Final ID: Su3137
Statewide Burden of Ischemic Heart Disease Attributable to High Temperature in India and its Burden from 1990-2021: A Benchmarking Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD) is the primary cause of death and disability among all cardiovascular diseases in India. As global warming escalates, the role of environmental changes, particularly high temperatures, has become a major concern. This study uniquely focuses on high temperatures (HT) as a significant environmental risk factor for IHD, providing the first estimates of its impact over the last three decades in India, including the initial two years of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Method: Using the global burden of disease 2021 standardized methodology, we estimated deaths, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and years of life lost (YLLs) due to IHD attributable to HT in India by age, sex, year and location from 1990-2021. The results were presented in absolute counts and age-standardized rate (per 100,000 person-years).
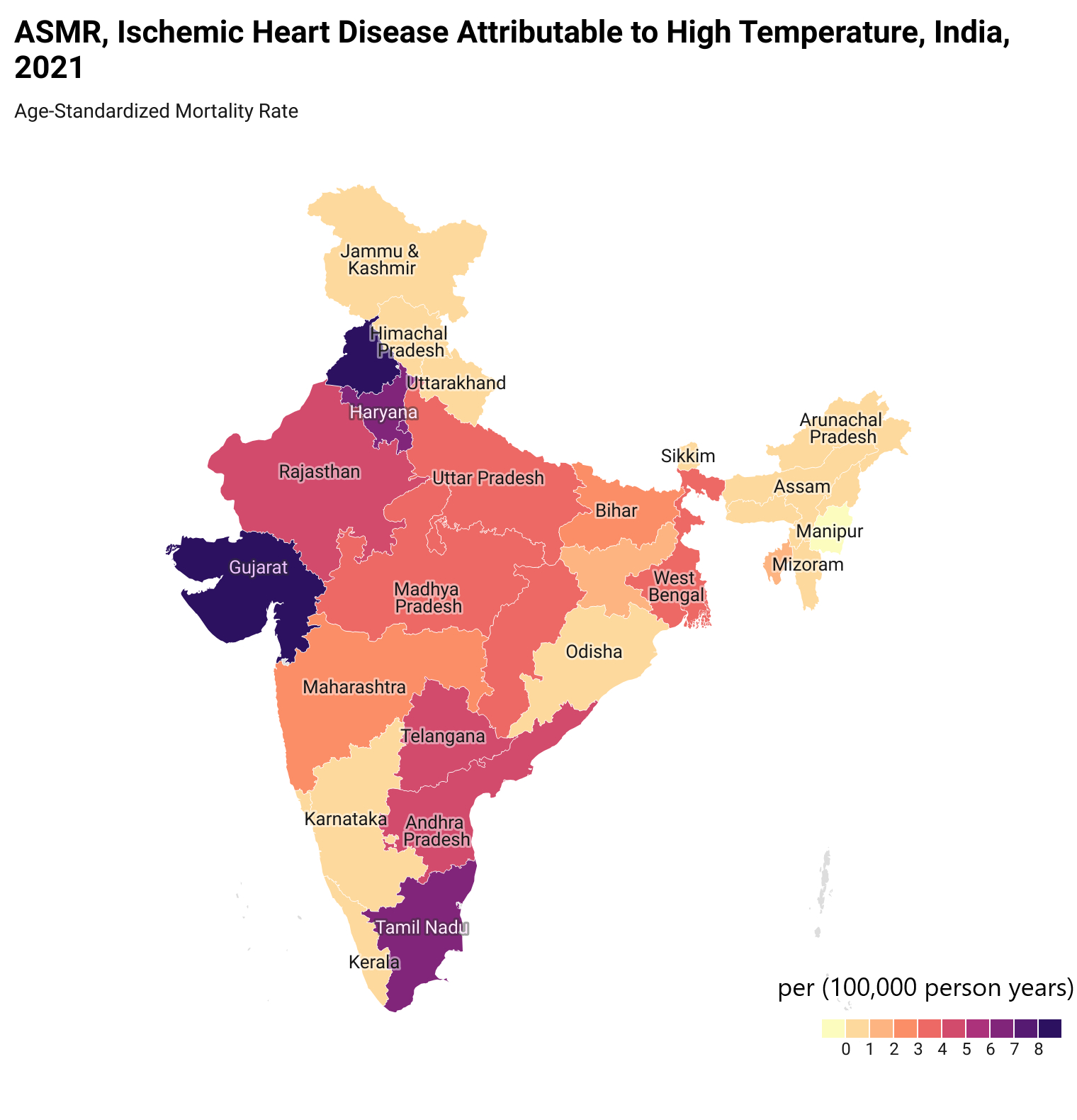
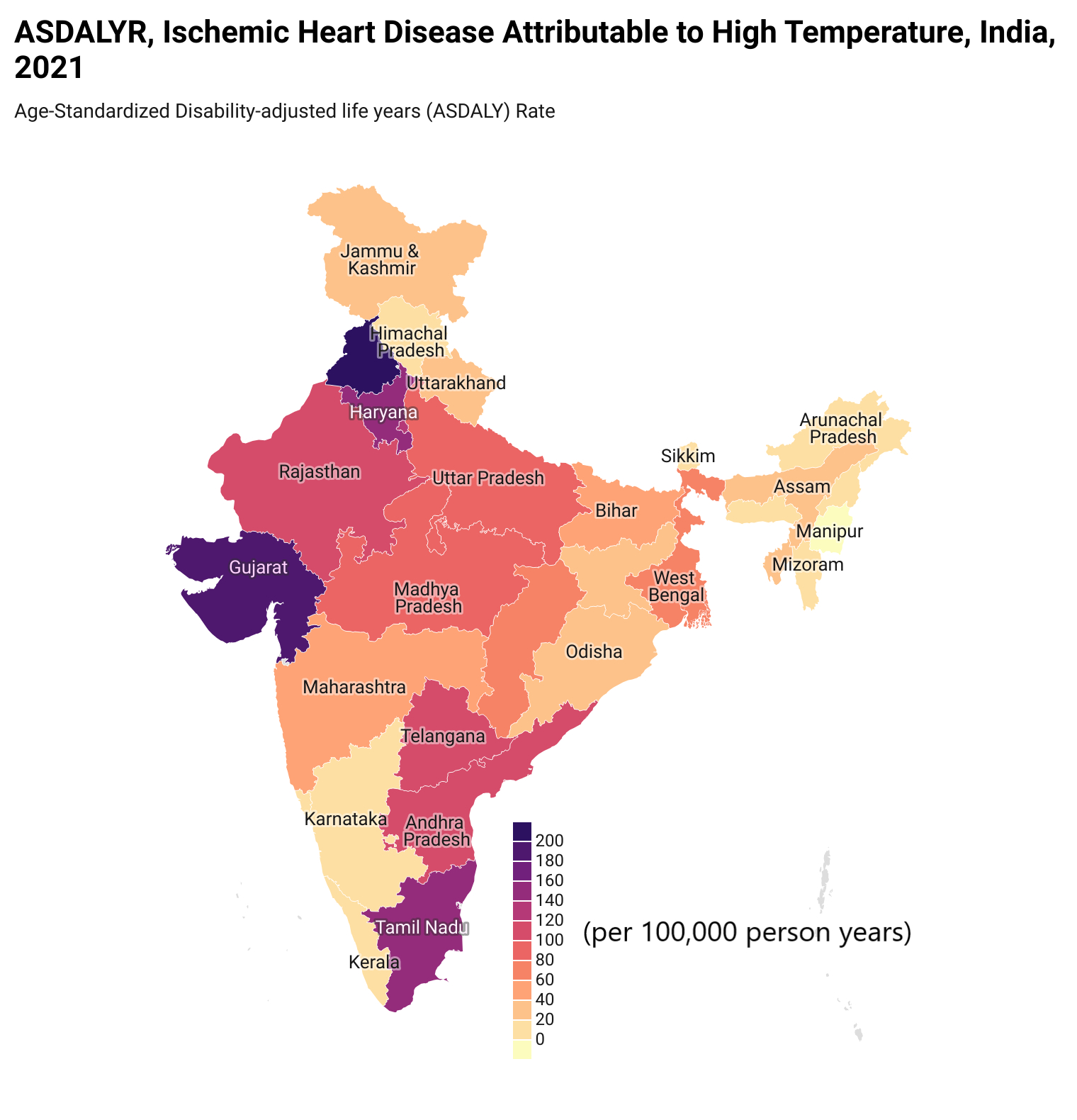
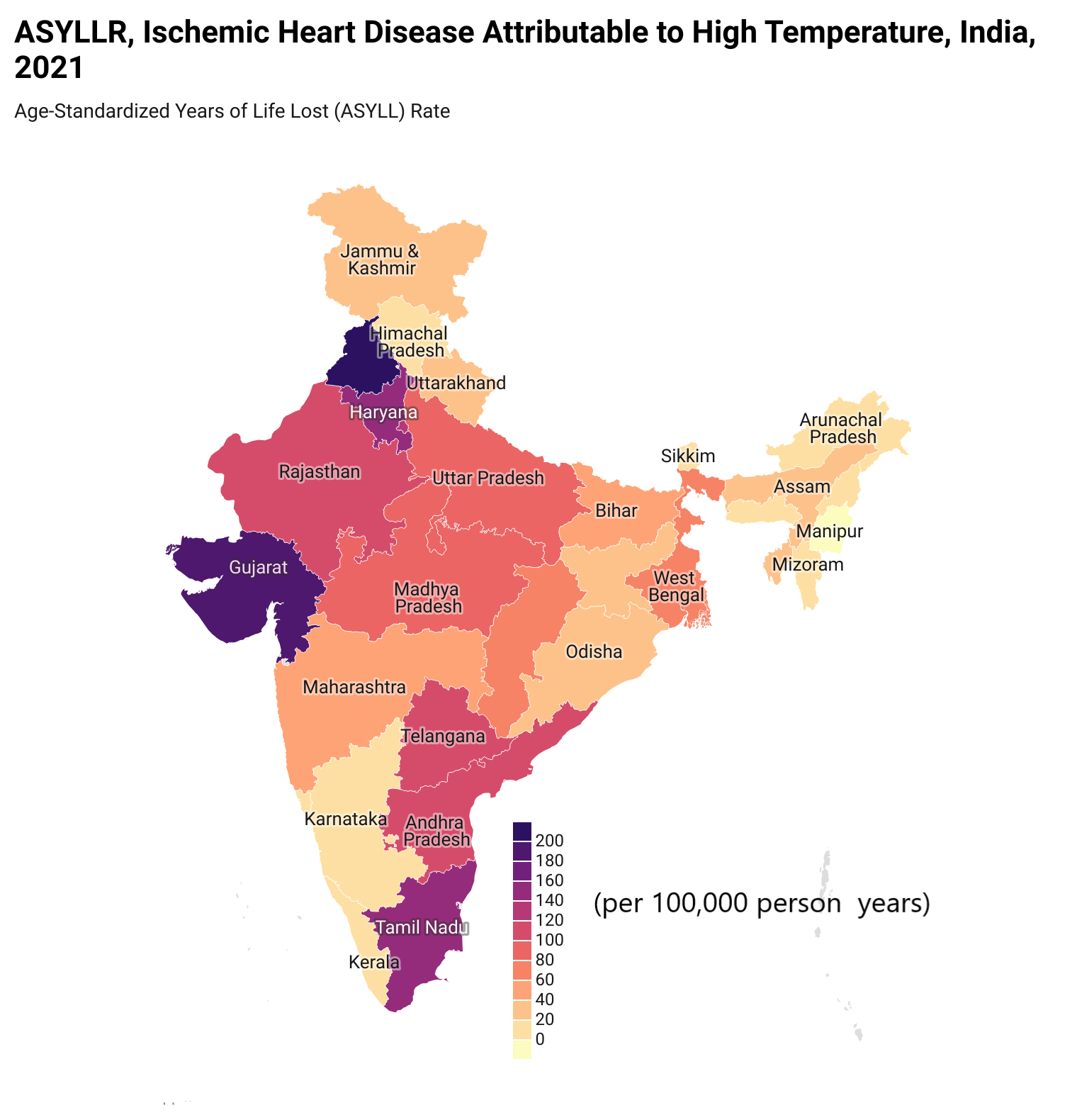
Results: From 1990 to 2021, the total number of deaths due to IHD attributable to HT in India rose from 10,874 (95% uncertainty interval: 2,320-19,061) to 40,245 (13,140-68,121). The age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) saw a total percentage change (TPC) of 42% (19%-178%), and the DALYs rate, (ASDALR) increased by 33% (11%-156%) during this period. Uttar Pradesh recorded the highest total number of deaths at 6,202, followed by Gujarat with 4,821. The highest death counts were in the 70-74 age group, totalling 5,704 (1,888-9,578), and the highest DALYs were in the 55-59 age group at 132,936 (42,040-227,650) in 2021. In terms of gender, males exhibited a consistently higher burden over the last three decades, with a TPC in deaths of 56% for males compared to 30% for females, and DALYs of 44% for males compared to 21% for females.
