Final ID: MDP1641
Global, National and Regional Burden of Cardiovascular Disease in Women in 204 Countries and Territories and its Trend from 1990-2021: A Global Benchmarking Analysis.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) is the primary cause of death and disability among women worldwide. Despite its escalating impact, there remains a significant gap in consistent and comparative global data on the burden of CVD in women. This groundbreaking study provides the first estimates of the CVD burden in women over the past three decades, including the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Method: Using the Global Burden of Disease 2021 framework, we estimated the prevalence, incidence, deaths, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and years lived with disability (YLDs) due to cardiovascular disease (CVD) in women. This analysis spans ages, years, and locations across 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2021.
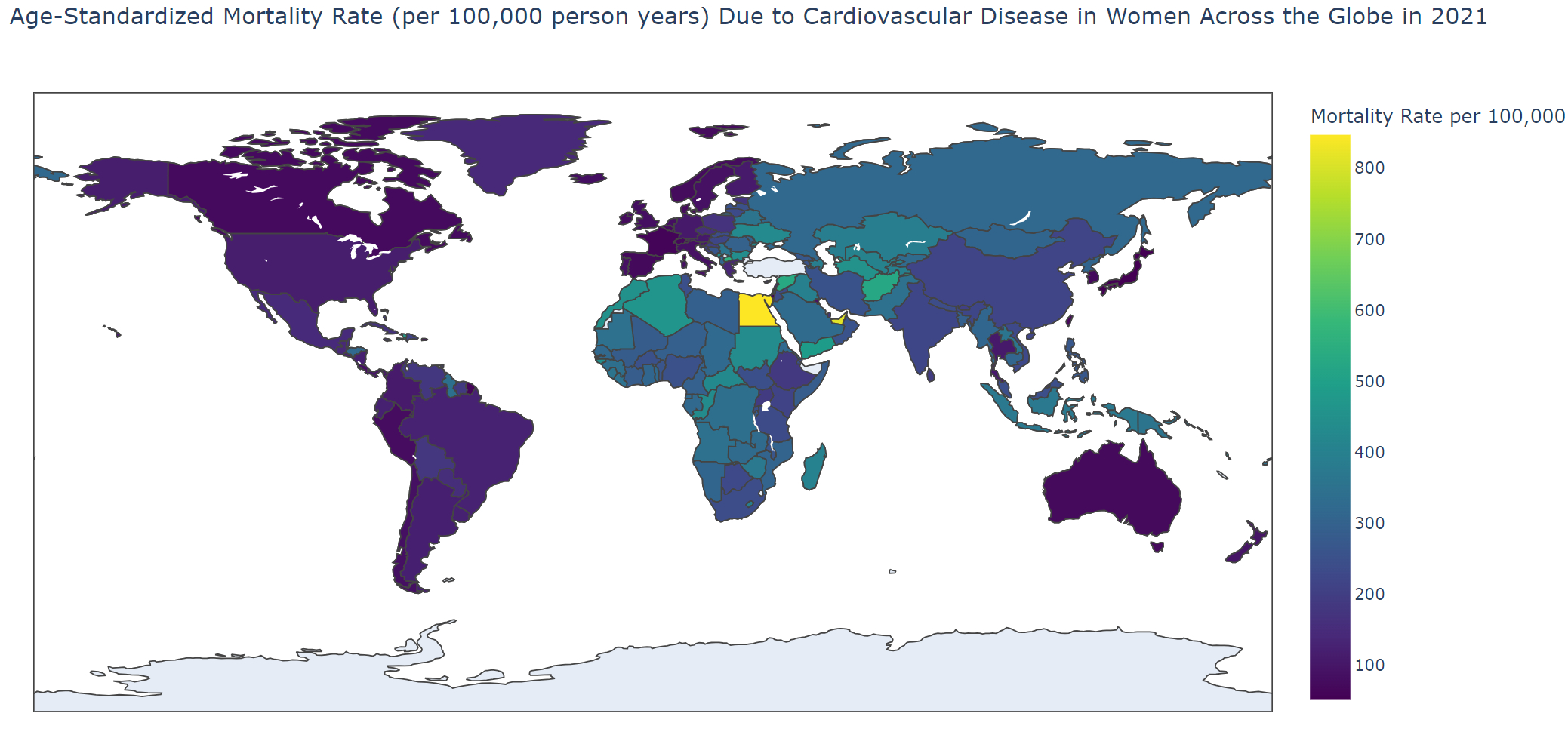
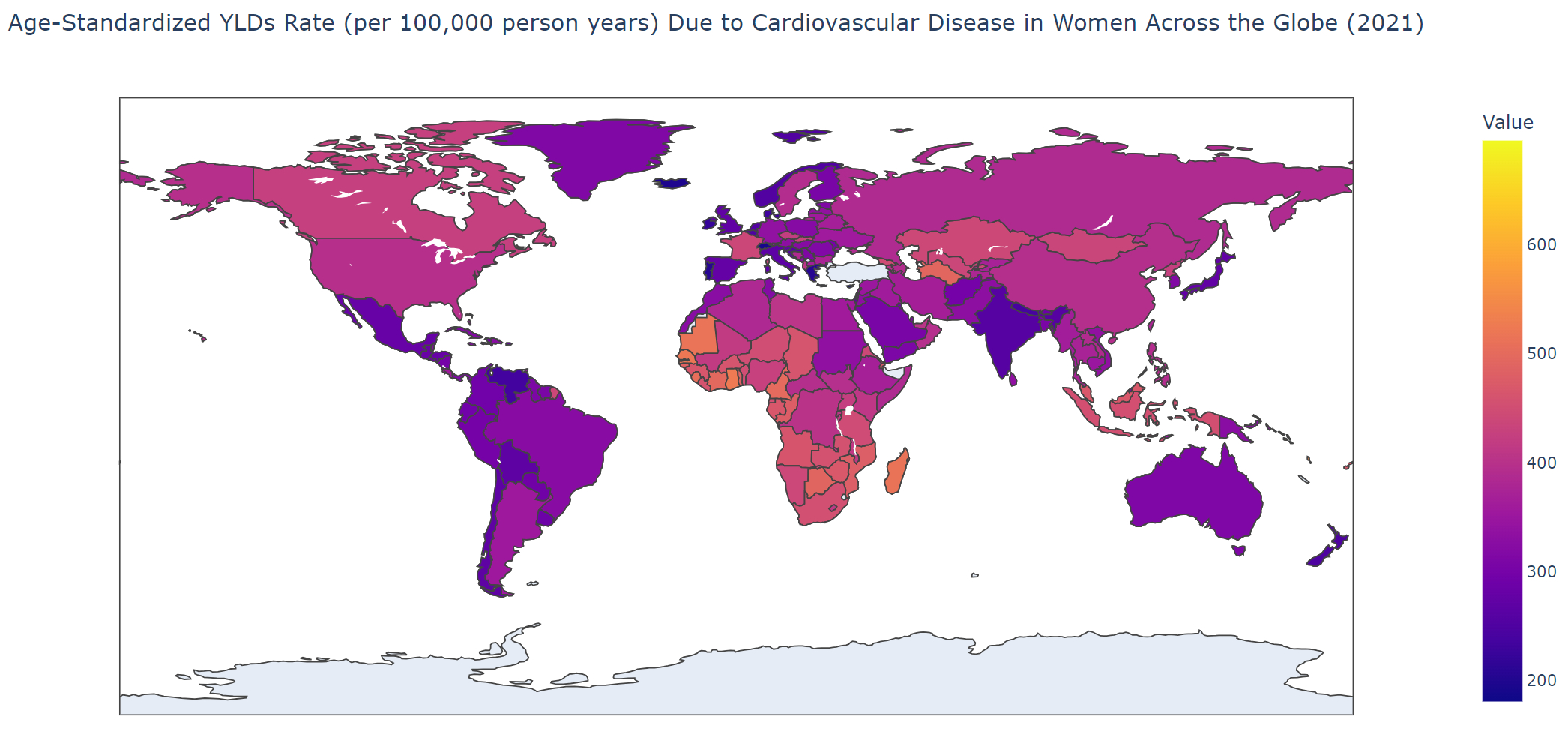
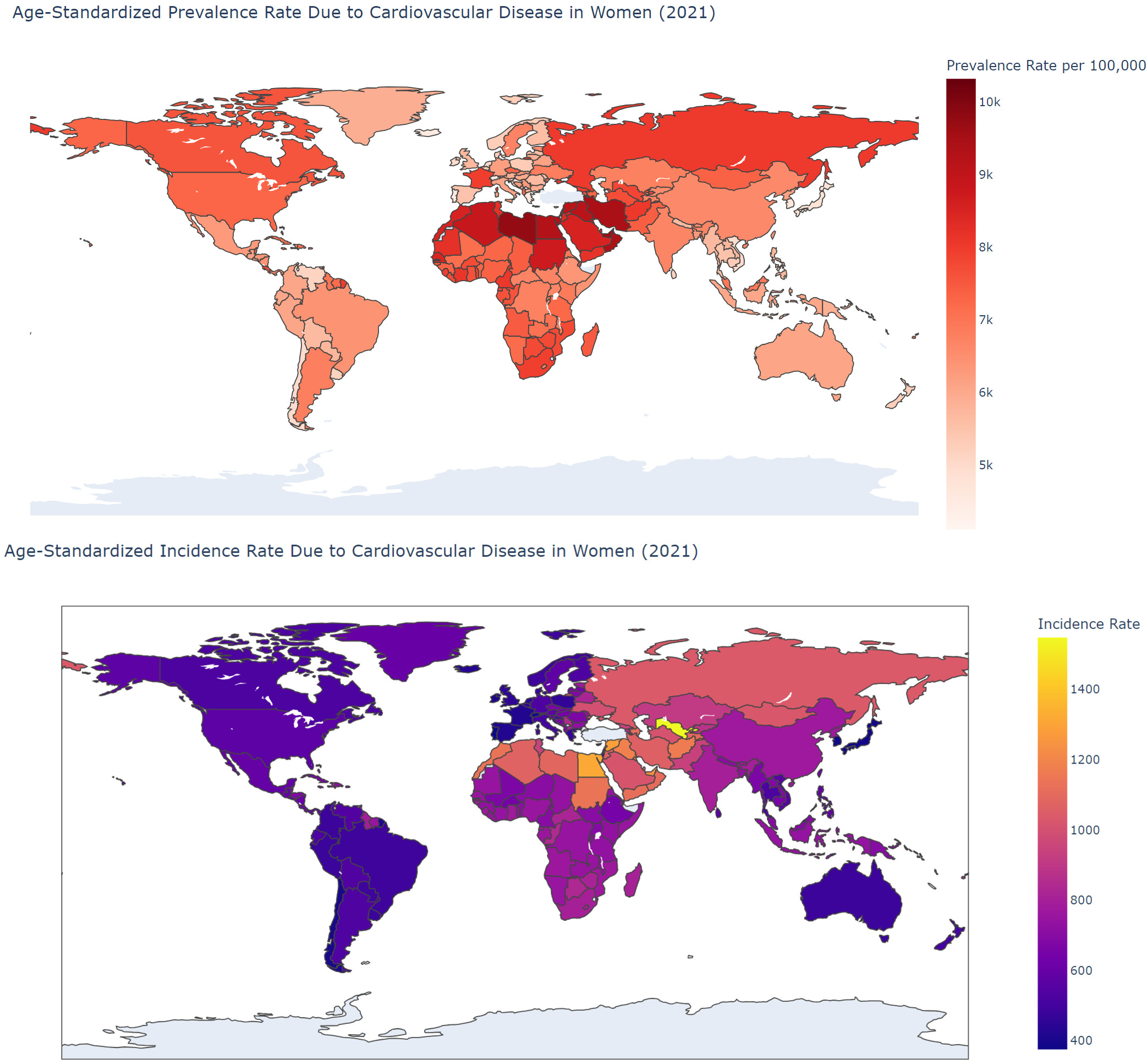
