Final ID: Sa2021
Systemic Inflammation Is Associated with Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Established Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease and Stage 3-4 Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the United States, affecting over 26 million people. Further, patients with ASCVD and co-existing chronic kidney disease (CKD) have a greater risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) than patients without CKD. Clinical trials have documented a residual risk of MACE linked to systemic inflammation after guideline directed medical therapy. This study aims to examine the risk of MACE among patients with established ASCVD and co-existing stage 3-4 CKD with vs. without systemic inflammation.
Methods
This retrospective study identified patients from the Komodo Healthcare Map (Jan 1, 2016 – Jun 30, 2024) based on diagnosis and procedure codes in medical claims. CKD and its stage were determined from medical claims or laboratory estimated glomerular filtration rate. Systemic inflammation was defined using high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) testing: with systemic inflammation, ≥1 hsCRP value of 2-10 mg/L; without systemic inflammation, all hsCRP values <2 mg/L. HsCRP test results >10 mg/L or conducted during acute illness were excluded. The study endpoints were revised 3-point MACE (non-fatal myocardial infarction [MI], non-fatal stroke or all-cause mortality) and 2-point MACE (non-fatal MI or non-fatal stroke). Survival analysis and Cox proportional hazard models were used.
Results
Among 6,351 patients with ASCVD + stage 3-4 CKD and a qualifying hsCRP, 53% were of female sex, and the mean age was 71 years. Of the eligible patients, 3,600 (57%) had systemic inflammation. Patients with systemic inflammation had a higher mean comorbidity index (1.1 vs. 0.9) and greater prevalence of hypertension (74% vs. 68%), type 2 diabetes (41% vs. 34%), and obesity (20% vs. 13%) than those without systemic inflammation.
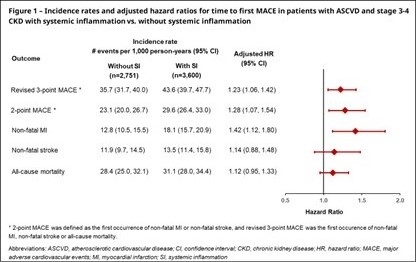
After adjusting for baseline characteristics, systemic inflammation was associated with a 23% increase in the risk of revised 3-point MACE (HR 1.23, 95% CI 1.06-1.42) and a 28% increase in the risk of 2-point MACE (HR 1.28, 95% CI 1.07-1.54). Specifically, systemic inflammation significantly increased the risk of non-fatal MI, but not non-fatal stroke or all-cause mortality (Figure 1).
Conclusion
Systemic inflammation was associated with an increased risk of MACE in patients with ASCVD + stage 3-4 CKD. Clinical trials are needed to evaluate the potential of anti-inflammatory therapy to reduce the residual inflammation risk in this population.
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the United States, affecting over 26 million people. Further, patients with ASCVD and co-existing chronic kidney disease (CKD) have a greater risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) than patients without CKD. Clinical trials have documented a residual risk of MACE linked to systemic inflammation after guideline directed medical therapy. This study aims to examine the risk of MACE among patients with established ASCVD and co-existing stage 3-4 CKD with vs. without systemic inflammation.
Methods
This retrospective study identified patients from the Komodo Healthcare Map (Jan 1, 2016 – Jun 30, 2024) based on diagnosis and procedure codes in medical claims. CKD and its stage were determined from medical claims or laboratory estimated glomerular filtration rate. Systemic inflammation was defined using high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) testing: with systemic inflammation, ≥1 hsCRP value of 2-10 mg/L; without systemic inflammation, all hsCRP values <2 mg/L. HsCRP test results >10 mg/L or conducted during acute illness were excluded. The study endpoints were revised 3-point MACE (non-fatal myocardial infarction [MI], non-fatal stroke or all-cause mortality) and 2-point MACE (non-fatal MI or non-fatal stroke). Survival analysis and Cox proportional hazard models were used.
Results
Among 6,351 patients with ASCVD + stage 3-4 CKD and a qualifying hsCRP, 53% were of female sex, and the mean age was 71 years. Of the eligible patients, 3,600 (57%) had systemic inflammation. Patients with systemic inflammation had a higher mean comorbidity index (1.1 vs. 0.9) and greater prevalence of hypertension (74% vs. 68%), type 2 diabetes (41% vs. 34%), and obesity (20% vs. 13%) than those without systemic inflammation.
After adjusting for baseline characteristics, systemic inflammation was associated with a 23% increase in the risk of revised 3-point MACE (HR 1.23, 95% CI 1.06-1.42) and a 28% increase in the risk of 2-point MACE (HR 1.28, 95% CI 1.07-1.54). Specifically, systemic inflammation significantly increased the risk of non-fatal MI, but not non-fatal stroke or all-cause mortality (Figure 1).
Conclusion
Systemic inflammation was associated with an increased risk of MACE in patients with ASCVD + stage 3-4 CKD. Clinical trials are needed to evaluate the potential of anti-inflammatory therapy to reduce the residual inflammation risk in this population.
More abstracts on this topic:
Age-standardized trends in Incidence Rates of Noncommunicable diseases among Adults Aged 30 to 79 in Senegal from 2000 to 2019
Gaye Ngone, Ka Mame, Kyem Damaris, Jobe Modou, Sattler Elisabeth, Gary-webb Tiffany, Gaye Bamba
A major effect of aprocitentan on albuminuria in patients with resistant hypertensionSchlaich Markus, Bakris George, Flack John, Gimona Alberto, Narkiewicz Krzysztof, Sassi-sayadi Mouna, Wang Jiguang, Weber Michael