Final ID: Sa1114
Clinical Usefulness of Pulmonary Embolism Response Team (PERT) among Pulmonary Embolism Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Despite the advancement in management, pulmonary embolism has challenges in its early diagnosis and initiation of the therapies. To counter this situation, the concept of a Pulmonary Embolism Response Team (PERT), a multidisciplinary team comprised of different healthcare providers, emerged in 2012 as an initiative to optimize care for pulmonary embolism patients. This approach shown to be effective in improving the early and effective management of PE patients, thus improving the clinical recovery in some studies yet remain inclusive in other studies. Given the trending PERT acceptance situation in PE management, we performed this systematic review and meta-analysis to analyze the clinical impact of the PERT approach on PE patient management.
Methods:
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis from pertinent studies published until May 2024 using PubMed, Embase, and Scopus databases comparing PERT vs standard approach for PE management. This study is registered with PROSPERO and data analysis was performed using the RevMan Web.
Results:
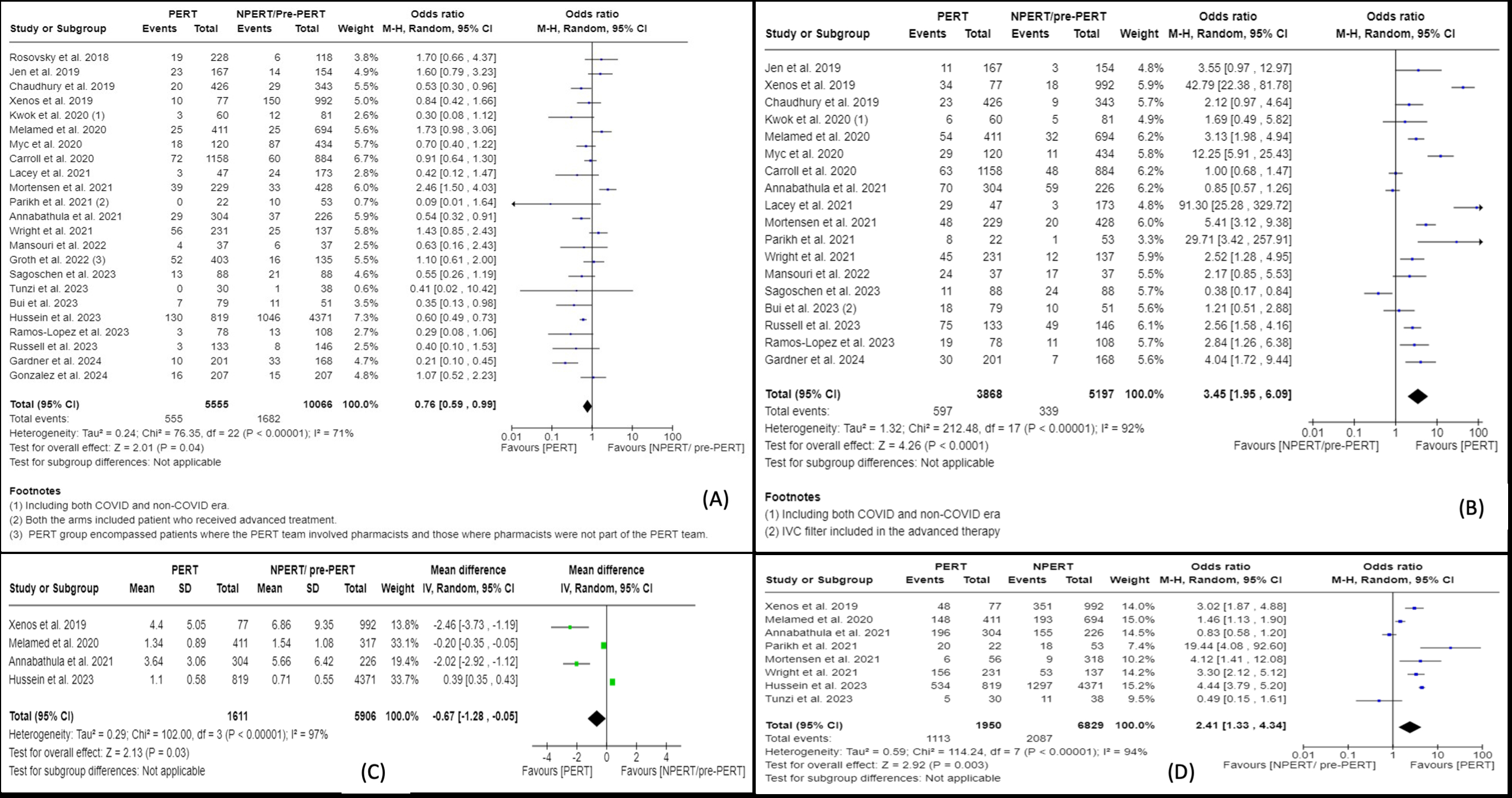
In this analysis, 15,621 PE patients who managed via the PERT or standard approach were included in 23 studies. The use of PERT was associated with significantly lower odds of short-term mortality (OR: 0.76, CI 0.59 to 0.99), and higher odds of utilization of advanced treatment strategy (OR: 3.45, CI 1.95 to 6.09). Additionally, PERT was associated with favorably lower odds of major bleeding (OR: 0.60, CI 0.34 to 1.05) and early achievement of therapeutic anticoagulation (MD: -1.39, CI -5.32 to 2.54). Despite higher odds of ICU admission, the length of stay in ICU was significantly lower in the PERT group (MD: -0.67, CI -1.28 to -0.05).
Conclusion:
Based on this meta-analysis, the PERT approach for PE management significantly increases the chances of utilization of advanced PE management strategies, thus shortening the ICU stays, and reducing mortality risk. Additionally, it could potentially reduce the major bleeding risk. PERT should be in the focus as one of the standards of care for area PE management.