Results: From 1990 to 2021, the total percentage change (TPC) in prevalence of the condition increased by 108%, followed by a 91% increase in incidence, and a 47% increase in deaths. Regionally, the highest TPC in age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) was observed in Central Asia at 14%, while the highest mortality rate (ASMR) was in Southern Sub-Saharan Africa at 15%, and the highest YLD rate (ASYLDR) was in Australasia at 8% from 1990 to 2021. Nationally, Uzbekistan saw the largest increase in ASIR at 69%, and the United Arab Emirates had the highest increase in ASMR at 82%. In terms of socio-demographic index, the highest ASYLDR was observed in middle SDI regions with a 1% increase, while other regions saw decreases. Regarding age, individuals aged 55 and over recorded the highest deaths at 8.4 million, followed by the 20-54 age group with 659,296, and under 20s at 37,034 in 2021. Ischemic heart disease constituted 43.46% of all CVD-related deaths in 2021.
Conclusion: Deaths due to cardiovascular disease (CVD) in women attributable to metabolic risk factors accounted for 70.75% of all CVD-related fatalities. This was followed by behavioral risk factors at 34.64% and environmental risk factors at 31.62%. The disproportionate impact of metabolic, behavioral, and environmental risk factors on cardiovascular disease-related deaths in women highlights the critical need for targeted intervention strategies. Addressing these risk factors through comprehensive public health initiatives could significantly reduce the global burden of CVD in women.