Conclusion: In 2021, deaths due to IHD attributable to HT accounted for 2.46% of all CVD-related deaths in India. The rapid urbanization, industrialization, and increasing pollution in India require urgent action from a public health policy perspective. Stakeholders, including government agencies and environmental groups, must collaborate to develop policies that address these issues effectively, aiming to reduce the health impact of environmental risks and enhance cardiovascular health across the nation.
Method: Using the global burden of disease 2021 standardized methodology, we estimated deaths, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and years of life lost (YLLs) due to IHD attributable to HT in India by age, sex, year and location from 1990-2021. The results were presented in absolute counts and age-standardized rate (per 100,000 person-years).
Results: From 1990 to 2021, the total number of deaths due to IHD attributable to HT in India rose from 10,874 (95% uncertainty interval: 2,320-19,061) to 40,245 (13,140-68,121). The age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) saw a total percentage change (TPC) of 42% (19%-178%), and the DALYs rate, (ASDALR) increased by 33% (11%-156%) during this period. Uttar Pradesh recorded the highest total number of deaths at 6,202, followed by Gujarat with 4,821. The highest death counts were in the 70-74 age group, totalling 5,704 (1,888-9,578), and the highest DALYs were in the 55-59 age group at 132,936 (42,040-227,650) in 2021. In terms of gender, males exhibited a consistently higher burden over the last three decades, with a TPC in deaths of 56% for males compared to 30% for females, and DALYs of 44% for males compared to 21% for females.
Conclusion: In 2021, deaths due to IHD attributable to HT accounted for 2.46% of all CVD-related deaths in India. The rapid urbanization, industrialization, and increasing pollution in India require urgent action from a public health policy perspective. Stakeholders, including government agencies and environmental groups, must collaborate to develop policies that address these issues effectively, aiming to reduce the health impact of environmental risks and enhance cardiovascular health across the nation.
More abstracts on this topic:
Ambulatory QT Interval Prolongation and Reduced T-Amplitude Help Identify Veterans with Heart Disease
Shah Amit, Colon-motas Kay, De Leon Katalina, Murtala Abdulkareem, Osei Jeffery, Mourad Rama, Chang Sarah, Ko Yi-an, Zeng Zhaohua, Sheikh Shafa-at, Xu Ying, Koscova Zuzana, Kim Kain, Akoto Natalie, Santana Eric, Alexander Abigail, Suvada Kara, Roberts Tatum, Stefanos Lewam, Vaccarino Viola, Clifford Gari, Li Qiao, Sameni Reza, Bahrami Rad Ali, Karimi Sajjad, Lampert Rachel, Mathew Lejy, Alagar Nikila
A Focus for Improvement - Factors for Lab Adherence in a Pediatric Preventive Cardiology ProgramHolsinger Hunter, Porterfield Ronna, Taylor Makenna, Dresbach Bethany, Seipel Brittany, Igwe Chukwuemeka, Alvarado Chance, Tran Andrew