Final ID: Mo3124
Young Adults with Migraine and Established Cardiovascular Disease Risk: Studying the Impact of Cannabis Use Disorder on Major Adverse Cardiac and Cerebrovascular Events in a Nationwide Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): BACKGROUND: With medical marijuana being used for migraine and high overlapping use of medicinal and recreational cannabis use with associated addiction potential, the impact on cardiovascular outcomes remains unexplored in the young population. Hence, we aim to analyze effect of cannabis use disorder (CUD) on major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE) in patients with migraine.
METHODS: The National Inpatient sample from 2016-2020 was queried with pertinent ICD-10 codes to find inpatient encounters of young adults with migraine. A 1:1 propensity score-matched analysis was performed to obtain balanced CUD and without CUD cohorts matched on demographics and substance abuse. Multivariate logistic regression was used to analyze MACCE outcomes along with gender-based subgroup analyses.
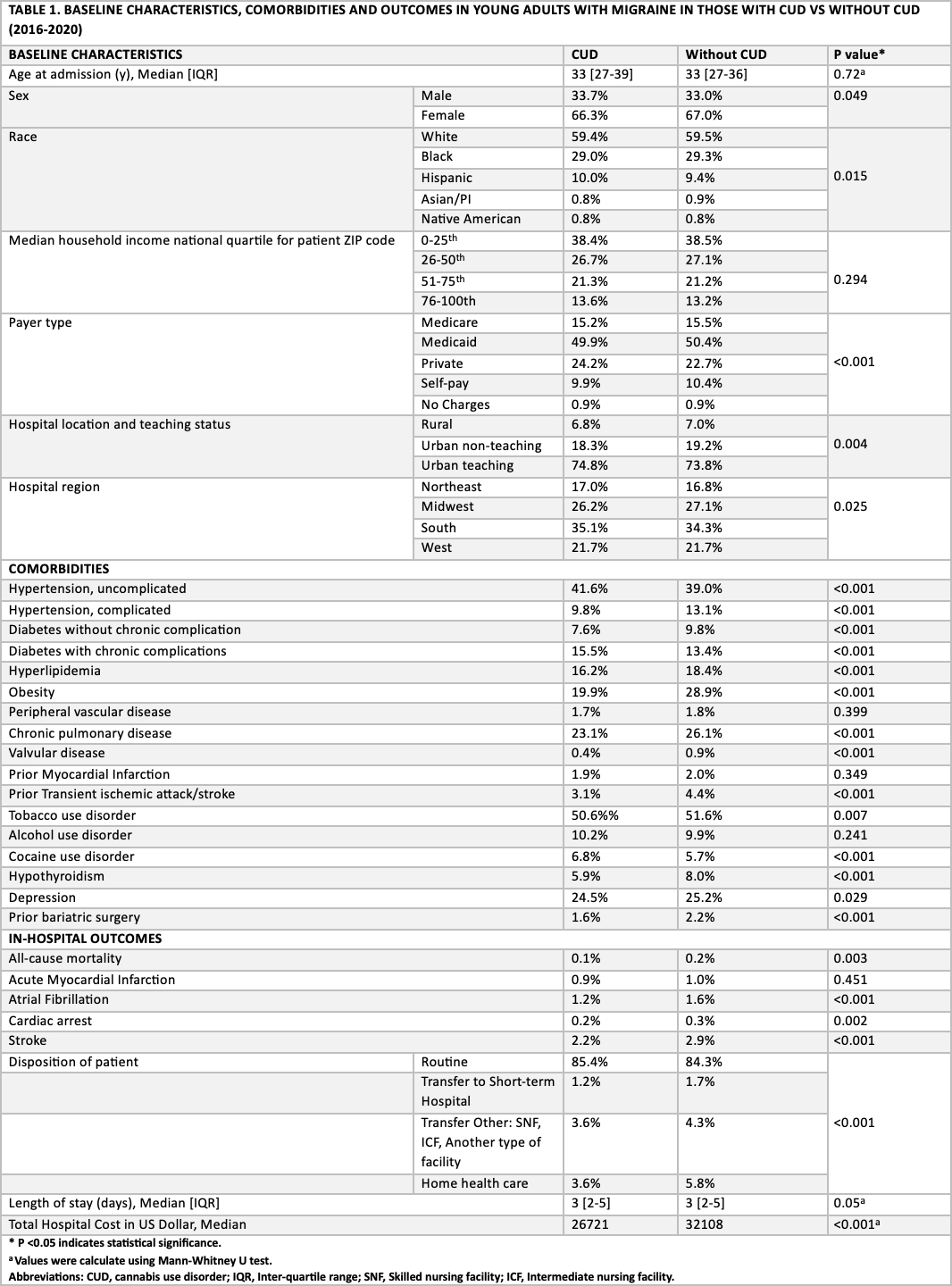
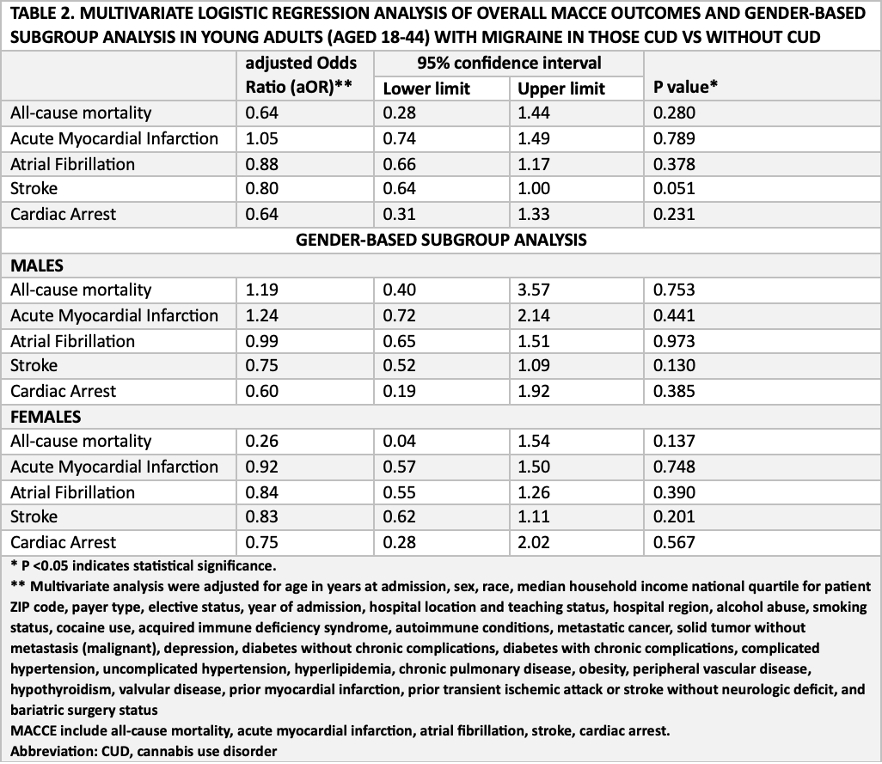
RESULTS: We analyzed 490955 adults admitted with migraine with equal distribution of patients in both CUD and without CUD cohorts. Both the cohorts had significantly more females and patients with white ethnicity. Patients with CUD had significantly higher concomitant cocaine use disorder (6.8% vs 5.7%) but lower tobacco use disorder (50.6% vs 51.6%) compared to those without CUD. Surprisingly, non-CUD cohort had higher cardiometabolic comorbidities such as complicated hypertension (13.1% vs 9.8%), uncomplicated diabetes (9.8% vs 7.6%, hyperlipidemia (18.4% vs 16.2%), obesity (28.9% vs 19.9%). Multivariate regression analysis did not show any significant difference in overall MACCE outcomes. The subgroup analysis also did not show any difference in MACCE outcomes. Without CUD cohort had higher hospitalization cost compared to CUD cohort (32108$ vs 26721$).
CONCLUSION: This nationwide covariate adjusted multivariate regression analysis shows no significant difference in all-cause mortality and other cardiovascular and cerebrovascular complications such as acute myocardial Infarction, atrial fibrillation, cardiac arrest, and stroke in young patients with migraine with and without CUD. Moreover, the subgroup analysis also shows comparable results in males and females.
