Final ID: LBP21
Acellular Tissue Engineered Vessels as Conduits for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Vascular conduit for coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) can be limited due to the availability and quality of autologous vein. A readily-available and biological conduit having good durability, patency, and biocompatibility would fill an important unmet need in CABG surgery. Here we evaluated the function and host remodeling of a small diameter Acellular Tissue Engineered Vessel (sdATEV) in a large primate model of CABG.
Methods: ATEVs comprised of human vascular extracellular matrix proteins, with an inner diameter of 3.5 mm and length of 20 cm, were grown and decellularized using a biomanufacturing platform. Five adult baboons (age 6-10 years, 33.0 ± 2.5 kg) underwent CABG from the aorta to the right coronary artery (RCA), and were followed for 6 months. Conduit blood flow and pulsatility index (PI) were measured at implant and explant while patency and cardiac function was assessed at 1, 3, and 6 months using computed tomography angiography (CTA). Immunohistochemistry and high-definition spatial transcriptomics were performed to characterize host recellularization and remodeling of the sdATEVs.
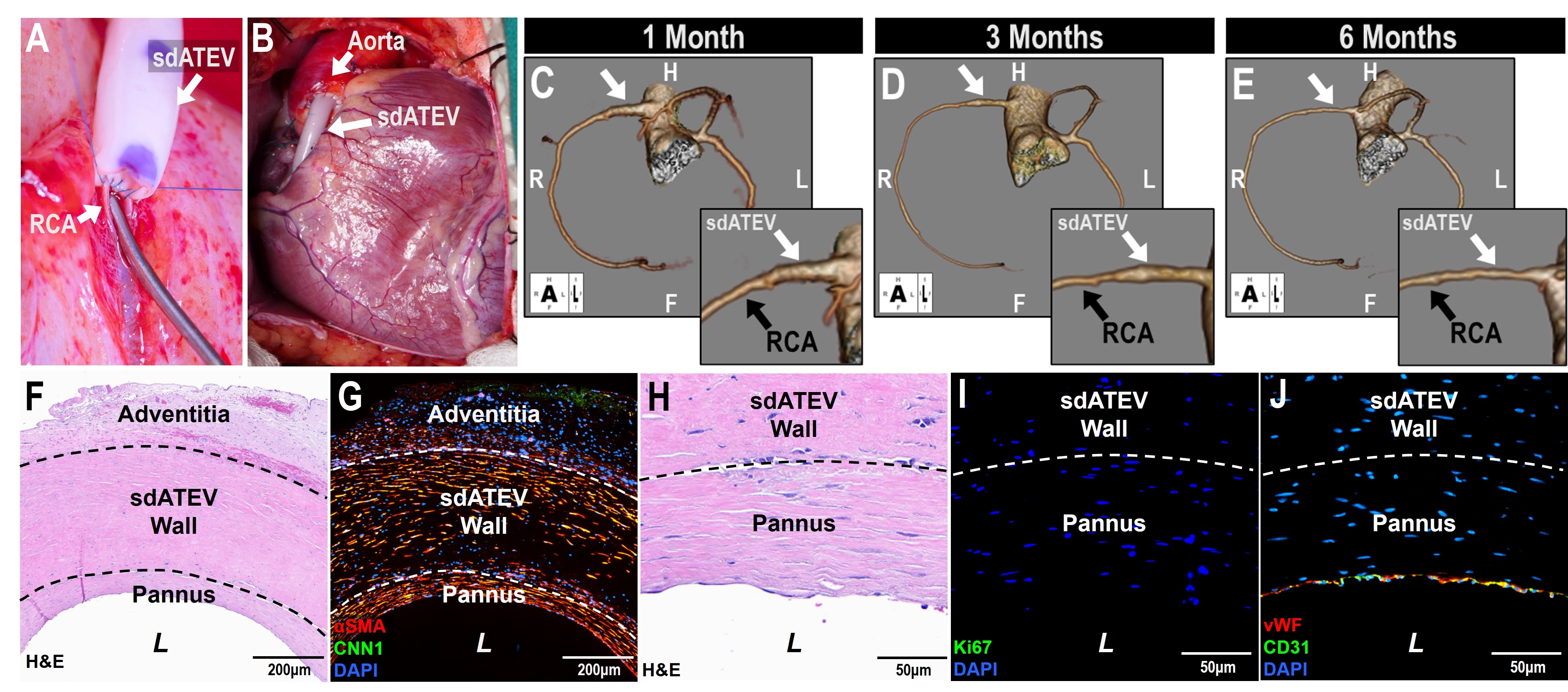
Results: All sdATEV CABG conduits remained patent with no evidence of dilatation, stenosis, or mechanical failure. Conduit blood flow was 32.4 ± 10.3 mL/min (PI: 1.7 ± 0.9) at implant and 34.8 ± 13.5 mL/min (PI: 1.2 ± 0.0) at explant. Luminal diameter of the sdATEV remodeled from 3.5 mm at implant to 2.3 ± 0.5 mm distally at 6 months, more similar to the 1.7 mm diameter of the RCA. Explant histology identified pannus ingrowth from native arteries as the mechanism for the progressive size matching of the sdATEV. At 6 months, pannus smooth muscle cells were mostly quiescent (Ki67-), which correlated with low localized TGFβ1 expression, and high endothelial nitric oxide synthase and prostacyclin synthase expression from adjacent luminal endothelial cells. In addition, the sdATEV wall was repopulated with cells expressing smooth muscle cell markers and surrounded by a neoadventitia containing capillaries lined with CD31+/vWF+ endothelial cells.
Conclusion: The sdATEV is an off-the-shelf conduit that exhibited both robust mechanical performance and adaptive host remodeling in a baboon CABG model.
