Final ID: Mo2040
Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Chronic Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in Adult Congenital Heart Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: SGLT2 inhibitors have demonstrated efficacy in reducing cardiovascular death and hospitalization and are recommended as first-line therapy for hear failure (HF) in adults due to acquired heart diseases. Our study aimed to assess the safety, tolerability, and outcomes of HF patients with adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) treated with SGLT2 inhibitors.
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive search of three major databases—PubMed, Scopus, and Embase—and collected articles on the use of SGLT2 inhibitors for HF in ACHD patients who were already receiving angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEi), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB), angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors (ARNI), beta-blockers (BB), and mineralocorticoid antagonists (MRA). We excluded articles related to acute decompensated HF and HF with preserved ejection fraction. The primary outcome was the change in NYHA functional class (FC). Secondary outcomes included changes in B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro-BNP (NT-proBNP) levels, as well as body weight. Additionally, we evaluated the safety and tolerability of SGLT2 inhibitors in ACHD HF patients. A pooled effect size was calculated based on mean differences (MD) or log odds ratio (LogOR).
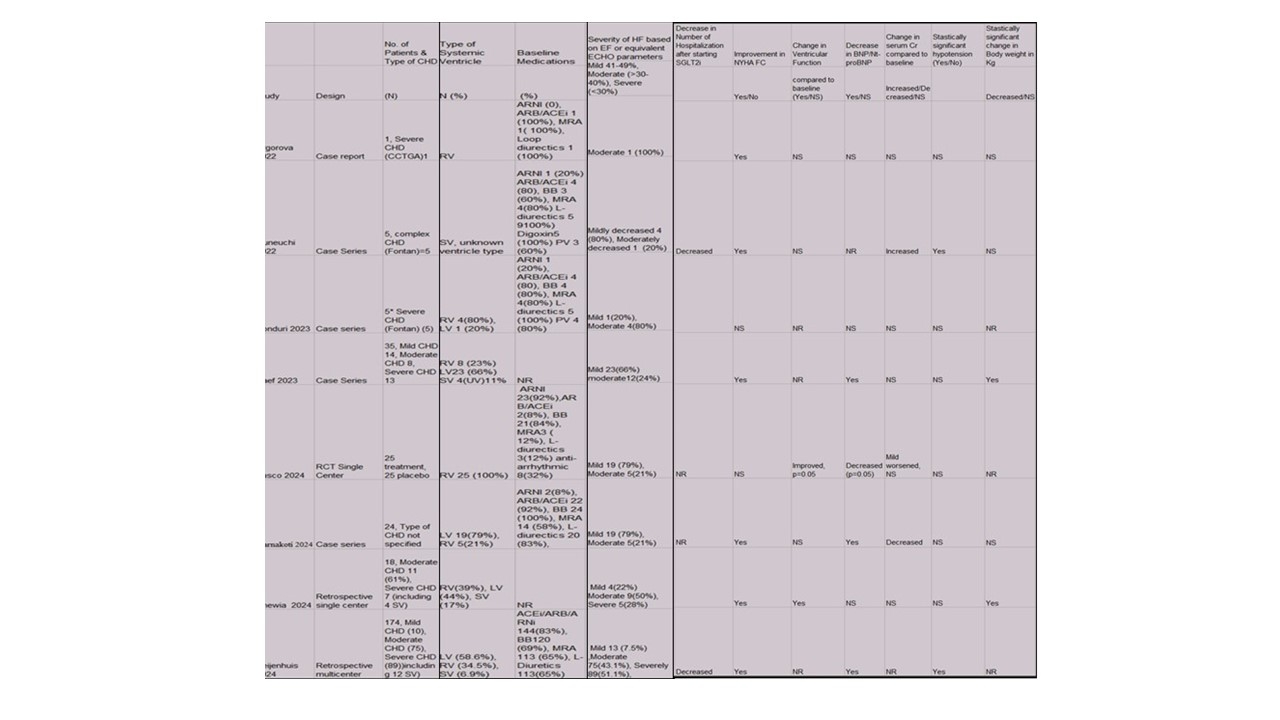
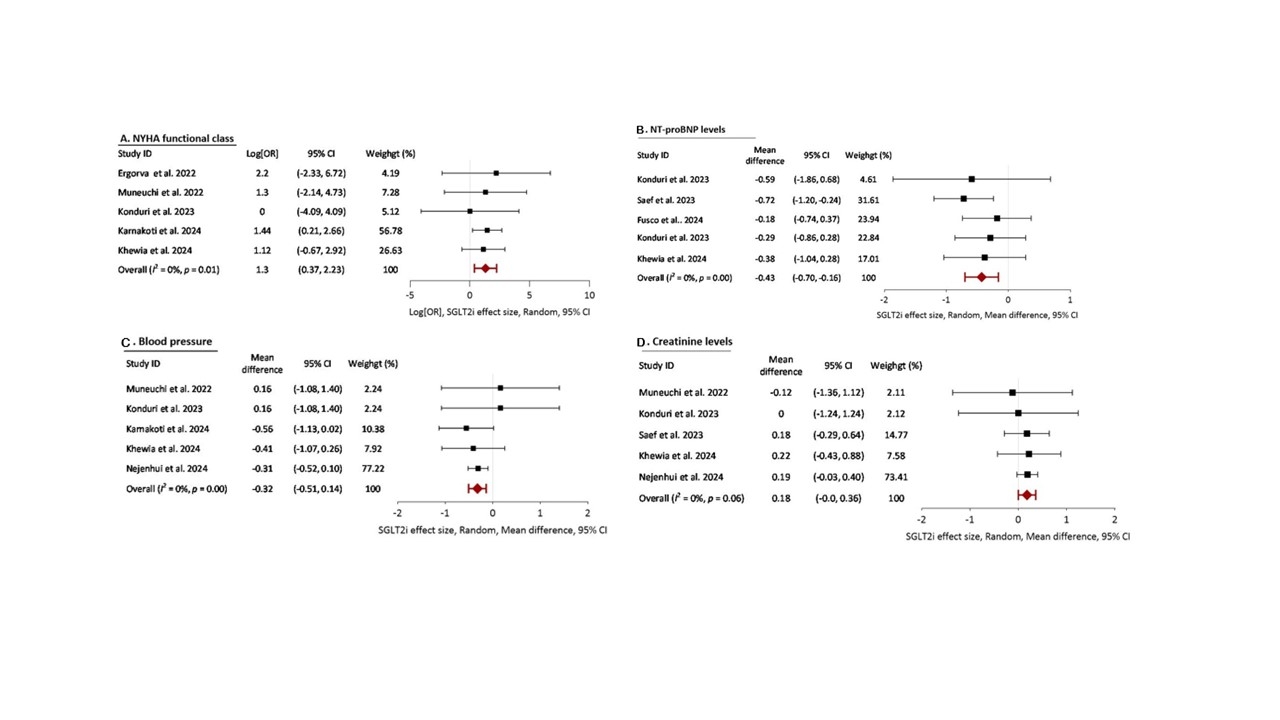
Results: Our meta-analysis included 9 studies with a total of 287 patients aged 19 to 67 (median 37.5 years) (Table). When SGLT2 inhibitors were added to combined therapies, they significantly improved NYHA FC (LogOR: 1.3, 95% CI: 0.37–2.23, p=0.01) (Figure 1A), decreased NT-proBNP (MD -0.43, 95% CI -0.70 to -0.16, p=0.00) (Figure 1B), were associated with a reduction in systolic blood pressure (MD = -0.32, 95% CI: -0.51 to 0.14, p=0.00) (Figure 1C), and led to an elevation of creatinine (Cr) levels (MD = 0.18, 95% CI -0.0 to 0.36, p=0.06) (Figure 1D). Only 4 patients experienced urinary tract infections (UTIs), and none had hypoglycemia or ketoacidosis.
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis demonstrates that SGLT2 inhibitors improve NYHA FC, decrease NT-proBNP, and are well-tolerated with safety features similar to adult HF clinical trials when added to combination HF therapies including ACEI/ARB/ARNI, BB and MRA. Future prospective studies are needed to assess long-term clinical outcomes in ACHD patients with HF.
