Final ID: Mo4137
Outcome of Impella vs. Other Temporary Mechanical Circulatory Support Devices in Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients with Cardiogenic Shock: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Cardiogenic shock (CS) affects up to 10% of hospitalized patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI), leading to over 30% mortality despite treatment. In patients with AMI-CS refractory to vasopressors and inotropes, temporary mechanical circulatory support (MCS) devices have been used to provide hemodynamic support. Recently, Impella demonstrated significant mortality benefit in AMI-CS in the DanGer shock trial. However, it has not demonstrated such benefit over other devices, such as IABP and ECMO in other trials (ISAR-Shock, IMPRESS in Severe Shock, IMPELLA-STIC). Here we performed this network meta-analysis of all available studies including the DanGer shock trial comparing Impella with other MCS devices in AMI-CS patients.
Method:
We performed a Bayesian network meta-analysis to synthesize direct and indirect evidence from relevant studies published until April 2024 using PubMed, Embase, and Scopus databases comparing Impella with other strategies for treating AMI-CS patients. The primary outcome was a short-term mortality defined as in-hospital or 30-day mortality. This study is registered with PROSPERO, and data analysis was performed using the “BUGSnet” package in R.
Result:
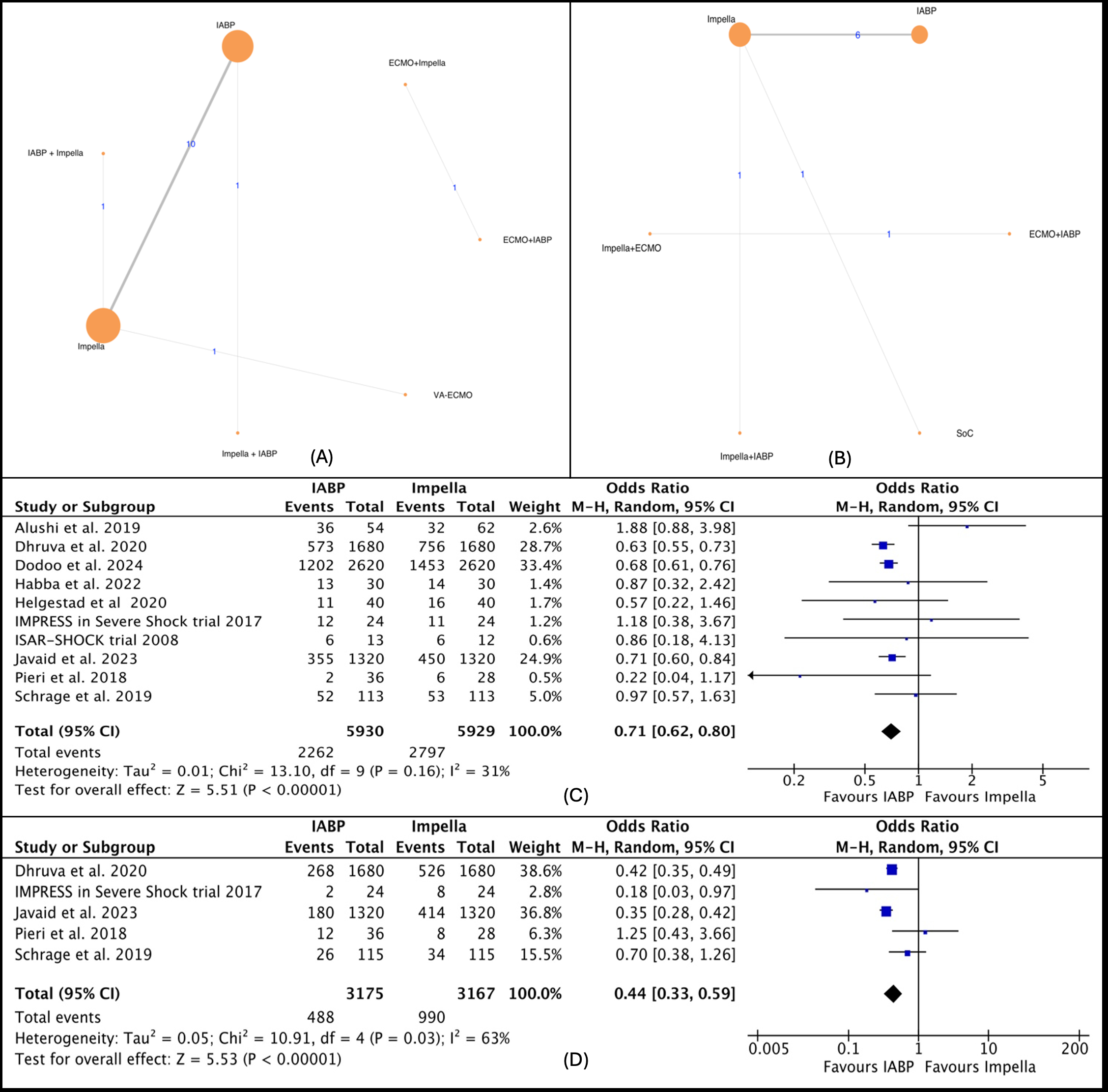
Out of 7,211 studies, 17 were deemed eligible. These included five RCTs and 12 observational studies, encompassing 16,654 patients with AMI-CS assigned to 3 different MSC interventions: Impella, IABP, and ECMO in 9 different combinations or alone. Based on SUCRA value, IABP was the most effective strategy in regard to short-term mortality (73.46), long-term mortality (75.59), major bleeding (66.4), renal replacement therapy (73.02); Impella along with IABP for stroke (95.24), ischemic stroke (99.68), device-related bleeding (90.22), MI (94.38); ECMO for hemolysis (91.66); standard of care for peripheral ischemic complications (88.66), sepsis (78.71). In sub-analysis using the RCTs only, Impella was ranked best for short-term mortality (74.53).
Conclusion:
Based on the findings of this network meta-analysis, IABP could potentially provide both short-term and long-term mortality benefits, as well as reduce the risk of bleeding. Meanwhile, combining it with Impella could potentially reduce the risk of cerebral ischemia.
