Final ID: MP472
Social Determinants of Guideline-Directed Oral Anticoagulation Prescription in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation without Contraindications: Findings from the AHA Get With The Guidelines–Atrial Fibrillation Registry
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Oral anticoagulants (OAC) are critically important to avoid preventable strokes in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib). However, OAC prescription for AFib in real-world practice may be influenced by social determinants of health (SDOH).
Aims: We aimed to (1) uncover institutional and patient SDOH associated with failure to prescribe guideline-directed OAC, and (2) to develop an SDOH-based scoring system to predict failure to prescribe OAC.
Methods: This study analyzed a nationwide AFib registry of 249 hospitals in the US—the AHA Get With The Guidelines-Atrial Fibrillation registry. We included adult patients hospitalized for AFib with class I indication for and no contraindications to OAC. Using a logistic regression model, we identified patient and institutional SDOH of failure to prescribe OAC and their odds ratios (ORs) adjusted for the other SDOH. Next, we developed a machine learning (ML)-based prediction model in a training dataset (half of the cohort) and examined the relative contribution of each SDOH. We compared the risk of failure to prescribe OAC in an independent test dataset (the remaining half) using the ML-derived prediction score at the Youden index threshold. We examined the predictive impact of adding institutional SDOH to patient SDOH and utilizing an ML algorithm.
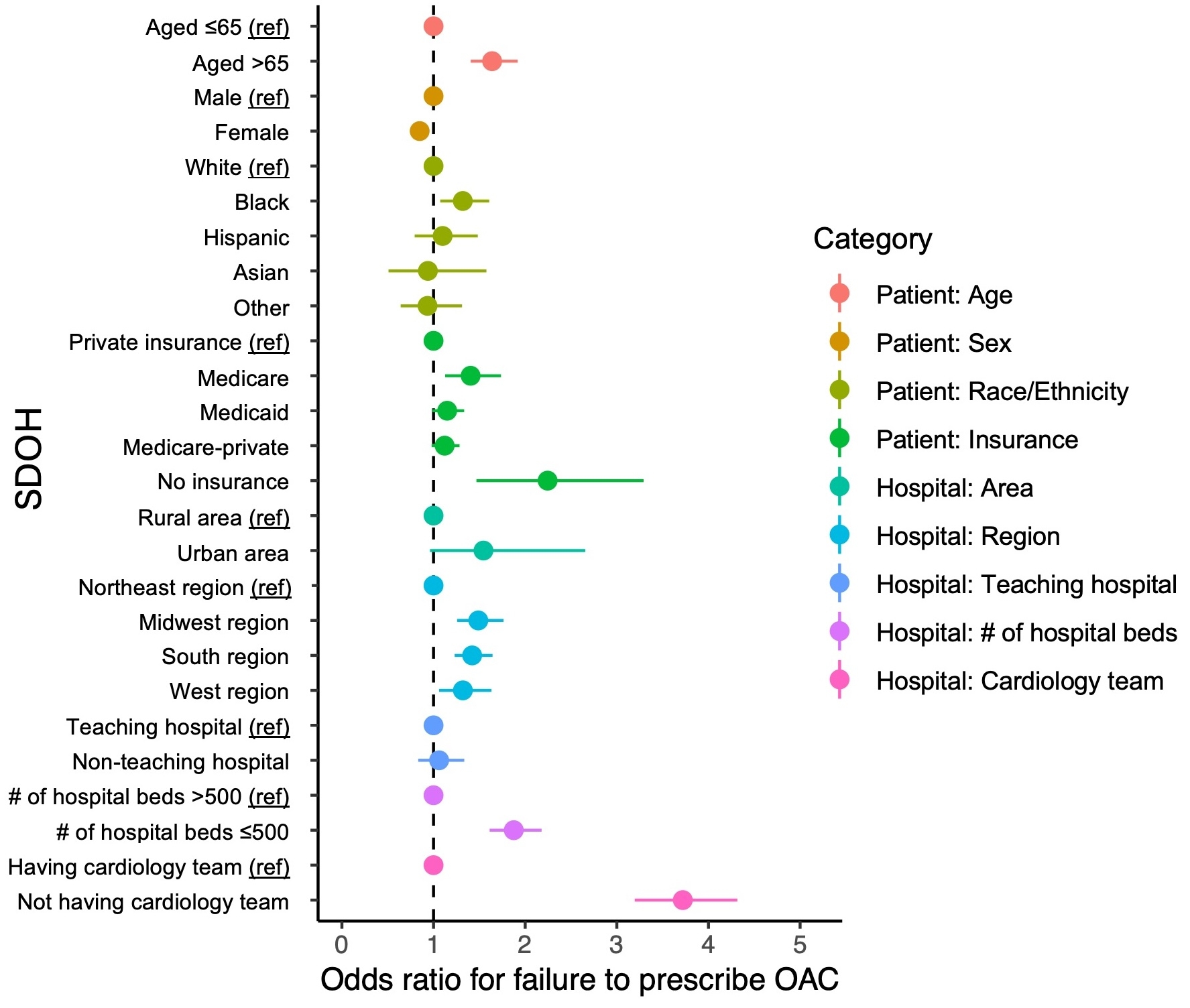
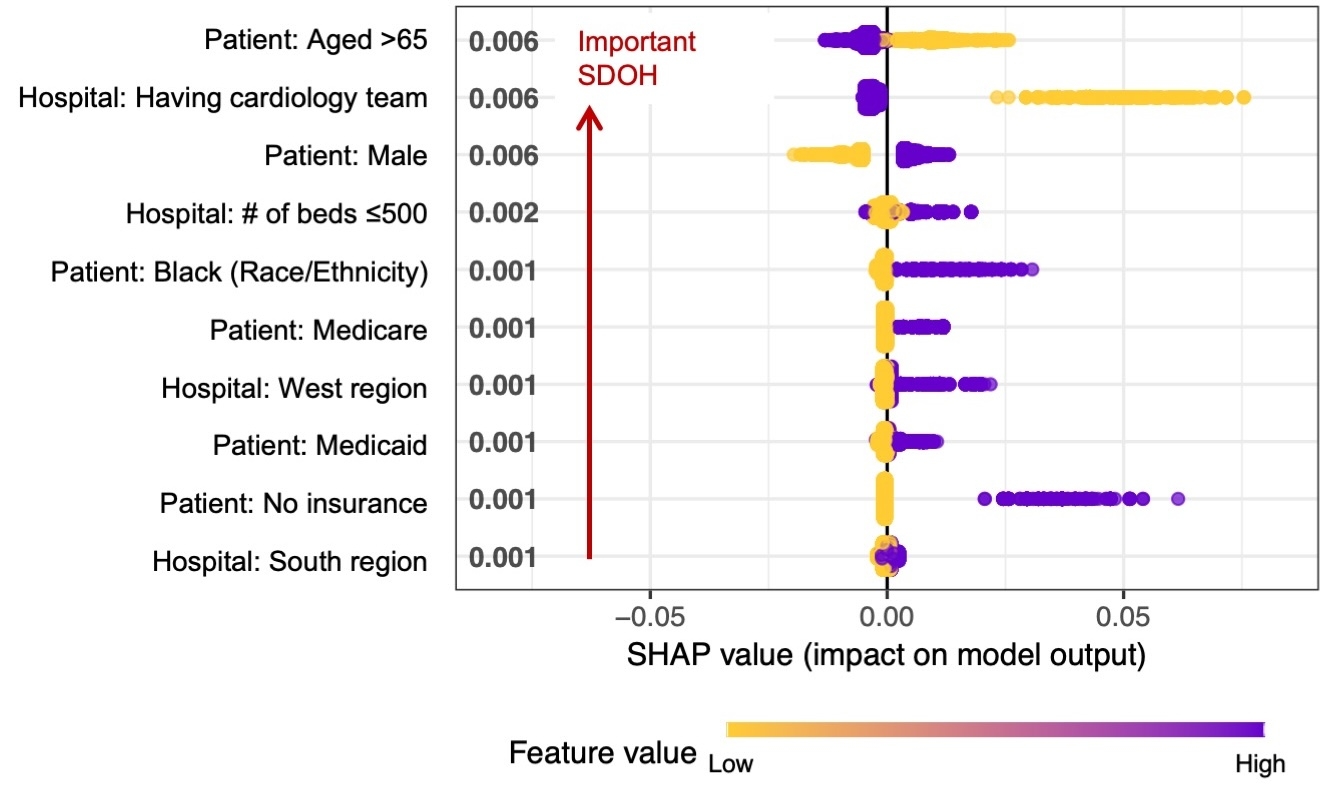
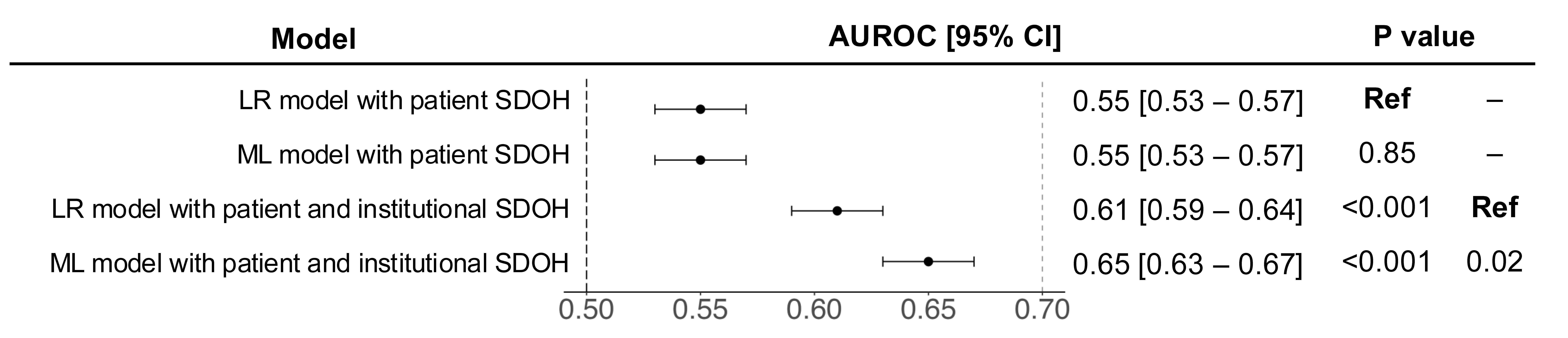
