Final ID: MDP620
Lower Extremity Extracorporeal Distal Revascularization (LEEDR) as a Novel Approach to Limb Salvage with Prolonged Ischemia
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Acute limb ischemia (ALI) requires prompt revascularization to preserve the extremity and minimize the effects of systemic reperfusion. Once ALI is recognized, delays in revascularization are generally due to system issues (e.g., transfer) and there is a need for a method of temporary extremity perfusion to reduce warm ischemic time. Lower Extremity Extracorporeal Distal Revascularization (LEEDR) is a percutaneous technique that uses a pump and circuit to deliver oxygenated blood into a pedal artery.
Hypothesis
Extracorporeal perfusion can improve survival from ALI.
Aims
The aim of this study is to use a swine model of prolonged hindlimb ischemia to compare survival and functional outcomes of LEEDR versus control (warm ischemia).
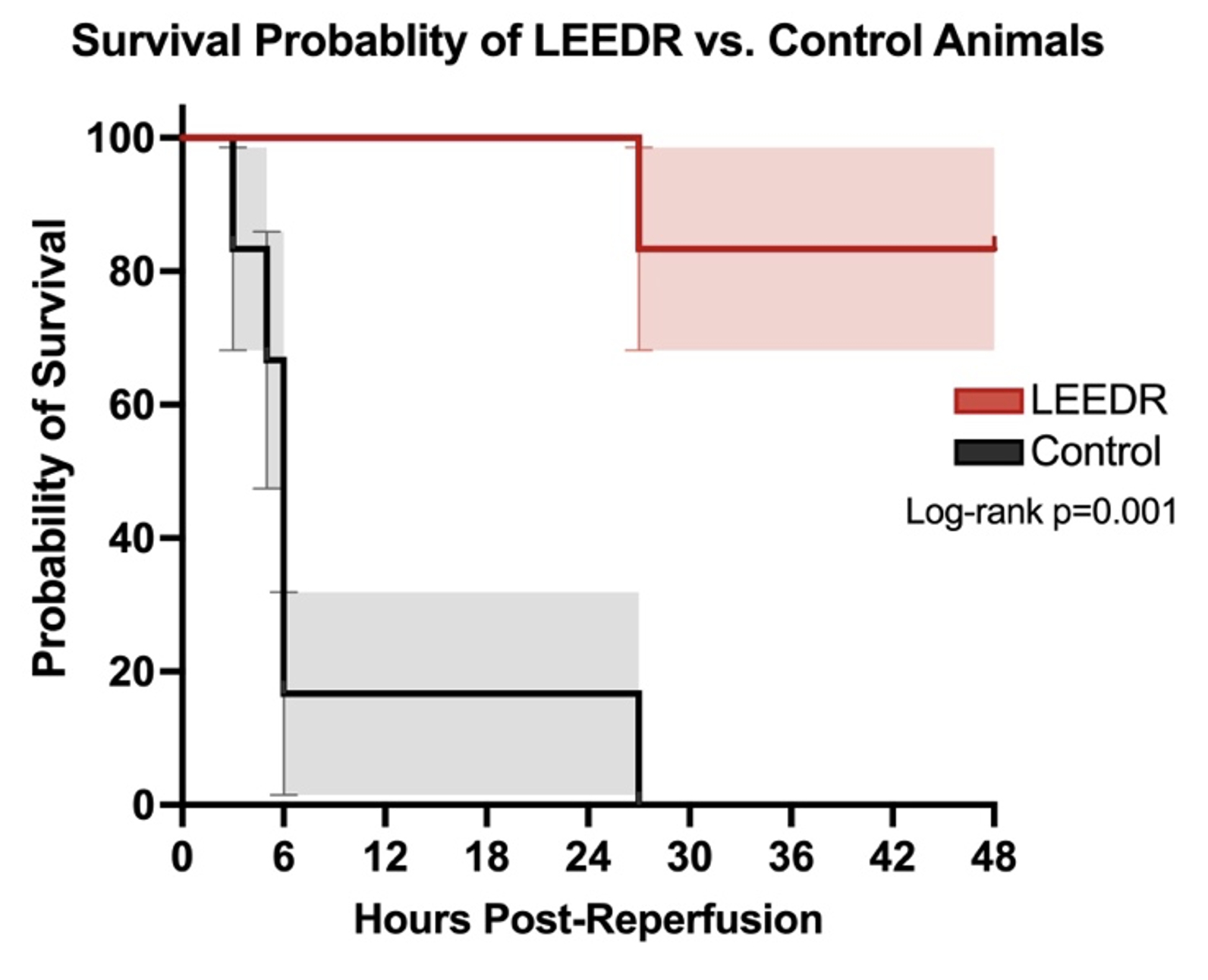
Methods: Anesthetized female Yorkshire swine (40-60kg) underwent hindlimb ischemia using endovascular balloon occlusion and were randomized to control (n=6) or LEEDR (n=6). Controls underwent 9 hours of ischemia. LEEDR animals underwent contralateral femoral and ipsilateral posterior tibial artery cannulation followed by 8 hours of extracorporeal perfusion into the ischemic limb. Subjects were revascularized by removing the endovascular balloons, restoring extremity blood flow, and undergoing a 4-hour critical care period before extubation and observation for 48 hours. Primary outcome was survival and secondary outcomes included functional extremity scores (Tarlov Gait Score), compartment pressures (mmHg) and biochemical markers of reperfusion.