Cardiogenic shock (CS) affects up to 10% of hospitalized patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI), leading to over 30% mortality despite treatment. In patients with AMI-CS refractory to vasopressors and inotropes, temporary mechanical circulatory support (MCS) devices have been used to provide hemodynamic support. Recently, Impella demonstrated significant mortality benefit in AMI-CS in the DanGer shock trial. However, it has not demonstrated such benefit over other devices, such as IABP and ECMO in other trials (ISAR-Shock, IMPRESS in Severe Shock, IMPELLA-STIC). Here we performed this network meta-analysis of all available studies including the DanGer shock trial comparing Impella with other MCS devices in AMI-CS patients.
Method:
We performed a Bayesian network meta-analysis to synthesize direct and indirect evidence from relevant studies published until April 2024 using PubMed, Embase, and Scopus databases comparing Impella with other strategies for treating AMI-CS patients. The primary outcome was a short-term mortality defined as in-hospital or 30-day mortality. This study is registered with PROSPERO, and data analysis was performed using the “BUGSnet” package in R.
Result:
Out of 7,211 studies, 17 were deemed eligible. These included five RCTs and 12 observational studies, encompassing 16,654 patients with AMI-CS assigned to 3 different MSC interventions: Impella, IABP, and ECMO in 9 different combinations or alone. Based on SUCRA value, IABP was the most effective strategy in regard to short-term mortality (73.46), long-term mortality (75.59), major bleeding (66.4), renal replacement therapy (73.02); Impella along with IABP for stroke (95.24), ischemic stroke (99.68), device-related bleeding (90.22), MI (94.38); ECMO for hemolysis (91.66); standard of care for peripheral ischemic complications (88.66), sepsis (78.71). In sub-analysis using the RCTs only, Impella was ranked best for short-term mortality (74.53).
Conclusion:
Based on the findings of this network meta-analysis, IABP could potentially provide both short-term and long-term mortality benefits, as well as reduce the risk of bleeding. Meanwhile, combining it with Impella could potentially reduce the risk of cerebral ischemia.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Deep Learning Approach for Prediction of Right Heart Failure After Left Ventricular Assist Device Implantation using Pulmonary Artery Pressure Tracings
Lamicq Melissa, Buchanan Cole, Lateef Azalfa, Atteya Miriam, Houston Brian, Tedford Ryan, Wehbe Ramsey
Abbreviated Ticagrelor-Based Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisHarmouch Wissam, Elbadawi Ayman, Thakker Ravi, Khalid Umair, Khalife Wissam, Kleiman Neal, Rangasetty Umamahesh, Kayani Waleed, Jneid Hani, Al Hemyari Bashar