Final ID: MDP1611
Proteomics Characteristics of Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) remains a significant cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, with its molecular characteristics at the protein level still poorly understood. This study aims to elucidate the proteomic signatures of ACS patients using a comprehensive proteomic approach.
Methods: 182 ACS patients and 62 age and gender-matched healthy controls (HC) were randomly selected from our longitudinal multi-omic ACS cohort. Circulating proteins levels were measured with the Olink-Explore 3072 panel. Spearman correlation was used to examine the associations between proteins and clinical variables. Differential expression of proteins was analyzed using Benjamini-Hochberg-corrected T-tests.
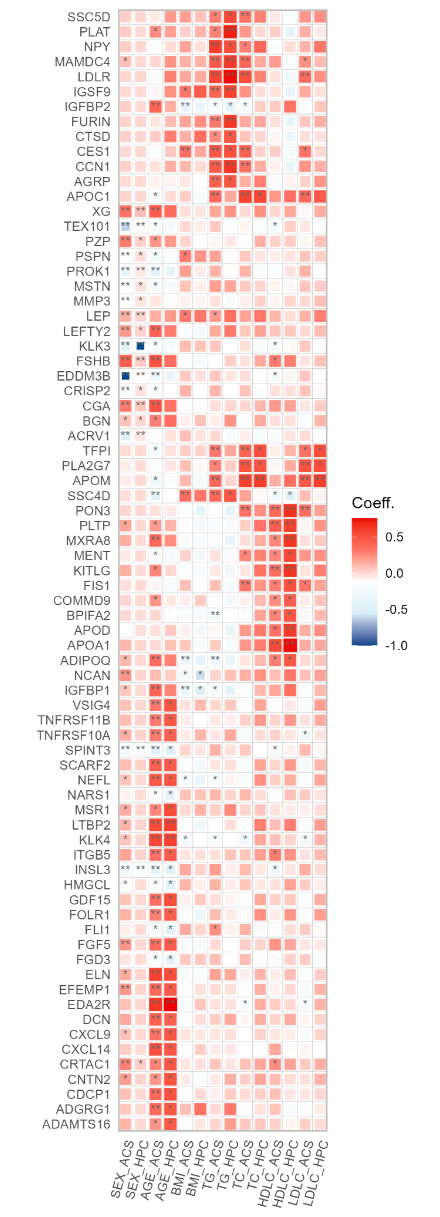
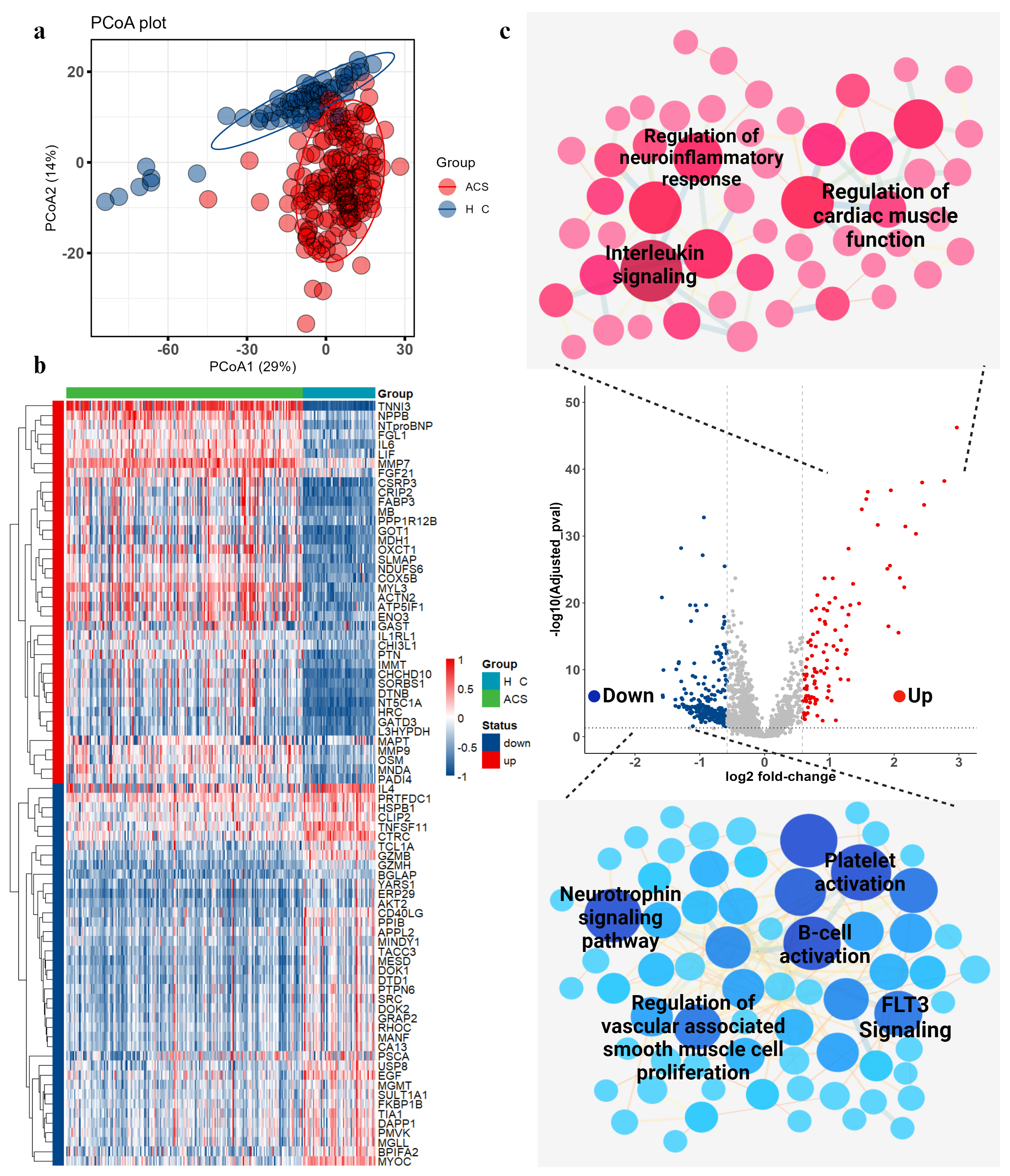
Results: Firstly, we screened proteins associated with clinical characteristics such as age, BMI and lipid profiles. As shown in figure 1, we identified several protein biomarkers associated with aging such as Elastin (ELN), Prokineticin 1 (PROK1), or exhibited gender-specific variations such as Kunitz Type 3 (SPINT3), and Insulin Like 3 (INSL3) in both healthy subjects and ACS patients. Proteins such as SSCD4 were significantly associated with BMI and lipids, suggesting a potential role in regulating lipid homeostasis. Then we analyzed the differential proteomic characteristics in ACS patients compared to HC patients and identified 1361 proteins with differential expression (false discovery rate, q<0.05 for all). We subsequently conducted a pathway enrichment analysis on the differential proteins. We found pathways involved in regulation of cardiac muscle function, interleukin signaling, and regulation of the neuro-inflammatory response were upregulated while pathways related to the regulation of vascular-associated smooth muscle cell proliferation and platelet activation were downregulated.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates the efficacy of plasma proteomics in discerning demographic variations and elucidating the proteomic landscape of ACS patients. The significant differential protein expression observed underlines the value of a comprehensive proteomic approach in advancing our understanding of ACS pathophysiology and potentially facilitating the discovery of novel biomarkers.