Results: Survival was higher in animals undergoing LEEDR (83% vs. 0%; p=0.001), with most control animals succumbing to acute lung injury. LEEDR animals had a higher functional gait score (5.9±0.3 vs. 2.5±0.7; p<0.001) and lower compartment pressure (8±2 vs. 28±4; p=0.002) compared to controls. Biochemically, the LEEDR group had lower potassium (4.5±0.3 vs. 5.3±0.4; p=0.001) and lactate (1.2±0.5 vs. 2.0±0.7; p<0.001) measurements compared to controls during reperfusion and recovery.
Conclusion: LEEDR can effectively mitigate 8 hours of extremity ischemia in a swine model, reducing mortality from reperfusion, while improving functional gait score and eliminating compartment syndrome. This percutaneous approach to ALI opens a new field of extracorporeal limb salvage, which can temporize extremity perfusion improving outcomes in patients who have traditionally had limited options due to prolonged warm ischemia.
Hypothesis
Extracorporeal perfusion can improve survival from ALI.
Aims
The aim of this study is to use a swine model of prolonged hindlimb ischemia to compare survival and functional outcomes of LEEDR versus control (warm ischemia).
Methods: Anesthetized female Yorkshire swine (40-60kg) underwent hindlimb ischemia using endovascular balloon occlusion and were randomized to control (n=6) or LEEDR (n=6). Controls underwent 9 hours of ischemia. LEEDR animals underwent contralateral femoral and ipsilateral posterior tibial artery cannulation followed by 8 hours of extracorporeal perfusion into the ischemic limb. Subjects were revascularized by removing the endovascular balloons, restoring extremity blood flow, and undergoing a 4-hour critical care period before extubation and observation for 48 hours. Primary outcome was survival and secondary outcomes included functional extremity scores (Tarlov Gait Score), compartment pressures (mmHg) and biochemical markers of reperfusion.
Results: Survival was higher in animals undergoing LEEDR (83% vs. 0%; p=0.001), with most control animals succumbing to acute lung injury. LEEDR animals had a higher functional gait score (5.9±0.3 vs. 2.5±0.7; p<0.001) and lower compartment pressure (8±2 vs. 28±4; p=0.002) compared to controls. Biochemically, the LEEDR group had lower potassium (4.5±0.3 vs. 5.3±0.4; p=0.001) and lactate (1.2±0.5 vs. 2.0±0.7; p<0.001) measurements compared to controls during reperfusion and recovery.
Conclusion: LEEDR can effectively mitigate 8 hours of extremity ischemia in a swine model, reducing mortality from reperfusion, while improving functional gait score and eliminating compartment syndrome. This percutaneous approach to ALI opens a new field of extracorporeal limb salvage, which can temporize extremity perfusion improving outcomes in patients who have traditionally had limited options due to prolonged warm ischemia.
More abstracts on this topic:
A New Analytical Approach for Noninvasive Reconstruction of the Entire Left Ventricular Pressure Waveform in Myocardial Ischemia and Infarction
Bilgi Coskun, Li Jiajun, Alavi Rashid, Dai Wangde, Matthews Ray, Kloner Robert, Pahlevan Niema
AI-Driven Gait Classification for Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Detection Using Machine Learning and Nonlinear Gait DynamicsMohammadzadeh Gonabadi Arash, Fallahtafti Farahnaz, Pipinos Iraklis, Burnfield Judith, Myers Sara