Final ID: 4147445
Framingham risk and major adverse cardiovascular events among patients with hypertension ineligible for SPRINT
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Among older adults with hypertension and increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), the SPRINT trial demonstrated benefit of intensive BP-lowering. However, several categories of individuals who are at increased CVD risk were not included in SPRINT, including persons with diabetes, advanced chronic kidney disease [CKD], or younger than age 50 years.
Objectives: In an integrated health system, we aimed to compare the cumulative incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) among patients with hypertension who (1) met all eligibility criteria for SPRINT and met all inclusion criteria for SPRINT but were excluded due to (2) diabetes, (3) advanced CKD, or (4) age <50 years.
Methods: In this retrospective analysis of electronic health records (EHR) from Kaiser Permanente Mid-Atlantic States between 2010-2018, we identified patients aged 18 years or older with a systolic BP 130-180mm Hg at increased risk of CVD as defined in SPRINT (Framingham predicted CVD risk>15%, prior CVD, or CKD with eGFR 20 to <60 mL/min/1.73m2). We compared MACE with Kaplan-Meier analysis among those who were (1) eligible for SPRINT, (2) with diabetes, (3) with stage 4 or 5 CKD (eGFR <20 mL/min/1.73m2 not on dialysis), (4) or younger than 50 years.
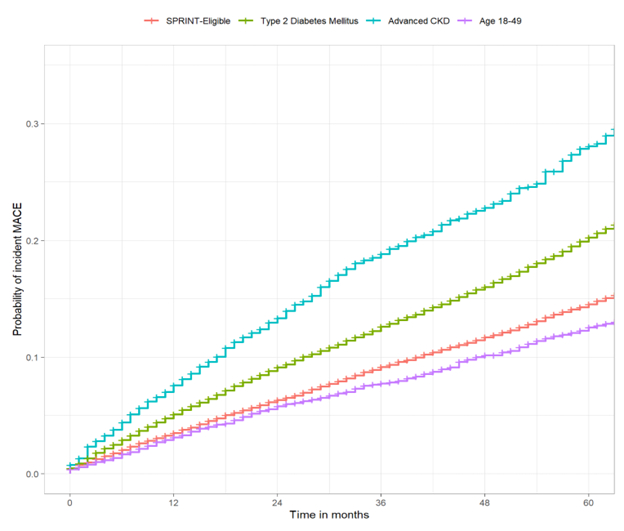
Results: In total, 104,757 individuals (47.3% female, 47.5% non-Hispanic Black) were identified with elevated BP and at increased CVD risk. Of these, 54.2% met all eligibility criteria for SPRINT, 32.2% had diabetes, 3.8% had advanced CKD, and 9.9% were aged 18-49y. At baseline, the 10-year Framingham CVD risk for each subgroup was: SPRINT-eligible: 24.2%; among those ineligible for SPRINT, those with diabetes: 32.2%; CKD: 25.0%; and adults aged 18-49 years: 18.8%. Over a median follow-up of 1.8 (IQR 0.9-3.8) years, the 3-year cumulative incidence of MACE (FIGURE) was SPRINT-eligible: 9.1% (95% CI 8.8-9.5%); among those ineligible for SPRINT, those with diabetes: 12.6% (12.1-13.0%); CKD: 18.8% (17.3-20.3%); and adults aged 18-49 years: 7.7% (7.0-8.4%).
Conclusions: A large proportion of patients with hypertension in a diverse real-world sample were not eligible for SPRINT. However, CVD event rates were high in all groups, which suggests risk-based approaches to BP-lowering should be evaluated among those at increased CVD risk not included in SPRINT.
Objectives: In an integrated health system, we aimed to compare the cumulative incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) among patients with hypertension who (1) met all eligibility criteria for SPRINT and met all inclusion criteria for SPRINT but were excluded due to (2) diabetes, (3) advanced CKD, or (4) age <50 years.
Methods: In this retrospective analysis of electronic health records (EHR) from Kaiser Permanente Mid-Atlantic States between 2010-2018, we identified patients aged 18 years or older with a systolic BP 130-180mm Hg at increased risk of CVD as defined in SPRINT (Framingham predicted CVD risk>15%, prior CVD, or CKD with eGFR 20 to <60 mL/min/1.73m2). We compared MACE with Kaplan-Meier analysis among those who were (1) eligible for SPRINT, (2) with diabetes, (3) with stage 4 or 5 CKD (eGFR <20 mL/min/1.73m2 not on dialysis), (4) or younger than 50 years.
Results: In total, 104,757 individuals (47.3% female, 47.5% non-Hispanic Black) were identified with elevated BP and at increased CVD risk. Of these, 54.2% met all eligibility criteria for SPRINT, 32.2% had diabetes, 3.8% had advanced CKD, and 9.9% were aged 18-49y. At baseline, the 10-year Framingham CVD risk for each subgroup was: SPRINT-eligible: 24.2%; among those ineligible for SPRINT, those with diabetes: 32.2%; CKD: 25.0%; and adults aged 18-49 years: 18.8%. Over a median follow-up of 1.8 (IQR 0.9-3.8) years, the 3-year cumulative incidence of MACE (FIGURE) was SPRINT-eligible: 9.1% (95% CI 8.8-9.5%); among those ineligible for SPRINT, those with diabetes: 12.6% (12.1-13.0%); CKD: 18.8% (17.3-20.3%); and adults aged 18-49 years: 7.7% (7.0-8.4%).
Conclusions: A large proportion of patients with hypertension in a diverse real-world sample were not eligible for SPRINT. However, CVD event rates were high in all groups, which suggests risk-based approaches to BP-lowering should be evaluated among those at increased CVD risk not included in SPRINT.
More abstracts on this topic:
Activated CD8+HLA-DR+ T Cells as Immune Biomarkers of Metabolic Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Risk in Prediabetes
Alrashed Fatema, Alsaeed Halemah, Alturaiki Wael, Akhter Nadeem, Alosaimi Bandar, Almutairi Saeedah, Mubarak Ayman, Al-mulla Fahd, Ahmad Rasheed
Blood Pressure Variability and Implications for Trial ScreeningSong Xing, Burns Jeffrey, Gupta Aditi, Supiano Mark, Conroy Molly, Chandaka Sravani, Abu-el-rub Noor, Young Kate, Mahnken Jonathan, Barlocker Jackson, King Jordan