Methods: 182 ACS patients and 62 age and gender-matched healthy controls (HC) were randomly selected from our longitudinal multi-omic ACS cohort. Circulating proteins levels were measured with the Olink-Explore 3072 panel. Spearman correlation was used to examine the associations between proteins and clinical variables. Differential expression of proteins was analyzed using Benjamini-Hochberg-corrected T-tests.
Results: Firstly, we screened proteins associated with clinical characteristics such as age, BMI and lipid profiles. As shown in figure 1, we identified several protein biomarkers associated with aging such as Elastin (ELN), Prokineticin 1 (PROK1), or exhibited gender-specific variations such as Kunitz Type 3 (SPINT3), and Insulin Like 3 (INSL3) in both healthy subjects and ACS patients. Proteins such as SSCD4 were significantly associated with BMI and lipids, suggesting a potential role in regulating lipid homeostasis. Then we analyzed the differential proteomic characteristics in ACS patients compared to HC patients and identified 1361 proteins with differential expression (false discovery rate, q<0.05 for all). We subsequently conducted a pathway enrichment analysis on the differential proteins. We found pathways involved in regulation of cardiac muscle function, interleukin signaling, and regulation of the neuro-inflammatory response were upregulated while pathways related to the regulation of vascular-associated smooth muscle cell proliferation and platelet activation were downregulated.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates the efficacy of plasma proteomics in discerning demographic variations and elucidating the proteomic landscape of ACS patients. The significant differential protein expression observed underlines the value of a comprehensive proteomic approach in advancing our understanding of ACS pathophysiology and potentially facilitating the discovery of novel biomarkers.
More abstracts on this topic:
Apolipoprotein A-I Proteoforms, Cardiometabolic Status, and Coronary Heart Disease: Insights from the Dallas Heart Study
Gangwar Anamika, Des Soye Benjamin, Saldanha Suzanne, Jaiswal Shailesh, Patel Parthvi Bharatkumar, Shah Amil, Pandey Ambarish, Wilkins John, Rohatgi Anand
A major uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate impairs macrophage efferocytosis and accelerates atherogenesis: a potential mechanism for cardiovascular risk in chronic kidney diseaseJha Prabhash, Kasai Taku, Vromman Amelie, Holden Rachel, Libby Peter, Tabas Ira, Singh Sasha, Aikawa Elena, Aikawa Masanori, Lupieri Adrien, Sonawane Abhijeet, Le Thanh-dat, Becker-greene Dakota, Chelvanambi Sarvesh, Turner Mandy, Nakamura Yuto, Passos Livia