Methods: ATEVs comprised of human vascular extracellular matrix proteins, with an inner diameter of 3.5 mm and length of 20 cm, were grown and decellularized using a biomanufacturing platform. Five adult baboons (age 6-10 years, 33.0 ± 2.5 kg) underwent CABG from the aorta to the right coronary artery (RCA), and were followed for 6 months. Conduit blood flow and pulsatility index (PI) were measured at implant and explant while patency and cardiac function was assessed at 1, 3, and 6 months using computed tomography angiography (CTA). Immunohistochemistry and high-definition spatial transcriptomics were performed to characterize host recellularization and remodeling of the sdATEVs.
Results: All sdATEV CABG conduits remained patent with no evidence of dilatation, stenosis, or mechanical failure. Conduit blood flow was 32.4 ± 10.3 mL/min (PI: 1.7 ± 0.9) at implant and 34.8 ± 13.5 mL/min (PI: 1.2 ± 0.0) at explant. Luminal diameter of the sdATEV remodeled from 3.5 mm at implant to 2.3 ± 0.5 mm distally at 6 months, more similar to the 1.7 mm diameter of the RCA. Explant histology identified pannus ingrowth from native arteries as the mechanism for the progressive size matching of the sdATEV. At 6 months, pannus smooth muscle cells were mostly quiescent (Ki67-), which correlated with low localized TGFβ1 expression, and high endothelial nitric oxide synthase and prostacyclin synthase expression from adjacent luminal endothelial cells. In addition, the sdATEV wall was repopulated with cells expressing smooth muscle cell markers and surrounded by a neoadventitia containing capillaries lined with CD31+/vWF+ endothelial cells.
Conclusion: The sdATEV is an off-the-shelf conduit that exhibited both robust mechanical performance and adaptive host remodeling in a baboon CABG model.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Pilot Study of Post-Discharge Atrial Fibrillation Using a Novel Mobile Electrocardiography Monitoring Device
Clickable Extracellular Vesicles for Localized Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair
Iribarne Alexander, Kramer Robert, Moquete Ellen, Hupf Jonathan, Duncan Prezley, Mihelis Efstathia, Borger Michael, Muir Andrew, Starnes Vaughn, Edegran Albin, Fenton Kathleen, Patel Nirav, Taddei-peters Wendy, Moskowitz Alan, Ogara Patrick, Gelijns Annetine, Alexander John, Gillinov A, Bagiella Emilia, D'alessandro David, Dimaio John, Bhavnani Sanjeev, Badhwar Vinay, Sengupta Partho, Johnson Linda, Gajewska-dendek Elzbieta
Clickable Extracellular Vesicles for Localized Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair
Marini Ande, Otto Ellen, Li Bo, Weinbaum Justin, Ren Xi, Campbell Phil, Curci John, Vorp David