METHODS: The National Inpatient sample from 2016-2020 was queried with pertinent ICD-10 codes to find inpatient encounters of young adults with migraine. A 1:1 propensity score-matched analysis was performed to obtain balanced CUD and without CUD cohorts matched on demographics and substance abuse. Multivariate logistic regression was used to analyze MACCE outcomes along with gender-based subgroup analyses.
RESULTS: We analyzed 490955 adults admitted with migraine with equal distribution of patients in both CUD and without CUD cohorts. Both the cohorts had significantly more females and patients with white ethnicity. Patients with CUD had significantly higher concomitant cocaine use disorder (6.8% vs 5.7%) but lower tobacco use disorder (50.6% vs 51.6%) compared to those without CUD. Surprisingly, non-CUD cohort had higher cardiometabolic comorbidities such as complicated hypertension (13.1% vs 9.8%), uncomplicated diabetes (9.8% vs 7.6%, hyperlipidemia (18.4% vs 16.2%), obesity (28.9% vs 19.9%). Multivariate regression analysis did not show any significant difference in overall MACCE outcomes. The subgroup analysis also did not show any difference in MACCE outcomes. Without CUD cohort had higher hospitalization cost compared to CUD cohort (32108$ vs 26721$).
CONCLUSION: This nationwide covariate adjusted multivariate regression analysis shows no significant difference in all-cause mortality and other cardiovascular and cerebrovascular complications such as acute myocardial Infarction, atrial fibrillation, cardiac arrest, and stroke in young patients with migraine with and without CUD. Moreover, the subgroup analysis also shows comparable results in males and females.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acoramidis Reduces All-Cause Mortality (ACM) and Cardiovascular-Related Hospitalization (CVH): Initial Outcomes From the ATTRibute-CM Open-Label Extension (OLE) Study
Judge Daniel, Masri Ahmad, Obici Laura, Poulsen Steen, Sarswat Nitasha, Shah Keyur, Soman Prem, Cao Xiaofan, Wang Kevin, Pecoraro Maria, Tamby Jean-francois, Gillmore Julian, Katz Leonid, Fox Jonathan, Maurer Mathew, Alexander Kevin, Ambardekar Amrut, Cappelli Francesco, Fontana Marianna, Garcia-pavia Pablo, Grogan Martha, Hanna Mazen
Achieving Guidelines within a 24-Hour Movement Paradigm and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality in United States AdultsBoudreaux Benjamin, Xu Chang, Dooley Erin, Hornikel Bjoern, Munson Alexandra, Shechter Ari, Palta Priya, Gabriel Kelley, Diaz Keith