Final ID: Mo2045
Prognostic Value of Peak Circulatory Power Versus Peak Oxygen Uptake in Patients with Repaired Tetralogy of Fallot
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) is an essential tool for identifying early signs of clinical deterioration in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD), primarily through the measurement of peak oxygen uptake (VO2). Circulatory power (CircP), a less commonly evaluated variable derived from CPET, has been proposed as a surrogate for cardiac power. However, there is limited direct comparative data on CircP to inform prognostic assessment in these patients.
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the prognostic value of peak CircP in individuals with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot (rToF) compared to peak VO2.
Methods: Forty-seven rToF patients underwent CPET between August 2014 and April 2018 at Memorial Healthcare System, Hollywood, Florida. The Cox proportional hazards model assessed CPET variables associated with major adverse cardiac events (MACEs), adjusting for covariates. Optimal cut-off values for CircP and peak VO2 were derived from the receiver operating curve (ROC). Kaplan-Meier survival plots illustrated the prognostic significance of CircP and peak VO2.
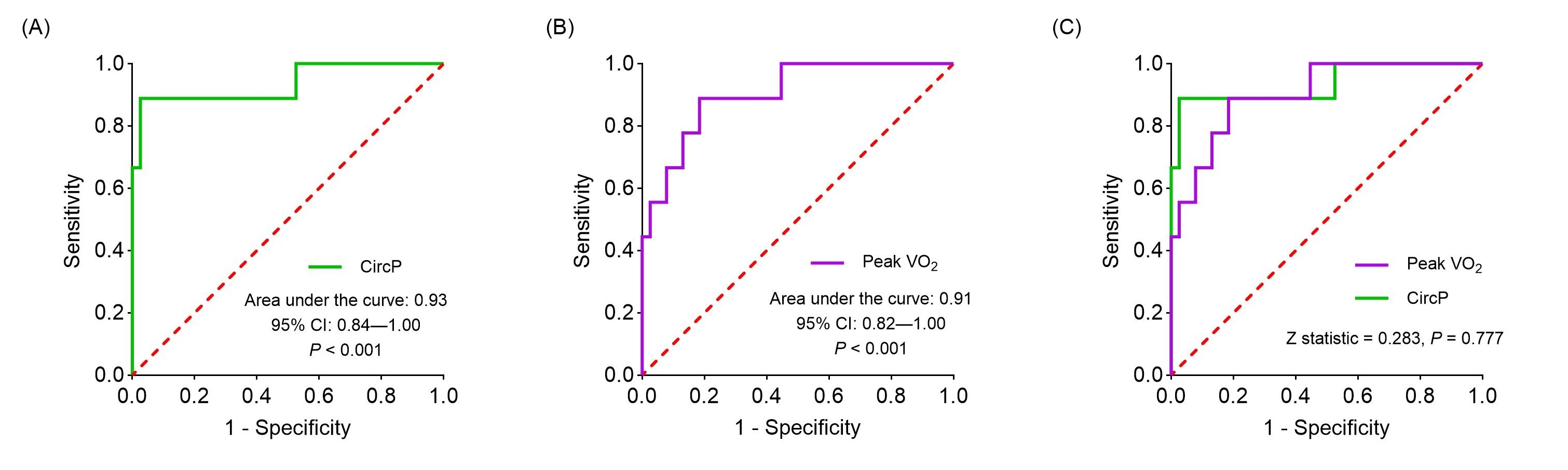
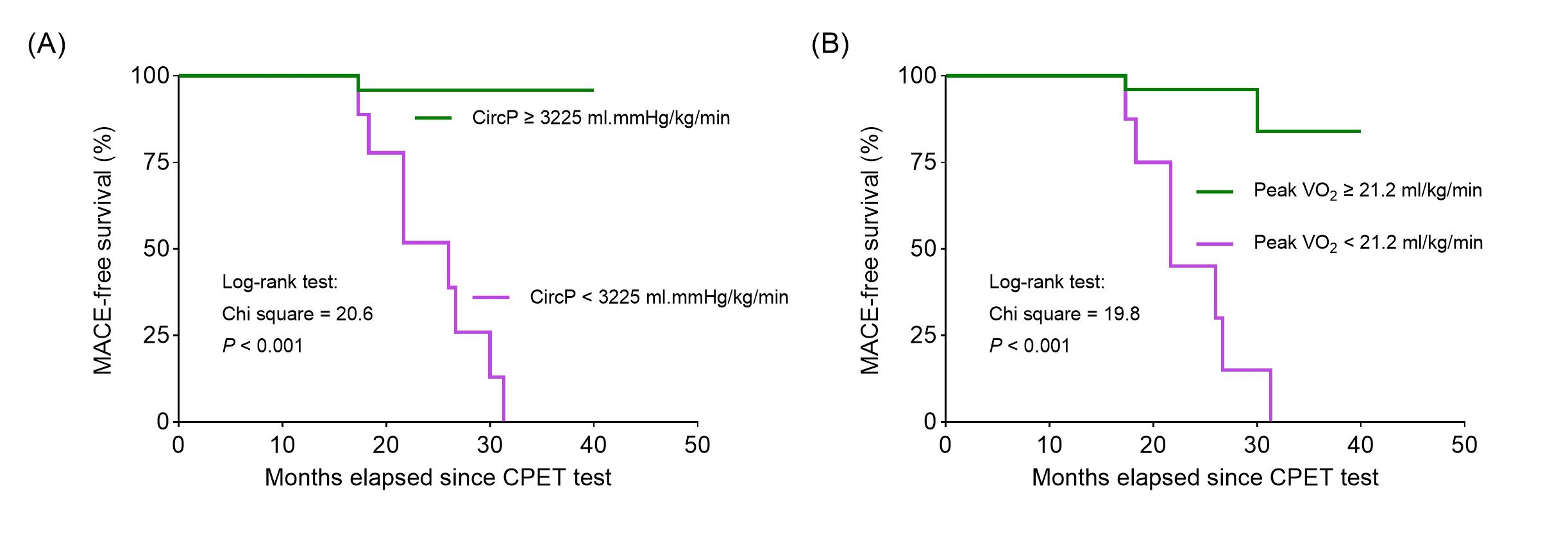
Results: Among the 47 patients, 9 experienced MACEs during the follow-up period. Multivariable Cox regression identified that both CircP and peak VO2 independently predicted MACEs (p = 0.029 and p = 0.041, respectively). The optimal prognostic threshold value for CircP was 3225 mm Hg mL/kg/min, with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.93 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.84-1.0, p < 0.001), sensitivity of 88.9%, and specificity of 92.1% (Figure 1A). The optimal prognostic threshold value for peak VO2 was 21.2 mL/kg/min (AUC = 0.91, 95% CI: 0.82-1.0, p < 0.001; sensitivity = 77.8%, specificity = 89.5%) (Figure 1B). AUC values were comparable between CircP and peak VO2 in predicting MACEs (0.93 vs 0.91, p = 0.777) (Figure 1C). Individuals with CircP < 3225 mm Hg mL/kg/min or peak VO2 < 21.2 ml/kg/min had a significantly higher MACE risk than those with CircP ≥ 3225 mmHg.ml/kg/min or peak VO2 ≥ 21.2 ml/kg/min (Figure 2, A and B).
Conclusions: The prognostic significance of peak CircP was comparable to peak VO2 in predicting MACEs in rToF patients. Peak CircP may serve as an independent marker for risk stratification in rTOF patients.
