Final ID: MDP980
Predicted Peak Oxygen Consumption in Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy is Highly Variable by Sex and Predictive Equation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction/Background
Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) can stratify risk of sudden cardiac death and determine eligibility for advanced therapies for patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). Achieving <80% of predicted peak oxygen consumption during physical exertion (pVO2) has negative prognostic value and has been used as an eligibility criterion in clinical trials.
Research questions/hypothesis
pVO2 predictive equations are derived from predominantly male historical cohorts, thus they may be unreliable for women.
Goals/aims
To determine the sex-based variability in pVO2 predictive equations in patients with HCM.
Methods/approach
This was an observational study of HCM patients undergoing symptom-limited CPET. Wasserman cycle and treadmill (±obesity correction), Jones cycle for men and women, Hansen/Jones, FRIEND, and FRIEND 2018 equations were used to generate predicted pVO2 values.
Results/data
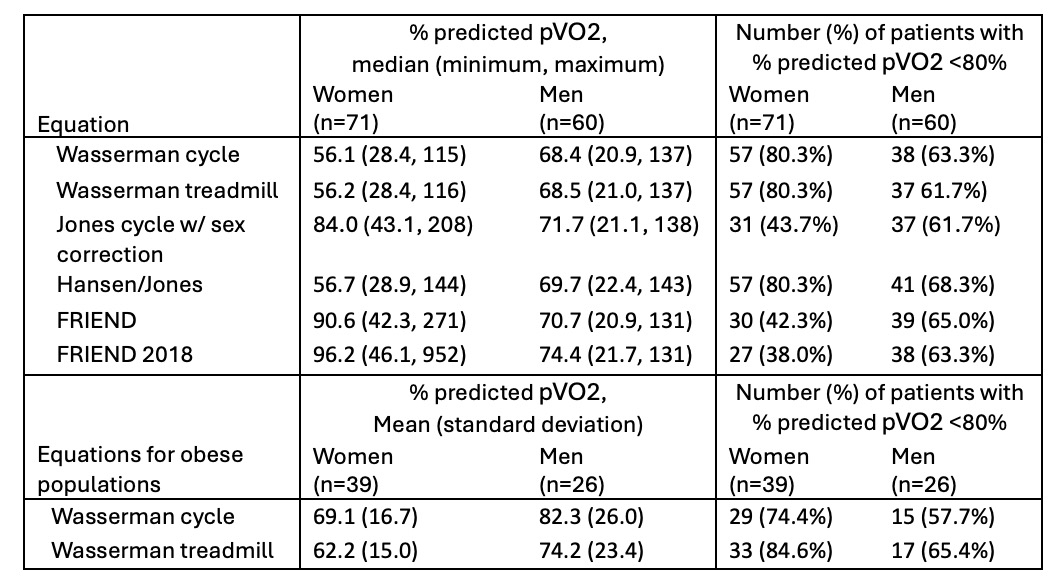
A total of 131 HCM patients (median age 47 years, range 18-86) underwent CPET and were included in the analysis; 71 (53.8%) were women. The table summarizes the differences in percent (%) predicted pVO2 by sex for each equation. Equations without built-in sex corrections (Wasserman cycle and treadmill ± obesity correction, Hansen/Jones) resulted in lower percent predicted pVO2 values in women vs men, whereas those with sex corrections resulted in higher values for women vs men. Across equations, there was a high degree of variability in percent predicted pVO2 for women (range for medians 56 to 96%) compared to men (range for medians 68 to 74%). In equations that incorporate sex corrections, fewer women were found to have percent predicted values <80%.
Conclusions
There is a high degree of variability among equations of percent predicted pVO2, especially in women. Such variability likely introduces unwanted biases in evaluation, risk prediction, and recruitment in clinical trials. Further investigation is warranted to evaluate which predictive equations provide meaningful prognostic value in HCM patients without introducing sex-based biases.
Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) can stratify risk of sudden cardiac death and determine eligibility for advanced therapies for patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). Achieving <80% of predicted peak oxygen consumption during physical exertion (pVO2) has negative prognostic value and has been used as an eligibility criterion in clinical trials.
Research questions/hypothesis
pVO2 predictive equations are derived from predominantly male historical cohorts, thus they may be unreliable for women.
Goals/aims
To determine the sex-based variability in pVO2 predictive equations in patients with HCM.
Methods/approach
This was an observational study of HCM patients undergoing symptom-limited CPET. Wasserman cycle and treadmill (±obesity correction), Jones cycle for men and women, Hansen/Jones, FRIEND, and FRIEND 2018 equations were used to generate predicted pVO2 values.
Results/data
A total of 131 HCM patients (median age 47 years, range 18-86) underwent CPET and were included in the analysis; 71 (53.8%) were women. The table summarizes the differences in percent (%) predicted pVO2 by sex for each equation. Equations without built-in sex corrections (Wasserman cycle and treadmill ± obesity correction, Hansen/Jones) resulted in lower percent predicted pVO2 values in women vs men, whereas those with sex corrections resulted in higher values for women vs men. Across equations, there was a high degree of variability in percent predicted pVO2 for women (range for medians 56 to 96%) compared to men (range for medians 68 to 74%). In equations that incorporate sex corrections, fewer women were found to have percent predicted values <80%.
Conclusions
There is a high degree of variability among equations of percent predicted pVO2, especially in women. Such variability likely introduces unwanted biases in evaluation, risk prediction, and recruitment in clinical trials. Further investigation is warranted to evaluate which predictive equations provide meaningful prognostic value in HCM patients without introducing sex-based biases.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Woman's Heart: Unveiling CMD as the Cause of Recurrent Syncope
Alvarez Betancourt Alejandro, Balasubramanian Suryakumar, Saladin Gustavo, Makaryus Amgad, Zeltser Roman
A Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Polygenic Score Modifies Penetrance of Pathogenic Hypertrophic and Dilated Cardiomyopathy Variants in Opposite DirectionsAbramowitz Sarah, Hoffman-andrews Lily, Depaolo John, Judy Renae, Owens Anjali, Damrauer Scott, Levin Michael