Final ID: MDP619
Magnetic Cell Capture of Autologous Blood Outgrowth Endothelial Cells to Promote the Healing of Magnetic Stent Grafts in a Porcine Pseudoaneurysm Model
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction-Stent grafts (SGs) are used to treat vascular pathologies such as aortic dissection, iliac artery atherosclerosis, and carotid artery pseudoaneurysms (PSAs). However, the large blood contacting surface of SGs delays healing and is a risk for thrombosis until covered by an endothelium. We investigated magnetic cell capture of autologous blood outgrowth endothelial cells (BOECs) to the surface of magnetizable SGs to promote healing in a porcine PSA model.
Methods-BOECs were generated from pig blood draws and dosed with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. PSAs were surgically created in both common carotid arteries of pigs with a bovine dura pouch. In each pig, control and magnetic SGs were delivered in opposite carotid arteries to treat the PSAs. Autologous BOECs labeled with live cell tracker DiI were delivered to both SGs. Angiography was used to assess patency of the PSAs and SGs at 3-(n=1), 10-(n=3), or 30-day(n=5) follow ups. Confocal microscopy assessed magnetic capture of DiI labeled cells at the 3-day endpoint. H&E staining was used to quantify % SG luminal surface covered by neointima and % stenosis at the 10- and 30-day endpoints. Angiographic and H&E outcomes were compared using a Fischer’s exact test and Mann-Whitney test, respectively, with p<0.05 defined as statistically significant.
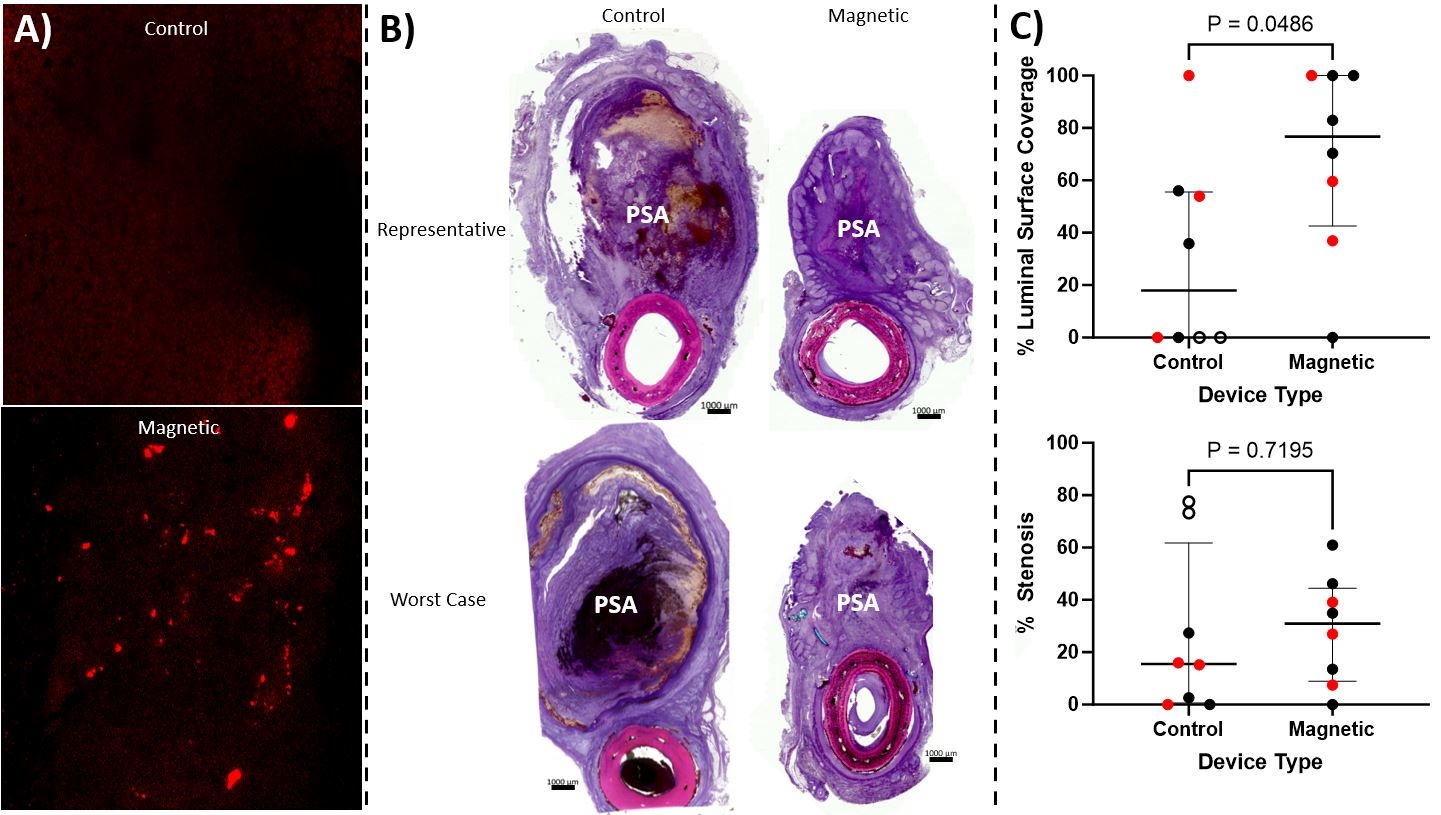
Results-The control and magnetic SGs occluded the PSA in 7/9 and 9/9 cases, respectively(p=0.461). The control and magnetic SGs completely occluded in 2/9 and 0/9 cases, respectively(p=0.470). The magnetic SG appeared to capture more DiI labeled cells than the control(Figure 1A). H&E stains are presented in Figure 1B. The magnetic SGs had a significantly higher % luminal surface covered by neointima(p=0.049); there was no difference in % stenosis between groups (p=0.720)(Figure 1C).
Conclusions- Cell capture increased the % SG luminal surface covered by neointima which may reduce the risk of thrombosis. More comprehensive evaluation of magnetic cell capture and SG endothelialization is ongoing.