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive search of three major databases—PubMed, Scopus, and Embase—and collected articles on the use of SGLT2 inhibitors for HF in ACHD patients who were already receiving angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEi), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB), angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors (ARNI), beta-blockers (BB), and mineralocorticoid antagonists (MRA). We excluded articles related to acute decompensated HF and HF with preserved ejection fraction. The primary outcome was the change in NYHA functional class (FC). Secondary outcomes included changes in B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro-BNP (NT-proBNP) levels, as well as body weight. Additionally, we evaluated the safety and tolerability of SGLT2 inhibitors in ACHD HF patients. A pooled effect size was calculated based on mean differences (MD) or log odds ratio (LogOR).
Results: Our meta-analysis included 9 studies with a total of 287 patients aged 19 to 67 (median 37.5 years) (Table). When SGLT2 inhibitors were added to combined therapies, they significantly improved NYHA FC (LogOR: 1.3, 95% CI: 0.37–2.23, p=0.01) (Figure 1A), decreased NT-proBNP (MD -0.43, 95% CI -0.70 to -0.16, p=0.00) (Figure 1B), were associated with a reduction in systolic blood pressure (MD = -0.32, 95% CI: -0.51 to 0.14, p=0.00) (Figure 1C), and led to an elevation of creatinine (Cr) levels (MD = 0.18, 95% CI -0.0 to 0.36, p=0.06) (Figure 1D). Only 4 patients experienced urinary tract infections (UTIs), and none had hypoglycemia or ketoacidosis.
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis demonstrates that SGLT2 inhibitors improve NYHA FC, decrease NT-proBNP, and are well-tolerated with safety features similar to adult HF clinical trials when added to combination HF therapies including ACEI/ARB/ARNI, BB and MRA. Future prospective studies are needed to assess long-term clinical outcomes in ACHD patients with HF.
More abstracts on this topic:
Abatacept Drug-Induced Loeffler Endocarditis: A Manifestation of Hypereosinophilic Syndrome
Sweeting Alexander, Atalay Michael, Agarwal Saurabh, Hulten Edward, Patel Yash
A Growing Burden of Electronic Medical Record Messages in ACHD CareDailey Schwartz Andrew, Alegria Jorge