Results: Among the 68,628 patients with AFib at high risk of stroke and no contraindications to OAC, 1,345 (2.0%) patients did not receive guideline-directed OAC prescription despite class I indication. The OAC prescription was influenced by both institutional (e.g., hospital region, hospital size, the absence of a cardiology team) and patient SDOH (e.g., sex, insurance) (Figures 1 and 2). The absence of a cardiology team was the most important predictor (adjusted OR [95% CI], 3.72 [3.20–4.32]; Figure 1). Patients with the higher-than-cutoff prediction score had higher risk of failure to prescribe OAC than those with the lower-than-cutoff prediction score (OR [95% CI], 3.11 [2.67–3.63]). Adding institutional SDOH to patient SDOH and utilizing an ML algorithm both improved model discrimination for identifying patients at higher risk of failure to prescribe OAC (Figure 3).
Conclusions: We identified both institutional and patient SDOH of guideline-directed OAC prescription failure in patients with AFib without contraindications. We further developed and validated a SDOH-based ML scoring system to predict failure to prescribe OAC.
Aims: We aimed to (1) uncover institutional and patient SDOH associated with failure to prescribe guideline-directed OAC, and (2) to develop an SDOH-based scoring system to predict failure to prescribe OAC.
Methods: This study analyzed a nationwide AFib registry of 249 hospitals in the US—the AHA Get With The Guidelines-Atrial Fibrillation registry. We included adult patients hospitalized for AFib with class I indication for and no contraindications to OAC. Using a logistic regression model, we identified patient and institutional SDOH of failure to prescribe OAC and their odds ratios (ORs) adjusted for the other SDOH. Next, we developed a machine learning (ML)-based prediction model in a training dataset (half of the cohort) and examined the relative contribution of each SDOH. We compared the risk of failure to prescribe OAC in an independent test dataset (the remaining half) using the ML-derived prediction score at the Youden index threshold. We examined the predictive impact of adding institutional SDOH to patient SDOH and utilizing an ML algorithm.