Methods-BOECs were generated from pig blood draws and dosed with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. PSAs were surgically created in both common carotid arteries of pigs with a bovine dura pouch. In each pig, control and magnetic SGs were delivered in opposite carotid arteries to treat the PSAs. Autologous BOECs labeled with live cell tracker DiI were delivered to both SGs. Angiography was used to assess patency of the PSAs and SGs at 3-(n=1), 10-(n=3), or 30-day(n=5) follow ups. Confocal microscopy assessed magnetic capture of DiI labeled cells at the 3-day endpoint. H&E staining was used to quantify % SG luminal surface covered by neointima and % stenosis at the 10- and 30-day endpoints. Angiographic and H&E outcomes were compared using a Fischer’s exact test and Mann-Whitney test, respectively, with p<0.05 defined as statistically significant.
Results-The control and magnetic SGs occluded the PSA in 7/9 and 9/9 cases, respectively(p=0.461). The control and magnetic SGs completely occluded in 2/9 and 0/9 cases, respectively(p=0.470). The magnetic SG appeared to capture more DiI labeled cells than the control(Figure 1A). H&E stains are presented in Figure 1B. The magnetic SGs had a significantly higher % luminal surface covered by neointima(p=0.049); there was no difference in % stenosis between groups (p=0.720)(Figure 1C).
Conclusions- Cell capture increased the % SG luminal surface covered by neointima which may reduce the risk of thrombosis. More comprehensive evaluation of magnetic cell capture and SG endothelialization is ongoing.
More abstracts on this topic:
The pioneer factor, ETV2, regulates networks to specify the embryonic endothelial lineage.
Das Satyabrata, Garry Mary, Garry Daniel, Ma Xiao, Hailemariam Kidus, Larson Thijs, Choi Young Geun, Le Anh, Leonard Riley, Sadek Hesham, Zhang Jianyi
Association of Hypoperfusion Intensity Ratio, Cerebral Blood Volume Index, and the CRISP2 Collateral Score with Good Outcome for Patients Transferred for ThrombectomyAsimos Andrew, Hines Andrew, Rhoten Jeremy, Karamchandani Rahul, Yang Hongmei, Strong Dale, Teli Katelynn, Clemente Jonathan, Defilipp Gary, Bernard Joe, Stetler William, Parish Jonathan