Method: Using the Global Burden of Disease 2021 framework, we estimated the prevalence, incidence, deaths, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and years lived with disability (YLDs) due to cardiovascular disease (CVD) in women. This analysis spans ages, years, and locations across 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2021.
Results: From 1990 to 2021, the total percentage change (TPC) in prevalence of the condition increased by 108%, followed by a 91% increase in incidence, and a 47% increase in deaths. Regionally, the highest TPC in age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) was observed in Central Asia at 14%, while the highest mortality rate (ASMR) was in Southern Sub-Saharan Africa at 15%, and the highest YLD rate (ASYLDR) was in Australasia at 8% from 1990 to 2021. Nationally, Uzbekistan saw the largest increase in ASIR at 69%, and the United Arab Emirates had the highest increase in ASMR at 82%. In terms of socio-demographic index, the highest ASYLDR was observed in middle SDI regions with a 1% increase, while other regions saw decreases. Regarding age, individuals aged 55 and over recorded the highest deaths at 8.4 million, followed by the 20-54 age group with 659,296, and under 20s at 37,034 in 2021. Ischemic heart disease constituted 43.46% of all CVD-related deaths in 2021.
Conclusion: Deaths due to cardiovascular disease (CVD) in women attributable to metabolic risk factors accounted for 70.75% of all CVD-related fatalities. This was followed by behavioral risk factors at 34.64% and environmental risk factors at 31.62%. The disproportionate impact of metabolic, behavioral, and environmental risk factors on cardiovascular disease-related deaths in women highlights the critical need for targeted intervention strategies. Addressing these risk factors through comprehensive public health initiatives could significantly reduce the global burden of CVD in women.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes Are Associated with Incident Peripheral Artery Disease, Results from the Women’s Health Initiative.
Jackson Elizabeth, Leblanc Erin, Haring Bernhard, Harrington Laura, Allison Matthew, Eaton Charles, Lamonte Michael, Hovey Kathleen, Andrews Chris, Wells Gretchen, Manson Joann, Levitan Emily, Spracklen Cassandra, Wild Robert
A multi-task deep learning algorithm for detecting obstructive coronary artery disease using fundus photographsZeng Yong, Ding Yaodong