Results: Among the 68,628 patients with AFib at high risk of stroke and no contraindications to OAC, 1,345 (2.0%) patients did not receive guideline-directed OAC prescription despite class I indication. The OAC prescription was influenced by both institutional (e.g., hospital region, hospital size, the absence of a cardiology team) and patient SDOH (e.g., sex, insurance) (Figures 1 and 2). The absence of a cardiology team was the most important predictor (adjusted OR [95% CI], 3.72 [3.20–4.32]; Figure 1). Patients with the higher-than-cutoff prediction score had higher risk of failure to prescribe OAC than those with the lower-than-cutoff prediction score (OR [95% CI], 3.11 [2.67–3.63]). Adding institutional SDOH to patient SDOH and utilizing an ML algorithm both improved model discrimination for identifying patients at higher risk of failure to prescribe OAC (Figure 3).
Conclusions: We identified both institutional and patient SDOH of guideline-directed OAC prescription failure in patients with AFib without contraindications. We further developed and validated a SDOH-based ML scoring system to predict failure to prescribe OAC.
More abstracts on this topic:
10-Year Trends in Last Known Well to Arrival Time in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients: 2014-2023
A Large Animal Model of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
Ferrone Nicholas, Sanmartin Maria, O'hara Joseph, Jimenez Jean, Ferrone Sophia, Wang Jason, Katz Jeffrey, Sanelli Pina
A Large Animal Model of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
Mostafizi Pouria, Goldman Steven, Moukabary Talal, Lefkowitz Eli, Ref Jacob, Daugherty Sherry, Grijalva Adrian, Cook Kyle Eric, Chinyere Ike, Lancaster Jordan, Koevary Jen