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the prognostic value of peak CircP in individuals with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot (rToF) compared to peak VO2.
Methods: Forty-seven rToF patients underwent CPET between August 2014 and April 2018 at Memorial Healthcare System, Hollywood, Florida. The Cox proportional hazards model assessed CPET variables associated with major adverse cardiac events (MACEs), adjusting for covariates. Optimal cut-off values for CircP and peak VO2 were derived from the receiver operating curve (ROC). Kaplan-Meier survival plots illustrated the prognostic significance of CircP and peak VO2.
Results: Among the 47 patients, 9 experienced MACEs during the follow-up period. Multivariable Cox regression identified that both CircP and peak VO2 independently predicted MACEs (p = 0.029 and p = 0.041, respectively). The optimal prognostic threshold value for CircP was 3225 mm Hg mL/kg/min, with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.93 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.84-1.0, p < 0.001), sensitivity of 88.9%, and specificity of 92.1% (Figure 1A). The optimal prognostic threshold value for peak VO2 was 21.2 mL/kg/min (AUC = 0.91, 95% CI: 0.82-1.0, p < 0.001; sensitivity = 77.8%, specificity = 89.5%) (Figure 1B). AUC values were comparable between CircP and peak VO2 in predicting MACEs (0.93 vs 0.91, p = 0.777) (Figure 1C). Individuals with CircP < 3225 mm Hg mL/kg/min or peak VO2 < 21.2 ml/kg/min had a significantly higher MACE risk than those with CircP ≥ 3225 mmHg.ml/kg/min or peak VO2 ≥ 21.2 ml/kg/min (Figure 2, A and B).
Conclusions: The prognostic significance of peak CircP was comparable to peak VO2 in predicting MACEs in rToF patients. Peak CircP may serve as an independent marker for risk stratification in rTOF patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
Comprehensive Genetic Analyses Combined with Animal Studies Provide New Insights into Genetic Modes of Outflow Tract Defects: A Large-Scale Japanese Investigation
Inoue Tadashi, Inai Kei, Terada Makiko, Azuma Kenko, Akagawa Hiroyuki, Yamagishi Hiroyuki, Uchida Keiko, Kodo Kazuki, Suzuki Nobuhide, Tsukamoto Satoshi, Mizushima Noboru, Greskovich Sarah, Garg Vidu, Furutani Yoshiyuki
Association of Moderate-Severe Tricuspid Regurgitation with Exercise Hemodynamics and Outcomes in Patients in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: Multicenter StudyDorsey Natalie, Caravita Sergio, Tedford Ryan, Rao Vishal N., Baratto Claudia, Biscopink Alec, Taylor Eric, Atkins Jessica, Amoroso Nicholas, Carnicelli Anthony, Houston Brian, Silkowski Molly