network, and oversight from a clinical champion. Emphasis was placed on individualized care planning, lifestyle modification, and pharmacologic optimization (Table 1). The program launched in August 2023; interim data through May 2025 were analyzed.
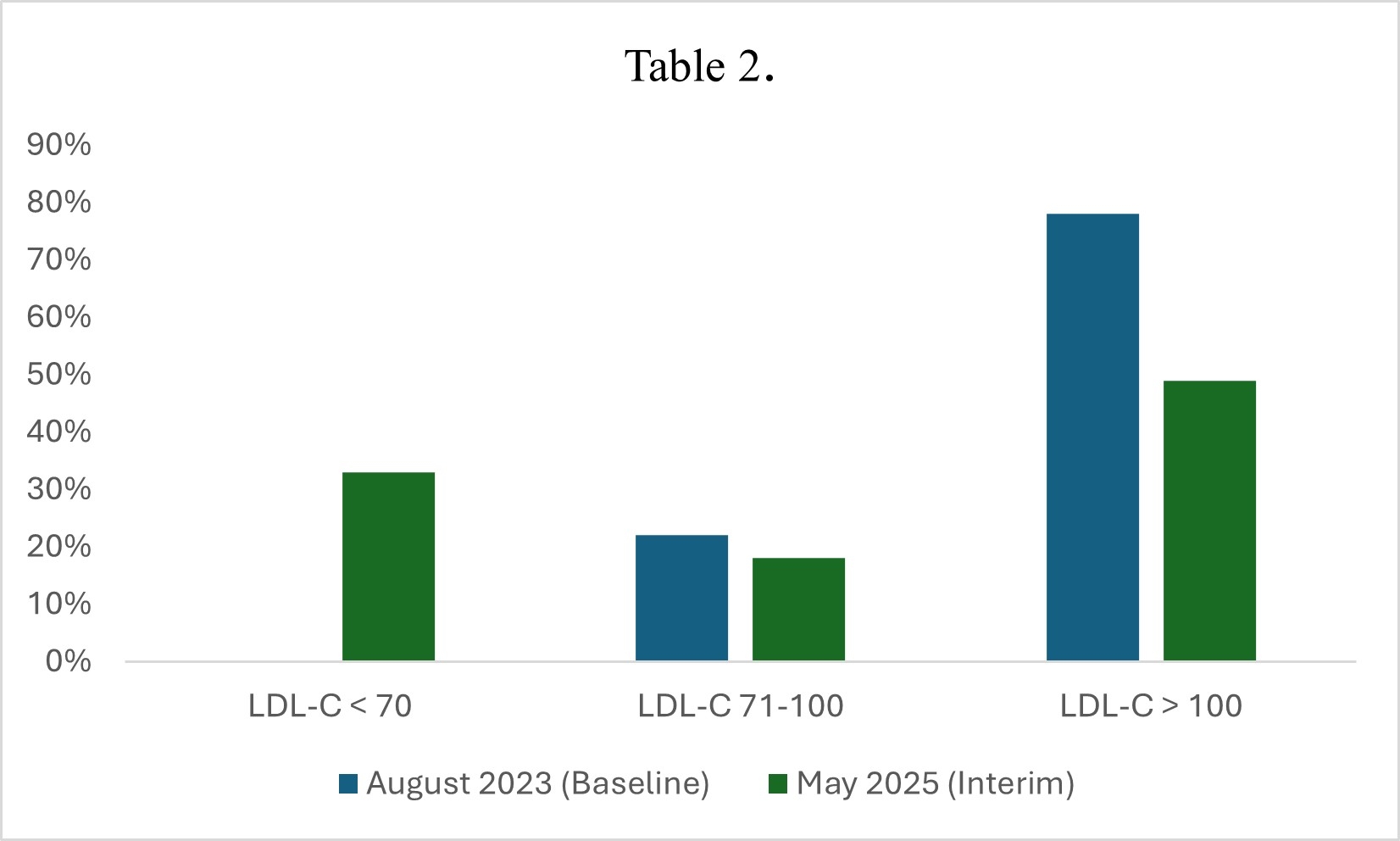
A total of 96 Veterans were included in the interim analysis. There was a total of 41 veterans in the baseline analysis. At baseline, August 2023, no patients had LDL-C levels below 70 mg/dL, and 78% had levels above 100 mg/dL. By May 2025, 33% had reached the target of LDL-C <70 mg/dL, and the proportion with levels >100 mg/dL dropped to 49% (Table 2). These results represent a substantial improvement in LDL-C control over the course of the intervention.
Our VALOR-QI strategy at LAJVAMC showed encouraging results, but it is premature to make final conclusions. Initial results demonstrate the clinical utility of incorporating a whole health approach into lipid management for high-risk veterans. By integrating behavioral support, shared decision-making, and multidisciplinary follow-up into routine care, this model produced meaningful early reductions in LDL-C. These findings underscore the potential for broader implementation of whole health strategies to optimize CV risk reduction. Future research will evaluate long-term outcomes, sustainability, and scalability of this approach within the LAJVAMC and beyond.
Veterans with ASCVD and baseline LDL-C >70 mg/dL were identified across primary care, cardiology, and pharmacy-led clinics. The intervention integrated health coaching, routine follow-up by a multidisciplinary provider network, and oversight from a clinical champion. Emphasis was placed on individualized care planning, lifestyle modification, and pharmacologic optimization (Table 1). The program launched in August 2023; interim data through May 2025 were analyzed.
A total of 96 Veterans were included in the interim analysis. There was a total of 41 veterans in the baseline analysis. At baseline, August 2023, no patients had LDL-C levels below 70 mg/dL, and 78% had levels above 100 mg/dL. By May 2025, 33% had reached the target of LDL-C <70 mg/dL, and the proportion with levels >100 mg/dL dropped to 49% (Table 2). These results represent a substantial improvement in LDL-C control over the course of the intervention.
Our VALOR-QI strategy at LAJVAMC showed encouraging results, but it is premature to make final conclusions. Initial results demonstrate the clinical utility of incorporating a whole health approach into lipid management for high-risk veterans. By integrating behavioral support, shared decision-making, and multidisciplinary follow-up into routine care, this model produced meaningful early reductions in LDL-C. These findings underscore the potential for broader implementation of whole health strategies to optimize CV risk reduction. Future research will evaluate long-term outcomes, sustainability, and scalability of this approach within the LAJVAMC and beyond.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Delayed Diagnosis of Anti-HMG-CoA Reductase Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy
Jadhav Reshma, Shekar Arush, Westenhaver Zack, Skandhan Amith
A Community-Based Intervention to Improve Cardiovascular Health Understanding in the Dallas-Fort Worth South Asian CommunityDeo Parminder, Rohatgi Anand, Sharma Parul, Sathyamoorthy Mohanakrishnan