Final ID: Mo1049
Comparison of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention vs Coronary Artery Bypass Graft for Left Main Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Prior Cerebrovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
The previous literature reports similar cardiovascular (CV) benefits for either percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) in patients with left main coronary artery disease (LMCAD). However, limited data exist on the influence of prior cerebrovascular disease (CEVD) in such patients. Thus, our aim is to compare the CV outcomes in patients with LMCAD and prior CEVD, undergoing either PCI or CABG.
Methods:
A comprehensive search of electronic databases, PubMed, SCOPUS, and Cochrane Central was conducted from their inception till May 2024. Outcomes of interest included all-cause mortality, major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE), Myocardial Infarction (MI), and risk of stroke in patients undergoing either PCI or CABG for LMCAD. Data were pooled and analyzed using a random effects model and presented as hazard ratios (HR) along with their 95% confidence intervals (CI). Heterogeneity was quantified using the I(2) index.
Results:
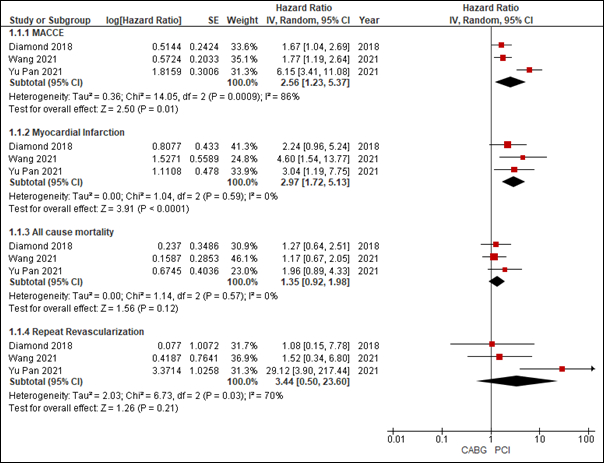
We included three studies in our analysis (n = 5,732). Our analysis demonstrated that in patients with prior CEVD, PCI lead to significantly increased risk of MACCE (HR = 2.56, 95% CI:[1.23, 5.37], p = 0.01] and MI (HR = 2.97, 95% CI: [1.72, 5.13], p< 0.01). While an elevated risk of all-cause mortality (HR: 1.35, 95% CI: [0.92, 1.98]; p = 0.12) and repeat stroke (HR: 1.67, 95% CI: [0.81, 3.42], p = 0.16) was observed, these were comparable across procedures. Similarly, an elevated but comparable risk of repeat revascularization was observed between the two procedures (HR: 3.44, 95% CI: [0.50, 23.60]; p = 0.21).
Conclusion:
Our results show that PCI significantly elevates the risk of MACCE and MI in patients with prior CEVD compared to CABG. However, risks of all-cause mortality, repeat stroke, and revascularization were comparable. The increased risk of adverse CV events in CEVD patients may be due to co-morbidities like hypertension, smoking, diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, renal insufficiency, inflammation, and hypercoagulability. We recommend including prior CEVD in pre-operative assessments for revascularization and developing novel strategies for patients with LMCAD and prior CEVD.
The previous literature reports similar cardiovascular (CV) benefits for either percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) in patients with left main coronary artery disease (LMCAD). However, limited data exist on the influence of prior cerebrovascular disease (CEVD) in such patients. Thus, our aim is to compare the CV outcomes in patients with LMCAD and prior CEVD, undergoing either PCI or CABG.
Methods:
A comprehensive search of electronic databases, PubMed, SCOPUS, and Cochrane Central was conducted from their inception till May 2024. Outcomes of interest included all-cause mortality, major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE), Myocardial Infarction (MI), and risk of stroke in patients undergoing either PCI or CABG for LMCAD. Data were pooled and analyzed using a random effects model and presented as hazard ratios (HR) along with their 95% confidence intervals (CI). Heterogeneity was quantified using the I(2) index.
Results:
We included three studies in our analysis (n = 5,732). Our analysis demonstrated that in patients with prior CEVD, PCI lead to significantly increased risk of MACCE (HR = 2.56, 95% CI:[1.23, 5.37], p = 0.01] and MI (HR = 2.97, 95% CI: [1.72, 5.13], p< 0.01). While an elevated risk of all-cause mortality (HR: 1.35, 95% CI: [0.92, 1.98]; p = 0.12) and repeat stroke (HR: 1.67, 95% CI: [0.81, 3.42], p = 0.16) was observed, these were comparable across procedures. Similarly, an elevated but comparable risk of repeat revascularization was observed between the two procedures (HR: 3.44, 95% CI: [0.50, 23.60]; p = 0.21).
Conclusion:
Our results show that PCI significantly elevates the risk of MACCE and MI in patients with prior CEVD compared to CABG. However, risks of all-cause mortality, repeat stroke, and revascularization were comparable. The increased risk of adverse CV events in CEVD patients may be due to co-morbidities like hypertension, smoking, diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, renal insufficiency, inflammation, and hypercoagulability. We recommend including prior CEVD in pre-operative assessments for revascularization and developing novel strategies for patients with LMCAD and prior CEVD.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Phase 2 Study Evaluating the Effects of Mivelsiran, an Investigational RNA Interference Therapeutic, on Hemorrhagic and Nonhemorrhagic Manifestations of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy
Greenberg Steven, Parikh Neal, Lee Jin-moo, Van Etten Ellis, Van Osch Matthias, Klijn Catharina, Sostelly Alexandre, Goteti Sasikiran, Sepehrband Farshid, Avbersek Andreja, Deering Robert
1-Year Outcomes After Cardioversion With and Without Anticoagulation in Patients With Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion: A Propensity-Matched AnalysisThangjui Sittinun, Trongtorsak Angkawipa, Kewcharoen Jakrin, Thyagaturu Harshith, Watson Hangyu, Mensah Samuel, Balla Sudarshan, Navaravong Leenhapong