Despite the advancement in management, pulmonary embolism has challenges in its early diagnosis and initiation of the therapies. To counter this situation, the concept of a Pulmonary Embolism Response Team (PERT), a multidisciplinary team comprised of different healthcare providers, emerged in 2012 as an initiative to optimize care for pulmonary embolism patients. This approach shown to be effective in improving the early and effective management of PE patients, thus improving the clinical recovery in some studies yet remain inclusive in other studies. Given the trending PERT acceptance situation in PE management, we performed this systematic review and meta-analysis to analyze the clinical impact of the PERT approach on PE patient management.
Methods:
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis from pertinent studies published until May 2024 using PubMed, Embase, and Scopus databases comparing PERT vs standard approach for PE management. This study is registered with PROSPERO and data analysis was performed using the RevMan Web.
Results:
In this analysis, 15,621 PE patients who managed via the PERT or standard approach were included in 23 studies. The use of PERT was associated with significantly lower odds of short-term mortality (OR: 0.76, CI 0.59 to 0.99), and higher odds of utilization of advanced treatment strategy (OR: 3.45, CI 1.95 to 6.09). Additionally, PERT was associated with favorably lower odds of major bleeding (OR: 0.60, CI 0.34 to 1.05) and early achievement of therapeutic anticoagulation (MD: -1.39, CI -5.32 to 2.54). Despite higher odds of ICU admission, the length of stay in ICU was significantly lower in the PERT group (MD: -0.67, CI -1.28 to -0.05).
Conclusion:
Based on this meta-analysis, the PERT approach for PE management significantly increases the chances of utilization of advanced PE management strategies, thus shortening the ICU stays, and reducing mortality risk. Additionally, it could potentially reduce the major bleeding risk. PERT should be in the focus as one of the standards of care for area PE management.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adherence to Guideline-Directed Oral Anticoagulant Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter Admitted in a Tertiary Private Hospital: A Retrospective Study
Wong Jasmine, Carandang Frances, Segundo Luigi Pierre
Among Older Adults With Atrial Fibrillation, First Anticoagulant Prescription Is Not Associated with Reduced Hazard of Ischemic Stroke but Is Associated with Increased Hazard of Major Bleeding: A Nationwide StudyLusk Jay, Li Fan, Mac Grory Brian, Nalawade Vinit, Wilson Lauren, Yarnell Stephanie, Song Ailin, Schrag Matthew, Poli Sven, Hammill Bradley, Xian Ying